ESP32 Pinout, Datasheet, Features & Applications
Hi Guys! I hope you’re doing great. Today, I am going to share Chapter Zero of the ESP32 Programming Course. I have called it Chapter 0 because today, we won't practically work on the ESP32. Instead, I’ll walk you through the detailed theoretical Introduction to the ESP32 Module, where we will discuss the ESP32 Pinout, Datasheet, Specifications, Features, Applications etc. in detail.
ESP32 is an embedded module that supports both WiFi and BT(dual-mode) connectivity and is thus used in Cloud-based IoT projects. ESP32 is the upgraded model of the ESP8266 module and is designed by Espressif Systems in China.
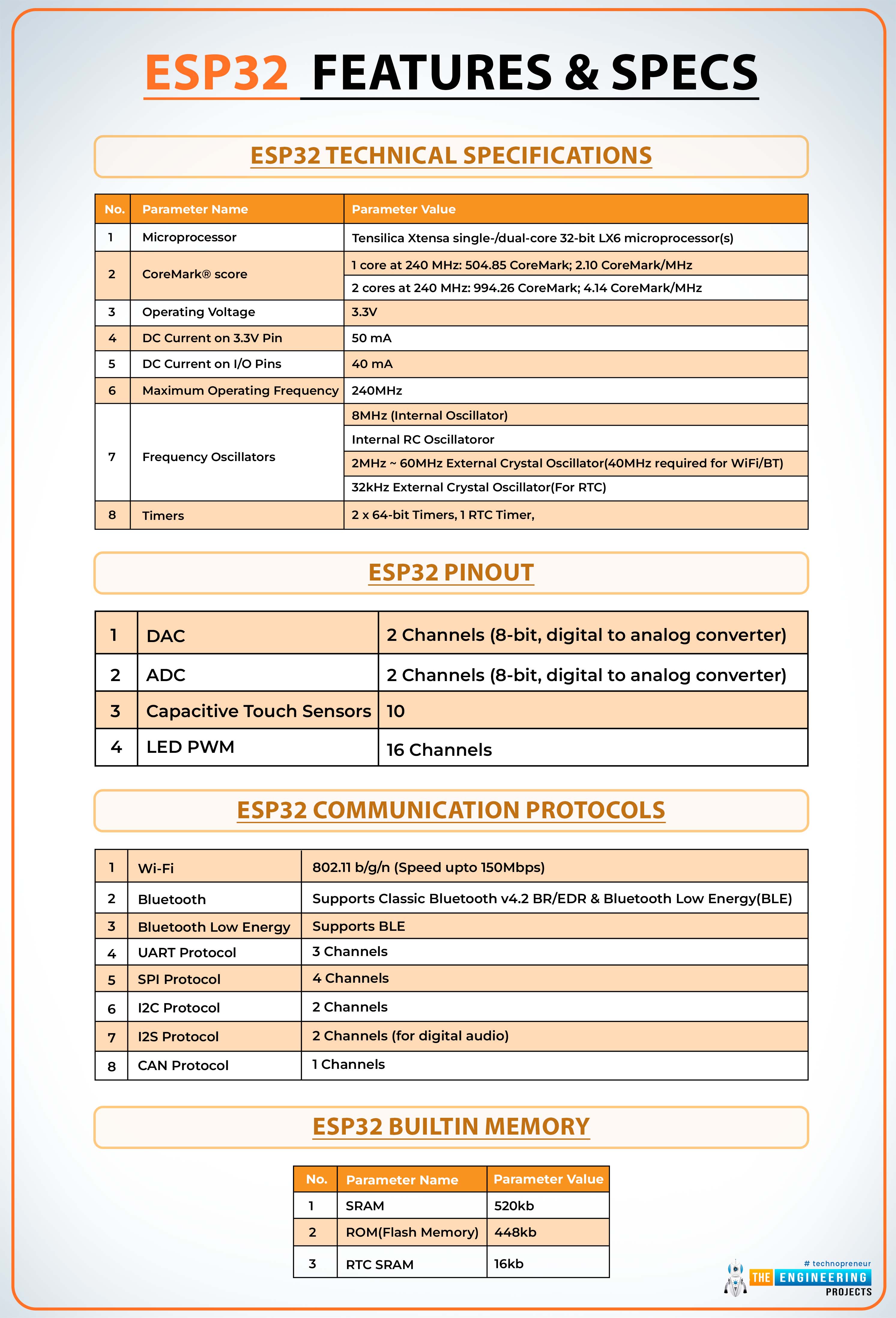
The following tables show the main features and technical specifications of the ESP32 module.
| ESP32 Technical Specifications | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Parameter Name | Parameter Value | ||
| 1 |
Microprocessor | Tensilica Xtensa single-/dual-core 32-bit LX6 microprocessor(s) | ||
| 2 |
CoreMark® score | 1 core at 240 MHz: 504.85 CoreMark; 2.10 CoreMark/MHz | ||
| 2 cores at 240 MHz: 994.26 CoreMark; 4.14 CoreMark/MHz | ||||
| 3 | Operating Voltage | 3.3V | ||
| 4 |
DC Current on 3.3V Pin | 50 mA | ||
| 5 |
DC Current on I/O Pins | 40 mA | ||
| 6 |
Maximum Operating Frequency | 240MHz | ||
| 7 |
Frequency Oscillators | 8MHz (Internal Oscillator) |
||
| Internal RC Oscillatoror |
||||
| 2MHz ~ 60MHz External Crystal Oscillator(40MHz required for WiFi/BT) | ||||
| 32kHz External Crystal Oscillator(For RTC) |
||||
| 8 |
Timers | 2 x 64-bit Timers, 1 RTC Timer, |
||
| ESP32 Pinout | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
DAC |
2 Channels (8-bit, digital to analog converter) |
||
| 2 |
ADC | 18 Channels (12-bit, analog to digital converter) |
||
| 3 |
Capacitive Touch Sensors |
10 |
||
| 4 |
LED PWM |
16 Channels |
||
| ESP32 Communication Protocols |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Wi-Fi | 802.11 b/g/n (Speed upto 150Mbps) | ||
| 2 |
Bluetooth | Supports Classic Bluetooth v4.2 BR/EDR & Bluetooth Low Energy(BLE) |
||
| 3 |
Bluetooth Low Energy | Supports BLE |
||
| 4 |
UART Protocol | 3 Channels |
||
| 5 |
SPI Protocol | 4 Channels | ||
| 6 |
I2C Protocol | 2 Channels | ||
| 7 |
I2S Protocol | 2 Channels (for digital audio) |
||
| 8 | CAN Protocol | 1 Channels | ||
| ESP32 Builtin Memory | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Parameter Name | Parameter Value | ||
| 1 | SRAM | 520kb |
||
| 2 | ROM(Flash Memory) | 448kb |
||
| 3 | RTC SRAM |
16kb |
||
So, let's get started with the Introduction to ESP32:
| Where To Buy? | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Components | Distributor | Link To Buy | |
| 1 | ESP32 | Amazon | Buy Now | |
Introduction to ESP32 Module
- The microprocessor used in the ESP32 chip is the Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor (single-core and dual-core).
