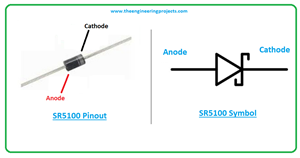
SR5100 Schottky Rectifier Datasheet, Pinout, Features & Applications




 1 user
1 user
 Limited Projects
Limited Projects
 Email Support
Email Support
 3 user
3 user
 Unlimited Projects
Unlimited Projects
 Social Support
Social Support
 25 user
25 user
 Unlimited Projects
Unlimited Projects
 Multi-Product Support
Multi-Product Support













 2
2




 2
2


 Continue Shop
Continue Shop