- A few LX6 based ESP32 ICs are:
- ESP32-D0WDQ6 (and ESP32-D0WD)
- ESP32-D2WD
- ESP32-S0WD
- ESP32-PICO-D4
ESP32 vs ESP8266
- Both the ESP32 and ESP8266 are inexpensive WiFi modules with low power consumption.
- Both modules are desirable for DIY projects in the areas of IoT (Internet of Things) and automation.
- The ESP32 is a dual-core 160Mhz 240Mhz CPU, while the ESP8266 has an 80Mhz single-core processor. Therefore, if your primary concern is processor speed, you should prioritize the ESP32 over the ESP8266.
- The ESP32 offers more GPIO than the ESP8266.
- ESP32 supports Bluetooth 4.2 and BLE(Bluetooth Low Energy).
- The ESP32 offers a 12-bit ADC, while the ESP8266 offers only a 10-bit ADC.
ESP32-WROOM-32
- ESP32-WROOM-32 is a 38-pin breakout board of ESP32, which is most commonly used in third-party ESP32 modules.
- As ESP32 IC is available in the QFN(Quad Flat No Leads) package, so it's quite difficult to solder the IC in embedded projects.
- So, to ease the process of using ESP32 IC, Espressif Systems designed numerous small modules(using ESP32 chip) that have a built-in antenna and easily usable pinout.
- Other ESP32 modules are ESP32-SOLO and ESP32-WROVER.
- One of the most commonly used breakout boards of ESP32 is ESP32-WROOM-32, shown in the below figure:
Third-Party ESP32 Development Modules
- Many embedded companies have used ESP32-WROOM-32 and designed different ESP32 development boards, which are plug-and-play modules and are thus normally used for learning and prototyping purposes.
- One of the most commonly used ESP32 development boards is called ESP32-DevkitC.
- ESP32-DevKitC is a 30-pin ESP32-based development board, designed by Espressif Systems and is used in embedded and IoT projects.
- All you need to do is plug this device using a USB cable and play with it on the fly.
- Boot mode and Reset buttons are incorporated on the board.
- USB micro connector and USB-UART Bridge, and LDO regulator are also included in the device.
Types of ESP32 Development Boards
- The following are the five different versions of ESP32-DevKitC.
- ESP32-DevKitC-32E
- ESP32-DevKitC-32UE
- ESP32-DevKitCVE
- ESP32-DevKitCVIE
- ESP32-DevKitCS1
So, that was the evolution of ESP32 from a simple IC to plug & play board. Now let's have a look at the Pinout of the ESP32 microcontroller and modules:
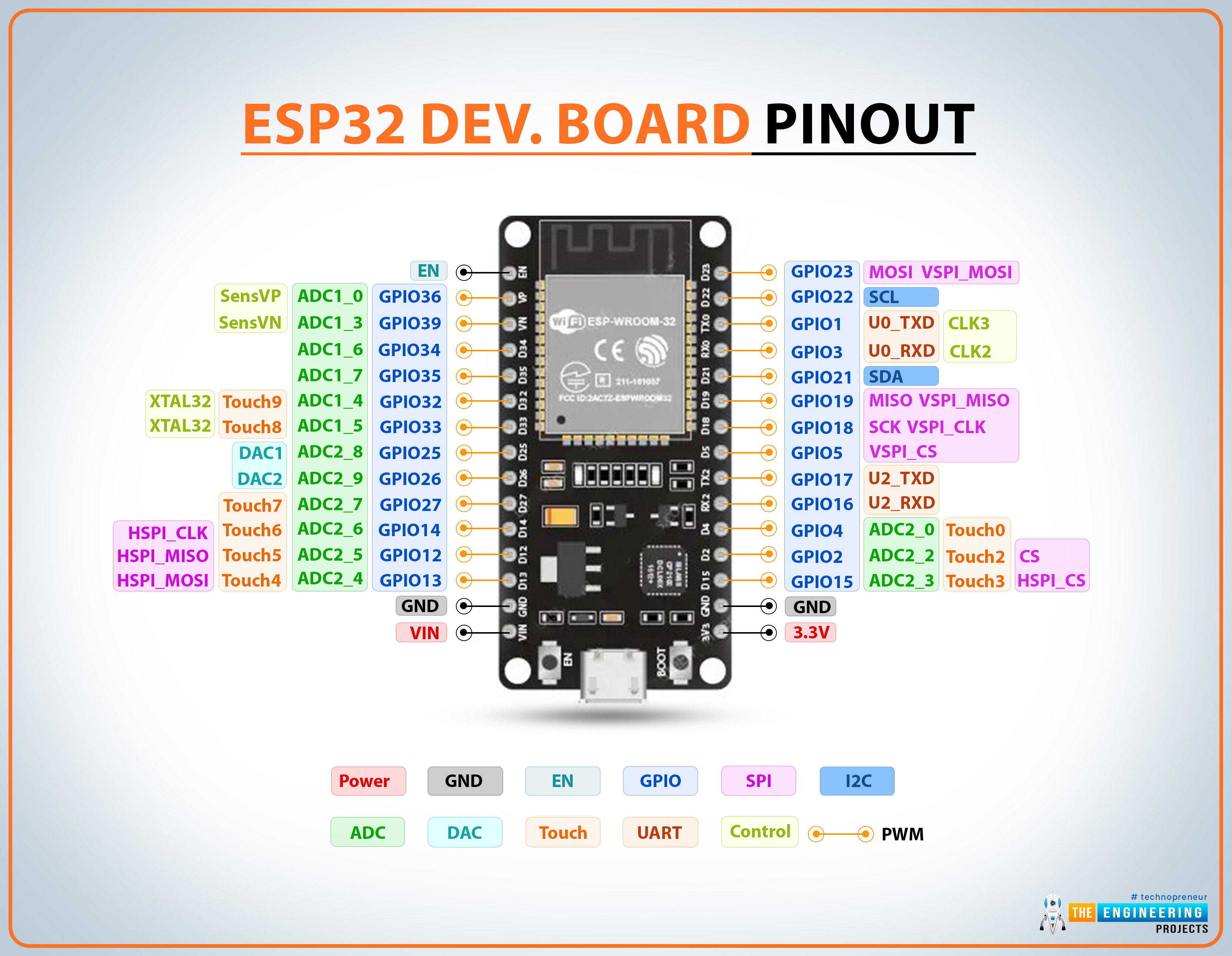
ESP32 Pinout
We have seen above that ESP32 has evolved first into ESP32-WROOM-32 and is further upgraded into ESP32-DevKitC. So, let's have a look at the pinout of all these boards, one by one:
Pinout of ESP32 IC
- ESP32 IC in its pure form consists of 48 pins in total.
- The following figure shows the labeled ESP32 Pinout diagram:
Pinout of ESP32-WROOM-32
- ESP32-WROOM-32 is a breakout board of ESP32 and consists of 38 pins in total.
- Here's the pinout of the ESP-WROOM-32 board:
Pinout of ESP32-DevkitC
- ESP32-DevKitC is a development board based on the ESP32 microcontroller and it has 36 pins in total.
- Here's the pinout diagram of ESP32 DevKitC:
ESP32 Pin Description
Now, let's have a look at the functions of ESP32 Pinout:
Power Pins in ESP32
- Power: Power is applied through Micro-USB, 3.3V pin, 5V pin, and GND. Regulated 5V is supplied to this pin which is further regulated to 3.3V to power up the board. And 3.3V pin directly supplies the 3.3V regulated to the board. And the ground is connected to GND.
- Enable: The enable pin is represented by ‘En’ on the board and is used to reset the microcontroller.
- AREF: It is marked as AREF which is used to provide a reference voltage for input voltage.
GPIO Pins in ESP32
ESP32 has 36 GPIO(general purpose input/output) pins to perform numerous operations(normally one at a time). Third-party ESP32 modules have different numbers of GPIO pins i.e. ESP32 Dev Kit V1 includes 30 GPIO pins. Let's have a look at the functionality of ESP32 GPIO Pins:
ADC Pins in ESP32
- ADC Pins: ESP32 has a total of 18 ADC channels(12-bit each) used to measure the analog voltage within the range of 0-3.3V.
ESP32 is equipped with two SAR analog-to-digital converter modules named ADC1 and ADC2. ADC1 has 10 Channels labeled from ADC2_1 to ADC2_7, while ADC2 has 10 Channels labeled from ADC2_0 to ADC2_9. The ADC output value ranges from 0 to 4093 at 12-bit resolution.
DAC Pins in ESP32
- DAC Pins: ESP32 features 2 distinct 8-bit digital-to-analog converters(DAC1 and DAC2) for translating digital values to analog signals. The DAC function is attached to below two GPIO pins:
- DAC1-GPIO25
- DAC2-GPIO26
The DAC employs a power supply as an input reference voltage and features an internal resistance network.
PWM Pins in ESP32
- PWM Pins: ESP32's PWM controller has 16 independent PWM channels with configurable frequency and duty cycles. Any GPIO pin can be used as a PWM pin.
PWM pulses are used to control the speed of motors or the brightness of LEDs. You can configure the frequency, channel, GPIO pin, and duty cycle of the PWM signal.
SPI Pins in ESP32
- SPI Pins: ESP32 has three SPI blocks that operate in both master and slave modes, named SPI, HSPI, and VSPI.
Among these 3 blocks, SPI is used as an interface to flash
memory. So, we are left with HSPI and VSPI for normal use:
- VSPI: ESP32 VSPI Pins are GPIO23 (MOSI), GPIO19 (MISO), GPIO18 (CLK) and GPIO5 (CS) used for SPI-1 communication.
- HSPI: ESP32 HSPI Pins are GPIO13 (MOSI), GPIO12 (MISO), GPIO14 (CLK) and GPIO15 (CS) used for SPI-2 communication.
I2C Pins in ESP32
The ESP32 has two I2C interfaces. The SCL and SDA pins of both I2C interfaces can be assigned by a user in the program. The default I2C pins are:
- SDA-GPIO21
- SCL-GPIO22
ESP32 Capacitive Touch Sensors
- ESP32 has 10 capacitive touch-sensing GPIO Pins(T0 to T9), which get electrostatically charged when a finger touches the respective GPIO pin.
Without any additional hardware, these touch GPIOs can be utilized to make capacitive touchpads. Variations in capacitance are evident.
RTC GPIO
- ESP32 has 18 Low-Power RTC GPIO Pins(RTCIO0 to RTCIO17) used to wake up the ESP32 board from deep sleep mode.
- Serial: Two serial pins are represented on boards as Tx and Rx. The Tx is used to transmit serial data while Rx is used to receive serial data.
- External Interrupts: All GPIO pins can be used as external interrupts.
ESP32 Datasheet
Before you incorporate this device into your electrical project, it’s wise to go through the datasheet of the component that features the main characteristics of the device. You can click the link given below to download the ESP32 datasheet.
Now, let's have a look at the features of ESP32:
ESP32 Features
Here are the main features of ESP32 IC:
- ESP32 has built-in integration of both WiFi and Bluetooth dual-mode.
- ESP32 has 34 programmable GPIOs present on the chip.
- ADC is of 12-bit SAR and can support up to 18 channels.
- DAC is 8-bit and it has 2 DAC channels.
- ESP32 also has 10 touch sensors embedded in it.
- ESP32 also has a Hall sensor in it.
- It supports 4 SPI channels.
- It also has 2 I²S channels.
- ESP32 has 2 I²C ports in it.
- It supports 3 UART channels.
- It also has 1 host(SD/MMC/SDIO) and 1 slave(SDIO/SPI).
- ESP32 also supports the Ethernet MAC interface with dedicated DMA and IEEE 1588 support.
- It supports Two-Wire Automotive Interface (TWAI®, compatible with ISO11898-1)
- LED PWM up to 16 channels
A few of ESP32's key features are discussed below in detail:
ESP32 WiFi Key Features
- Wireless Networking Standard: 802.11 b/g/n
- Wireless Standard: 802.11 n (2.4 GHz), up to 150 Mbps
- WiFi Multimedia(WMM)
- WiFi Aggregation: TX/RX A-MPDU, RX A-MSDU
- Immediate Block ACK: suitable for high bandwidth & low latency traffic.
- Automatic Beacon monitoring (hardware TSF)
- Simultaneous support for SoftAP, Infrastructure Station and Promiscuous modes.
- Diverse Antenna
- Defragmentation to smoothen the data.
- Supports 4 virtual WiFi Interfaces.
ESP32 Bluetooth Key Features
- Compliant with Bluetooth v4.2 BR/EDR
- Class-1, Class-2 and Class-3 transmitters without external power amplifier
- Increased Power Control
- Transmission Power: +12 dBm
- BLE sensitivity: –94 dBm (NZIF receiver)
- Adaptive Frequency Hopping (AFH)
- Standard HCI supports SDIO/SPI/UART
- High-speed UART HCI, up to 4 Mbps
- Bluetooth 4.2 BR/EDR BLE dual-mode controller
- CVSD and SBC for audio codec
- Classic BT and BLE support Multiple connections.
- It can advertise and scan simultaneously.
- Bluetooth Piconet and Scatternet
ESP32 Microcontroller Key Features
- ESP32 uses an Xtensa® single-/dual-core 32-bit LX6 microprocessor(s) .
- It supports data rates up to 600 MIPS (200 MIPS for ESP32-S0WD/ESP32-U4WDH)
- It has a Flash Memory of 448 KB.
- It has an SRAM memory of 520 KB.
- 16 KB SRAM in RTC
- QSPI supports multiple flash/SRAM chips.
ESP32 Clocks & Timers Key Features
- ESP32 has a calibrated 8MHz crystal oscillator (internal)
- Calibrated RC oscillator (internal)
- External 2 MHz ~ 60 MHz crystal oscillator (40 MHz only for Wi-Fi/BT functionality)
- External 32 kHz crystal oscillator for RTC with calibration
- Two timer groups, including 2 × 64-bit timers and 1 × main watchdog in each group
- ESP32 also has one RTC timer.
- RTC watchdog is also present in ESP32.
ESP32 Projects & Applications
ESP32 modules have brought a revolution in embedded and especially IoT projects. As these boards are small-sized, low-powered and support both WiFi & BT, thus are gaining popularity in IoT-based handheld devices. A few applications of the ESP32 module are as follows:
- Used in Network projects.
- Employed for beginner-level DIY projects.
- Employed in the prototyping of IoT devices.
- Used in cloud-based smart security projects.
- Used in low-power battery-operated applications.
That was all about the Introduction to ESP32 module. If you have any questions, you can approach me in the comment section below. I’ll help you according to the best of my expertise. You’re most welcome to share your valuable feedback and suggestions around the content we share so we keep coming up with quality content customized to your exact needs and requirements. Thank you for reading the article.
LM747 Datasheet, Pinout, Features, Equivalent & Applications
Hi Guys! I hope you’re well today. Happy to see you around. In this post today, I’ll walk you through the Introduction to LM747.
LM747 is a general-purpose dual-operational amplifier IC. This chip contains two operational amplifiers on board and belongs to the LM’xx’ family where LM stands for linear monolithic. In this chip, analog components are incorporated into silicon.
I suggest you buckle up as I’ll detail the complete Introduction to LM747 covering datasheet, pinout, features, equivalents, and applications. Let’s jump right in.
Introduction to LM747
- Designed by National Semiconductor, LM747 is a general-purpose dual-operational amplifier integrated chip.
- Two operational amplifiers are incorporated that share common power supply leads and a bias network.
- And these amplifiers are capable of performing two different operations at the same time which makes them a suitable pick for several applications. Though these amplifiers share a common bias network, they are completely independent of each other
- As two general-purpose amplifiers are used in this chip, it is used to construct op-amp circuits like differential amplification, comparator, and mathematical operations.
- This device features offset pins which are mainly used to make the output more accurate and efficient.
- It comes with no latch-up when the input common-mode range is exceeded which sets it free from oscillations.
LM747 Datasheet
Before you incorporate this device into your electrical project, it’s better to scan through the datasheet of the component that features the main characteristics of the component. You can download the datasheet of LM747 from the link given below.LM747 Pinout
LM747 incorporates 14 pins on board. The following figure shows the pinout diagram of LM747.| Pin Description of JRC4558 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin No. | Pin Description | Pin Name | ||
| 1 | Inverting input of op-amp 1 | 1IN- | ||
| 2 | A non-inverting input of op-amp 1 | 1IN+ | ||
| 3 | The offset null pin is used to remove the offset voltage and control the input voltages for op-amp 1 | OFFSET NULL 1 | ||
| 4 | Common negative supply voltage for both Op-amps | V- | ||
| 5 | The offset null pin is used to remove the offset voltage and control the input voltages for op-amp 1 | OFFSET NULL 2 | ||
| 6 | The non-inverting input of op-amp 2 | 2IN+ | ||
| 7 | Inverting input of op-amp 2 | 2IN- | ||
| 8 | The offset null pin is used to remove the offset voltage and control the input voltages for the op-amp 2 | OFFSET NULL 2 | ||
| 9 | Positive supply voltage for op-amp 2 | V2+ | ||
| 10 | The output pin of the op-amp 2 | 2OUT | ||
| 11 | No connection | NC | ||
| 12 | The output pin of the op-amp 1 | 1OUT | ||
| 13 | Positive supply voltage for op-amp1 | V1+ | ||
| 14 | The offset null pin is used to remove the offset voltage and control the input voltages for op-amp 1 | OFFSET NULL 1 | ||
- Offset null pins remove the offset voltage and balance the output voltages for both operational amplifiers.
- While pin 11 is not connected. It is not used for any purpose.
LM747 Features
The following are the main features of LM747.- No latch-up
- Large differential voltage and common mode range
- Low noise interference among op-amps
- Total power dissipation = 800mW
- Differential input voltage = ±30V
- Low power consumption
- Supply voltage Max. = ±22V
- Frequency Compensation is not required
- Comes with short-circuit protection
- Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR = 90dB
- Operating temperature range = -55ºC to +125ºC
LM747 Applications
The following are the main applications of LM747.- Employed in mathematical operations
- Used in amplifiers
- Used in analog circuits
- Used for Measuring instruments
- Incorporated in voltage comparators
- Employed for Industrial applications
- Used in Peak detectors
That was all about the Introduction to LM747. If you’re unsure or have any questions, you can leave your query in the section below. I’d love to help you according to the best of my expertise. Feel free to share your valuable feedback and suggestions around the content we share so we keep sharing quality content tailored to your exact needs and requirements. Thank you for reading the article.
LF353N Dual JFET Input Op-Amp Datasheet, Pinout, Features & Applications
Hi Folks! I hope you’re well today. I welcome you on board. Happy to see you around. In this post today, I’ll walk you through the Introduction to LF353N.
The LM393N is a wide bandwidth and high input impedance Dual Input JEFET op-amp that is widely used in high-speed integrators and low noise circuits. The low bias current and input noise make it a good pick for audio amplifier applications. It carries a high slew rate (13V/uS) and wide bandwidth around (4MHz).
I suggest you read this post all the way through, as I’ll detail the complete introduction to LF353N covering datasheet, pinout, features, and applications. Let’s dive in.
Introduction to LF353N
- Introduced by the Texas Instrument, the LM393N is a high input impedance dual op-amp where the input of this device is attached through a high voltage JFET.
- It is widely used in low current, low noise fast switching applications.
- There are two outputs available on the device i.e. Output A and Output B. And two inputs where each input contains further two inputs i.e. inverting input (-) and non-inverting input (+).
- This chip incorporates two independent op-amps that operate over a wide range of voltages from a single power supply.
- High slew rate and high input impedance device, LF353N comes with internally compensated input offset voltage.
- It is also available with a power supply voltage range of ±18 V and with a differential input voltage of around 30V.
- The power dissipation Pd is 500mW which is defined as the maximum energy dissipated during the working of this device.
LF353N Datasheet
Before you incorporate this device into your electrical project, it’s wise to scan through the datasheet of the component that features the main characteristics of the component. Click the link below to download the datasheet of LF353N.LF353N Pinout
The following figure shows the pinout diagram of LF353N.| Pin Description of LF353N | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin No. | Pin Description | Pin Name | ||
| 1 | The output of Op-Amp 1 | OUT (A) | ||
| 2 | Inverting Input of Op-Amp 1 | INPUT- A(-) | ||
| 3 | Non-Inverting Input of Op-Amp 1 | INPUT- A(+) | ||
| 4 | Ground or Negative supply terminal | Power (-Vs) | ||
| 5 | Non-Inverting Input of Op-Amp 2 | INPUT- B(+) | ||
| 6 | Inverting Input of Op-Amp 2 | INPUT- B(-) | ||
| 7 | The output of Op-Amp 2 | OUTPUT B | ||
| 8 | Positive supply terminal | +Vcc | ||
LF353N Features
- Dual Op-Amp that comes with JFET Input
- High slew rate 13V/µs
- High Input Impedance 1012?
- Low Input Noise current
- Low input noise voltage
- Supply Current = 6.5mA (max)
- Bandwidth Gain = 4MHz
- Supply Voltage = ±18V
- Available Packages = 8-pin SOIC & PDIP Package
LF353N Equivalent
The following are the equivalents of LF353N.- LM1558
- TL074
- MCP6002
While working with the alternatives, make sure you cross-check the pinout of them. It’s quite likely the pinout of the alternatives might differ from the pinout of LF353N.
LF353N Applications
The LF353N is used in the following applications.
- Used in High-Input Impedance designs
- Employed in Low-noise Audio circuits
- Used in High-Speed Integrator
- Incorporated in Sample and Hold Circuit
That’s all for today. I hope you’ve loved reading this article. If you have any questions, you can approach me in the section below, I’d reply to you according to the best of my experience. Feel free to share your valuable suggestions and feedback around the content we share, so we keep producing quality content customized to your needs and requirements. Thank you for reading this article.
MID400 Optocoupler Datasheet, Pinout, Features, Equivalent & Applications
Hi Everyone! I hope you’re well today. Happy to see you around. In this post today, I’ll walk you through the Introduction to MID400.
The MID400 is an 8-pin optically isolated AC line-to-logic Power Line Monitor Optocoupler. The AC line voltage is detected by two back-to-back LEDs that are connected in series with an external resistor. When this device identifies the AC voltage, the output pin goes low and when there is no AC voltage detected, it remains high.
This feature of detecting the AC line voltage is widely employed in AC to DC control and relay latching applications. I suggest you buckle up as I’ll walk you through the complete introduction to MID400 covering datasheet, pinout, features, equivalents, and applications. Let’s dive right in.
Introduction to MID400
- The MID400 is an 8-pin optically isolated AC line-to-logic Power Line Monitor Optocoupler that identifies the AC line voltage using two back-to-back LEDs that are attached in series with an external resistor.
- It features high voltage isolation between input and output and comes with an externally adjustable AC voltage sensing level.
- This device is available with an 8-pin compact DIP package and SMD Package.
- It is the best pick for AC to DC control applications where remarkable solid-state reliability and excellent optical isolation are needed.
- It is also applied to low-frequency operations where small size, low power, and TTL compatibility are required.
MID400 Datasheet
While working with this device, it’s wise to go through the datasheet of the component before installing this device into your project. The datasheet highlights the main characteristics of the component. Click the link below if you want to download the datasheet of MID400.MID400 Pinout
The following figure represents the pinout diagram of MID400.
The following table demonstrates the pin description of MID400.
| Pin Description of MID400 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin No. | Pin Description | Pin Name | ||
| 1 | AC Live wire is connected to this Pin | AC Live | ||
| 2 | No connection | Not used | ||
| 3 | AC Neutral wire is connected to this pin | AC Neutral | ||
| 4 | No connection | Not used | ||
| 5 | The ground pin of the device | Ground | ||
| 6 | Open collector output pin | V Output | ||
| 7 | Used to control time delay and AC voltage sensing by adding a capacitor to this pin | Auxiliary | ||
| 8 | Device Operating Voltage | Vcc | ||
You can see from the table above… out of 8 pins, two pins(2 & 4) are not used for any connection. Pin 5 is the ground and Pin 8 is the voltage supply pin.
MID400 Features
The following are the main features of MID400.
- Working Insulation Voltage Max. = 630Vpeak
- LED on-state input current = ±30mA
- Power Line Monitor IC
- Low-level Output Current = 20mA
- Low-level Output Voltage = 0.18V
- LED forward voltage drop = 1.5V
- Supply Voltage (Vcc) = 7V
- Turn-on and Turn-off Time = 1ms each
- Available Packages = 8-pin DIP and SMD Package
MID400 Sample Application Circuit
The following figure shows the sample application circuit of MID400.- MID400 is an AC line monitor where the phase wire is connected to the first pin of the device and the neutral wire is connected to the third pin of the device using a resistor of 22-kilo ohm. This resistor is used to control and limit the current flowing through the AC line voltage.
- Pin 6 is the output pin that remains high when there is no AC voltage and it remains low when AC line voltage is detected.
- Optocoupling property is used in this device which keeps both output voltage and AC line completely isolated.
- Pin 6 is the output pin or open collector pin that is attached to the pull-up resistor of 300 ohms which is further connected with the Vcc pin of the device… as shown in the figure above.
- The capacitor is attached to pin 7 which is mainly used to control the time delay and sensing level of the output.
MID400 Alternative
The following are the alternatives to MID400:
- ACS71020
- UC1903
While working with the alternatives, double-check the pinout of the alternatives, as the pinout of the alternatives might differ from the pinout of MID400.
MID400 Applications
MID400 is used in the following applications.
- Employed in AC sensing applications
- Employed in Latching circuits
- Incorporated in Isolation switch
- Used in AC to DC control applications
- Used in AC to DC converters
That was all about the Introduction to MID400. If you’re unsure or have any queries, you can pop your question in the section below. I’d love to help you the best way I can. You’re most welcome to share your valuable suggestions and feedback around the content we share, so we keep producing quality content tailored to your exact needs and requirements. Thank you for reading the article.
TDA7265 Audio Amplifier Datasheet, Pinout, Features & Applications
Hi Friends! I hope you’re well today. I welcome you on board. In this post today, I’ll walk you through the Introduction to TDA7265.
TDA7265 is a +25-watt class AB dual audio power stereo amplifier. This multi-watt package IC is carefully designed for high-quality audio power amplification applications. This device receives a low-input audio signal and amplifies it into a high-quality audio output.
I suggest you buckle up as I will detail the complete introduction to TDA7265 covering datasheet, pinout, features, and applications. Let’s jump right in.
Introduction to TDA7265
- TDA7265 is a +25-watt class AB dual audio power stereo amplifier that is mainly employed in audio amplifiers and woofer amplifiers.
- This device gets a low-input audio signal and converts it into a high-output audio signal.
- This chip features output short circuit protection and comes with a mute-enabled pin.
- Only a few components are required to put this device into working condition.
- Total power dissipation is 30W which is the amount of energy released during the working of this device.
- It comes with an operating voltage range of ±5 to ±25V.
- The operating temperature range is -20°C to +85°C while the storage temperature range is -40°C to +150°C.
TDA7265 Datasheet
Before you apply this component to your electrical project, it’s wise to scan through the datasheet of the device that comes with the main characteristics of the component. Click the link below and download the datasheet of TDA7265.
Additional circuit configurations are available in the datasheet of this chip. You can use any configuration to put this chip in working condition.
TDA7265 Pinout
The TDA7265 incorporates 11 pins on the device. The following figure shows the pinout diagram of TDA7265.
The table below demonstrates the pin name and pin description of each pin on the board.
| Pin Description of TDA7265 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin No. | Pin Description | Pin Name | ||
| 1 | A negative power supply is connected to this pin | -Vs | ||
| 2 | This pin receives the amplified output of channel A | OUTPUT 1 | ||
| 3 | A positive power supply is connected to this pin | +Vs | ||
| 4 | This pin receives the amplified output of channel B | OUTPUT 2 | ||
| 5 | This pin is triggered low to disable the audio output | MUTE | ||
| 6 | A negative power supply is connected to this pin | -Vs | ||
| 7 | A non-inverting input of channel B amplifier | IN+(2) | ||
| 8 | Inverting input of channel B amplifier | IN-(2) | ||
| 9 | This pin is connected to the ground | GND | ||
| 10 | Inverting input of channel A amplifier | IN-(1) | ||
| 11 | A non-inverting input of channel A amplifier | IN+(1) | ||
TDA7265 Features
The following are the main features of TDA7265.
- Comes with a wide operating supply voltage range
- Available with High output power : 25 + 25 W @ RL = 8 ?, Vs = ± 20V
- Features output short circuit protection
- Comes with a mute enable pin
- Incorporates thermal overload protection
- A few components are required to put the amplifier in working condition
- Stand-by feature (low Iq)
- Total power dissipation = 30W
- Split supply
- Maximum supply voltage = ±25V
- Operating voltage range = ±5 to ±25V
- Repetitive current allowed to draw through each output Max = 4.5A
- Storage Temperature = -40°C to +150°C
- Operating temperature = -20°C to +85°C
- No pop at turn-on/off
TDA7265 Operational Circuit
The following figure shows the operational circuit diagram of TDA7265. You need to connect the components as shown in the figure below. Doing this will put your amplifier in working condition.
- Two power supplies are used to power up this circuit one with the negative voltage V- and the other with the positive voltage V+.
- Pin no. 11 of this chip is given with the audio input signal for channel B and the resulting amplified output is heard through the right speaker. The Pin no. 07 of this chip is given with the audio input signal for channel A and the resulting amplified output is heard through the left speaker.
- A positive voltage supply source is used to power up the TDA7265 chip while the separate control unit is used to trigger the mute pin low. The two amplified outputs behave as a dual supply operation.
TDA7265 Applications
The TDA7265 is used in the following applications.- Employed in stereo TV sets
- Incorporated in woofer amplifiers
- Used in audio power amplifiers
- Used in music players
- Used in student and hobby projects
- Employed in guitar amplifiers
- Used in Hi-Fi music centers
That’s all for today. I hope you’ve enjoyed reading this article. If you’re unsure or have any questions, you can ask me in the section below. I’d love to help you the best way I can. Feel free to share your valuable suggestions and feedback around the content we share, so we keep producing quality content customized to your exact needs and requirements. Thank you for reading the post.
LM4558 Dual Op-Amp Datasheet, Pinout, Features & Applications
Hi Friends! I welcome you on board. Happy to see you around. In this post today, I’ll walk you through the Introduction to LM4558.
LM4558 is a dual-operational amplifier that comes with two amplifiers on board. This device belongs to the LM’xx’ family where LM stands for linear monolithic which means, it is made of analog components that are incorporated into the silicon piece.
This component comes with an internal frequency compensation method that guarantees the device's stability without the need for external components.
I suggest you read this post all the way through as I’ll detail the complete Introduction to LM4558 covering datasheet, pinout, features, and applications. Continue reading.
Introduction to LM4558
- LM4558 is a monolithic dual-operational amplifier that carries two amplifiers on board.
- This device belongs to the LM’xx’ family where LM stands for linear monolithic which demonstrates the availability of analog components that are incorporated on the silicon piece.
- It comes with a high common-mode input voltage range and no latch-up on this device makes it an ideal pick for voltage-follower applications.
- This chip comes with an internal frequency compensation method that guarantees the device's stability. Moreover, it is protected against short-circuiting.
- The device can be utilized in the op-amp operation circuits including differential amplification, comparators, and mathematical operations.
- As this component exhibits two independent amplifiers on board, it is capable of performing two completely different operations at the same time which makes it a suitable pick for several applications.
- The LM4558 comes with an operating temperature range from 0ºC to 70ºC while the total power dissipation is 200mW.
- The common-mode Rejection Ratio CMRR is 80dB and these amplifiers feature low noise interference.
LM4558 Datasheet
While working with this device, it’s wise to go through the datasheet of the component that features the main characteristics of the component. You can download the datasheet of LM4558 by clicking the link below.
LM4558 Pinout
This chip is an 8-pin device. The following figure shows the pinout diagram of LM4558.
The following table represents the pin name and pin description incorporated on the chip.
| Pin Description of JRC4558 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin No. | Pin Description | Pin Name | ||
| 1 | The output pin of the Op-amp 1 | 1OUT | ||
| 2 | The inverting input of Op-amp 1 | 1IN- | ||
| 3 | The non-inverting input of Op-amp 1 | 1IN+ | ||
| 4 | Ground or Negative supply terminal | GND | ||
| 5 | A non-inverting input of Op-amp 2 | 2IN+ | ||
| 6 | The inverting input of Op-amp 2 | 2IN- | ||
| 7 | The output pin of the Op-amp 2 | 2OUT | ||
| 8 | Positive supply terminal | VCC | ||
LM4558 Features and Specifications
The following are the main features and specifications of LM4558.
- Low noise interference among op-amps
- Dual Supply Operation = +15V and -15V
- No frequency Compensation Required
- Operating temperature = 0ºC to 70ºC
- Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR = 80dB
- Two independent operational amplifiers
- Built-in Short-Circuit Protection
- No latch-up
- Large common mode and differential voltage range
- Total power dissipation = 200mW
- Parameter tracking over a temperature range
- Carries low noise input transistors
- Phase and gain match between amplifiers
- Moisture Sensitivity Level 3
- Single Supply Operation = +5.0 V to +15 V
LM4558 Applications
The LM4558 is used in the following applications.
- Used in Measuring instruments
- Employed in Industrial applications
- Incorporated in Logic voltage translation
- Used in voltage comparators and peak detectors
- Employed in oscillators and amplifiers
- Used in mathematical operations
That’s all for today. I hope you’ve enjoyed reading this article. If you have any questions, you can pop your queries in the section below, I’d love to help you the best way I can. You are most welcome to share your valuable feedback and suggestions around the content we share so we keep coming back with quality content customized to your exact needs and requirements. Thank you for reading the article.
JRC4558 Op-Amp Datasheet, Pinout, Features, Alternatives & Applications
Hi Guys! Happy to see you around. I welcome you on board. Thank you for clicking this read. In this post today, I’ll walk you through the Introduction to JRC4558.
The JRC4558 is a single silicon-chip monolithic dual operational amplifier. This amplifier is a high-performance device and is internally compensated. It is widely used in sample and hold amplifiers and pedal circuit designs. The JRC4558 is available with a remarkable input impedance of around 5 MO, a high voltage gain of around 100 dB, and a good slew rate of around 1.7V/µs.
I suggest you buckle up as I will walk you through the complete introduction to JRC4558 covering datasheet, pinout, features, alternatives, and applications. Let’s jump right in.
Introduction to JRC4558
- The JRC4558 is a single silicon-chip monolithic dual operational amplifier that comes with high voltage gain and good input impedance.
- It is applied in portable instrumentation and Intrusion Alarm Systems.
- There are a total of eight pins incorporated on the device, where PIN 8 is the voltage supply pin and pin no 4 is the ground pin. And you’ll get two outputs at the same time.
- There are two inputs i.e. input A and input B and both inputs contain one inverting input (-) with Voltage V- and non-inverting input (+) with voltage V+.
- The ideal op-amps are different from the real op-amps used in this chip. The ideal op-amp comes with infinite gain while the voltage gain of this device is finite and is around 100dB.
- The slew rate of this device is around 1.7V/µs which is achieved when the output voltage of the amplifier reaches its maximum rate of change.
- This chip is incorporated with two independent, good input impedance and internally frequency compensated operational amplifiers that are carefully designed to run over a wide range of voltages from a single power supply.
- The JRC4558 produces an output signal that is much larger than the potential difference at the input.
- It is also applied in general-purpose operational amplifier circuits like differential amplification, comparators, and mathematical operations.
- This device is carefully designed and requires only a 5V standard voltage supply to operate in electronic circuits. You don’t need to include an additional -5V supply to run this device.
- Moreover, it is also employed in single-supply voltage systems, amplification blocks, and transducer amplifiers.
- This device is capable of performing two different operations at the same time as it incorporates two op-amps on board.
- The versatility of this device makes it a good pick for analog circuits.
- It is widely used in scientific devices and industrial and consumer applications.
- This device can be used individually or as a component of most complex integrated circuits.
JRC4558 Datasheet
Before applying this device to your electrical project, it’s wise to go through the datasheet of the component that contains the main characteristics of the component. Click the link below and download the datasheet of JRC4558.
JRC4558 Pinout
The following figure shows the pinout diagram of JRC4558.
The JRC4558 comes with a total of 8 pins as mentioned below in the table.
| Pin Description of JRC4558 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin No. | Pin Description | Pin Name | ||
| 1 | The output pin of Op-amp A | OUT (A) | ||
| 2 | The Inverting input pin of the Op-Amp A | Inverting Input (A) | ||
| 3 | The Non-Inverting Input Pin of Op-Amp A | Non- Inverting Input (A) | ||
| 4 | Ground or Negative supply terminal | Power (-Vs) | ||
| 5 | The non-inverting Input Pin of Op-Amp B | Reference | ||
| 6 | The Inverting input pin of the Op-Amp B | Output | ||
| 7 | The output pin of Op-amp B | Power (+Vs) | ||
| 8 | Positive supply terminal | +VS | ||
JRC4558 Features
The following are the main features of the JRC4558.
- No. of Amplifiers = 2
- Voltage Gain = 100 dB
- Device Slew Rate = 1.7V/µs
- Input Impedance = 5 MO
- Available Bandwidth = 3MHz
- Operating Temperature Max = 70°C
- Supply Voltage Range = ± 5V to ± 15V
- of Pins on the component = 8
- Operating Temperature Min = 0°C
- Available Package = 8-Pin DIP and SOP Package
JRC 4558 Alternatives
The following are the alternatives to JRC4558.
- LM158
- LM358
- LM358A
- LM2904Q
- LM158A
- LM2904
- LM747
- LM4558
JRC4558 Applications
The JRC4558 is used in the following applications.
- Applied in Sample and Hold Amplifiers
- Used in Portable Instrumentation
- Employed in Instrumentation Amplifiers
- Used in Long-Duration Timers/Multivibrators
- Incorporated in Intrusion Alarm System
- Employed in Photocurrent Instrumentation
- Used in Comparators and Function Generators
That’s all for today. I hope you’ve enjoyed reading this article. If you are unsure or have any queries, you can pop your question in the section below. I’d love to help you the best way I can. Feel free to share your valuable suggestions and feedback around the content we share, so we keep sharing quality content customized to your exact needs and requirements. Thank you for reading the article.
LM2576 Buck Converter Datasheet, Pinout, Features & Applications
Hi Everyone! I welcome you on board. Thank you for clicking this read. In this post today, I’ll walk you through the Introduction to LM2576.
LM2576 is a step-down voltage regulator, also known as a buck converter, mainly employed as a pre-regulator in linear regulators. The customized output version of this buck converter gives you the ability to set the output voltage as you like better. It is available with a remarkably good load and line regulation. Moreover, it is used to drive load under 1A and is available in fixed output voltages with 3.3V, 5V, 12V, and 15V.
I suggest you buckle up and read this post all the way through, as in this post I’ll detail the Introduction to LM2576 covering the datasheet, pinout, features, and applications. Let’s jump right in.
Introduction to LM2576
- LM2576 is a voltage regulator, also called a buck converter, mainly used as a pre-regulator in linear regulators.
- It is a simplified version of switching power supplies where it houses all functions needed to step down the circuit voltage.
- This buck converter comes with an integrated switch that drives load under 1A.
- LM2576 is available with remarkable load regulation and load line.
- LM2576 is available in two versions: version with fixed output voltage featuring 3.3V, 5V, 12V, & 15V and version with adjustable output that comes with the ability to choose your desired output.
- It is also known as the DC-to-DC power converter mainly used to step down the voltage from the input supply to its output load. The current is increased during this occurrence of voltage regulation.
- This buck converter comes with a fixed-frequency oscillator of around 52 kHz. It is also available with an in-built frequency compensation method.
- Frequency compensation is used to minimize the oscillation and vibration in the electrical circuit. Resistance-capacitance networks are applied for this frequency method to work.
- Apart from the excellent load and line regulation, this component is available with a manual shutdown option using an external ON/OFF pin.
LM2576 Datasheet
Before you apply this component to your electrical project, it’s better to go through the datasheet of the component that features the main characteristics of the device. You can download the datasheet of LM2576 by clicking the link below.
LM2576 Pinout
The following figure shows the pinout diagram of lm2576.
LM2576 is available with five terminals:
- ON/OFF: This pin is used to shut down the voltage regulator when the input supply current is decreased to 50uA. The threshold voltage is 1.3V. When the voltage on this pin is set to below the threshold voltage, it will turn on the voltage regulator. When the voltage on this pin goes above the threshold voltage it will turn off the device. And when this pin is connected to the ground or leave it open, it will remove the shutdown feature from the device. Whether you connect this pin to the ground or leave it open, in both cases the regulator remains turned on.
- VIN: This pin is connected to the bypass capacitor that reduces the voltage transients along with providing the switching current.
- Output: This terminal behaves like an internal switch where voltage potential goes back and forth between (Vin – Vsat) and -0.5V. The Vout/Vin is this pin duty cycle. The coupling is reduced due to the presence of PCB copper attached to this pin.
- Ground: This is the ground pin.
- Feedback: For the feedback loop, this pin defines the regulated output voltage.
LM2576 Features
The following are the main features of LM2576.
- Output Voltage available for variable type regulator = 1.23V to 37V
- Internal Oscillator frequency = 52-kHz (this is a Fixed Frequency)
- Output Current = 3A
- Used as a switch-mode step-down voltage regulator
- Comes with In-built Current Limit and Thermal Shutdown Protection
- Output Voltage available for fixed voltage regulator = 3.3V, 5V, 12V or 15V
- Maximum Input Voltage = 40V
- Available packages = TO-263 & TO-220
LM2576 Applications
The following are the main applications of LM2576.
- Incorporated as a pre-regulator in linear regulator
- Used in On-card switching regulators.
- Employed to drive load under 1A.
- Employed in a simple efficient step-down regulator.
- Used in a positive-to-negative converter.
That was all about the Introduction to LM2576. Hope you’ve enjoyed reading this article. If you have any queries, you can pop your question in the section below, I’d love to help you the best way I can. Feel free to share your valuable feedback and suggestions around the content we share, so we keep producing quality content customized to your exact needs and requirements. Thank you for reading the article.
1n4734 Zener Diode Datasheet, Pinout, Features & Applications
Hi Folks! I hope you’re well today. I welcome you on board. In this post today, I’ll walk you through the Introduction to 1n4734.
The 1n4734 is a silicon planner power Zener diode that is employed as a low current voltage regulator. It is incorporated as a shunt regulator in many applications. This Zener diode conducts the current in both directions in contrast to the regular diode that conducts in one direction only i.e. regular diode conducts in forward biased condition only. This Zener diode conducts in both conditions forward biased condition and reverse biased condition. Power dissipation in this Zener diode is 1W and standard Zener voltage tolerance is ±10%.
I suggest you read this entire post till the end, as I’ll detail the complete Introduction to 1n4734 covering datasheet, pinout, main features, and applications. Let’s dive in.
Introduction to 1N4734
- The 1n4734 is a Zener diode employed as a low-current voltage regulator. It is also employed in clipping circuits with high power ratings. This Zener diode is made of semiconductors and is used in voltage protection circuits.
- The current flows from the anode side to the cathode side in the regular diode in a forward-biased condition. On the other hand, in the case of the Zener diode, current conducts in both conditions i.e. forward biased condition and reverse biased condition. Forcing regular diodes to conduct in both conditions will damage the device.
- The Zener diode is normally used in modern electronics and is constructed by plenty of different voltages.
- While picking the Zener diode there are two parameters that you should consider… one is the power dissipation and the other is the power Zener voltage. When a higher reverse voltage is applied to the Zener device it creates the Zener voltage.
- Some Zener diodes experience sharp and highly doped p-n junction when they undergo a Zener effect or Clarence Zener.
- The power dissipation inside the Zener diode is used to identify the amount of current flow. More power dissipation results in more current flow. Power dissipation in this Zener diode is 1W.
- Zener diodes are utilized to generate low-power supply rails using higher voltages. Reference voltages in the electrical circuits are also produced by these Zener diodes.
- In some electrical circuits, there is a limit to the applied voltage. The voltage applied above this limit can damage the device. These Zener diodes are used in those circuits to prevent circuits from overvoltage.
1N4734 Datasheet
Before you apply this component to your project, it’s wise to have a look at the datasheet of the component that contains the main characteristics of the device. Click the link below if you want to download the datasheet of 1n4734.1N4734 Pinout
The following figure shows the pinout diagram of 1n4734.- The 1n4734 comes with two terminals named anode and cathode. The anode terminal is positive while the cathode terminal is negative.
- The current enters the diode through the positive anode terminal while the current leaves the diode through the negative cathode terminal.
- The current flows in both conditions in 1n4734 i.e. forward biased condition and reverse biased condition.
1N4734 Features
The following are the main features of the 1n4734 Zener diode.- Package = DO-41
- Zener Voltage (VZ) = 5.1V
- Used as shunt regulators.
- Power dissipation (PZ) = 1W
- Zener regulator current (Izt) = 49mA
1n4734 Applications
- Used in voltage protection circuits.
- Used as voltage protection for Microcontrollers.
- Used as a low current voltage regulator.
- Used for clipping circuits with high power ratings.
- Used in voltage stabilizing circuits.
That’s all for today. I hope you’ve enjoyed reading this article. If you’re unsure or have any questions, you can ask me in the section below, I’d love to help you the best way I can. Feel free to share your thoughts and feedback around the content we share, so we keep sharing quality content customized to your needs and requirements. Thank you for reading the article.
7 Most Commonly used Types of PCB (Printed Circuit Board)
Hello everyone, how are you doing and I hope everybody is doing great. i am going to discuss today the Types of PCB (Printed Circuit Board). Thank you, everyone, for coming back to our website and it means so much. we are grateful for your engagement and most importantly for choosing to educate yourself over anything else in the world.
PCB circuit boards are everywhere and we daily use dozens of circuit boards and interact with them. There is no doubt in saying that the PCB has made our lives easier and advanced. For example, the first thing in the morning your alarm goes off, and wherever you hit snooze, every time you send a signal through its circuit board. And probably the list goes on as you turn the light on off etc.
Let's begin!
What is PCB
The abbreviation of the Printed circuit board is PCB, and it is the core of electronic products. But all of them are not equal. They are available in different types and made from different materials and specifications for a wide range of applications. Since the early 1900 PCBs are manufacturing and there is a major evolution of PCB happened in the last few years. PCB is a board that interconnects different electronic and electrical components. It is necessary for building a circuit. This article will bring a deeper understanding of the types of the circuit board and help you in finding the most suitable PCB for your needs. If you are working on some electronics project and want to design or fabricate PCB / PCBA, then we would suggest you to try PCBWay Fabrication House. They have an experienced team, eager to guide you throughout the process. & they always provide excellent results as per your requirements.Different Types of Circuit board
- As I mention before that printed circuit board comes in a different size because of their characteristics and different requirements.
- The copper rails on circuit boards are used to connect different points of locations. They are easy to recognise.
- Their design makes them different from each circuit.
- Most of the PCBs are made of fibreglass, composite epoxy, and other composite materials.
- For simple electronics most of the time only one or single layer PCB use. But for the sophisticated or complex one such as motherboards and computer graphics card multi-layers PCBs used.
Single Sided PCBs
A single-sided circuit board is the simplest one and made out after a different process. Let's find out.- It is the least complicated one.
- Contain one layer of substrate or base material
- One layer of the substrate is covered with the thin layer of metal or copper (it is excellent conductor)
- After the copper base painting usually a protective solder mask is applied.
- A silkscreen coat is applied to complete the look
Double Sided PCBs
Double Sided Printed circuit boards are more common as compare to single sided PCBs. Because of their high properties.- Both sides have metal conductive layers and parts are connected to both sides
- Electric components are separated evenly on the entire board
- Holes are drilled through the board to connect to the other side too.
- For connecting both sides used through holes or with the surface-mount.
What is Through Hole
Through holes in double-sided PCBs means that small wires (known as leads) are fed through the holes with each end of the leads and then joined to the right component.What is Surface Mount
In the surface mount wires are not used as connectors. Alternatively, small leads are soldered directly to the board. Simply put, that board itself is used as a wiring surface for the many components.- Less space
- Allowing the board to complete more function by freeing up space
- Lighter weight and higher speed than through hole
Multi Layers PCBs
The Multi Layers PCBs are more complex than double sided PCBs. It consists of a series of three or more double layers. These are using advanced technology in double sided boards.- More than two layers of the substrate on the board
- The insulating material used on every layer
- The same latest technology of double sided is used to connect the different components
- The largest multilayer PCB was fifty layers thick.
Rigid PCBs
Rigid Circuit boards are made of the solid substrate like printed circuit boards. Printed circuit board are not just classified based on layers and sides.- It prevents the board from twisting.
- A most common example is a rigid motherboard
- The main difference is the number of layers
- Rigid PCBs consist of different rigidity
Flex PCBs
Flex is a short form of flexible. You can guess it with a name that it will make the flexible PCBs with the flexible plastic.- Fit into different shapes
- Bend the board anytime and keep it safe
- Costly than other designs
- PCBs are light in weight and used in advanced technology
Rigid-Flex PCBs
As shows in name that it is the combination of rigid and flex. It is the last type a litle bit confusing but the main concept behind it was to use it with the strongest boards.- Bothe flexibe and rigid
- Circuit board is rigid but its connect layers with the flex circuit board
- Difficult to make
- Consist of multi layers of flexible PCBs
It have many advantages of using over flex and rigid PCBs. These are found in cell phone applications, digital cameras and automobile etc.