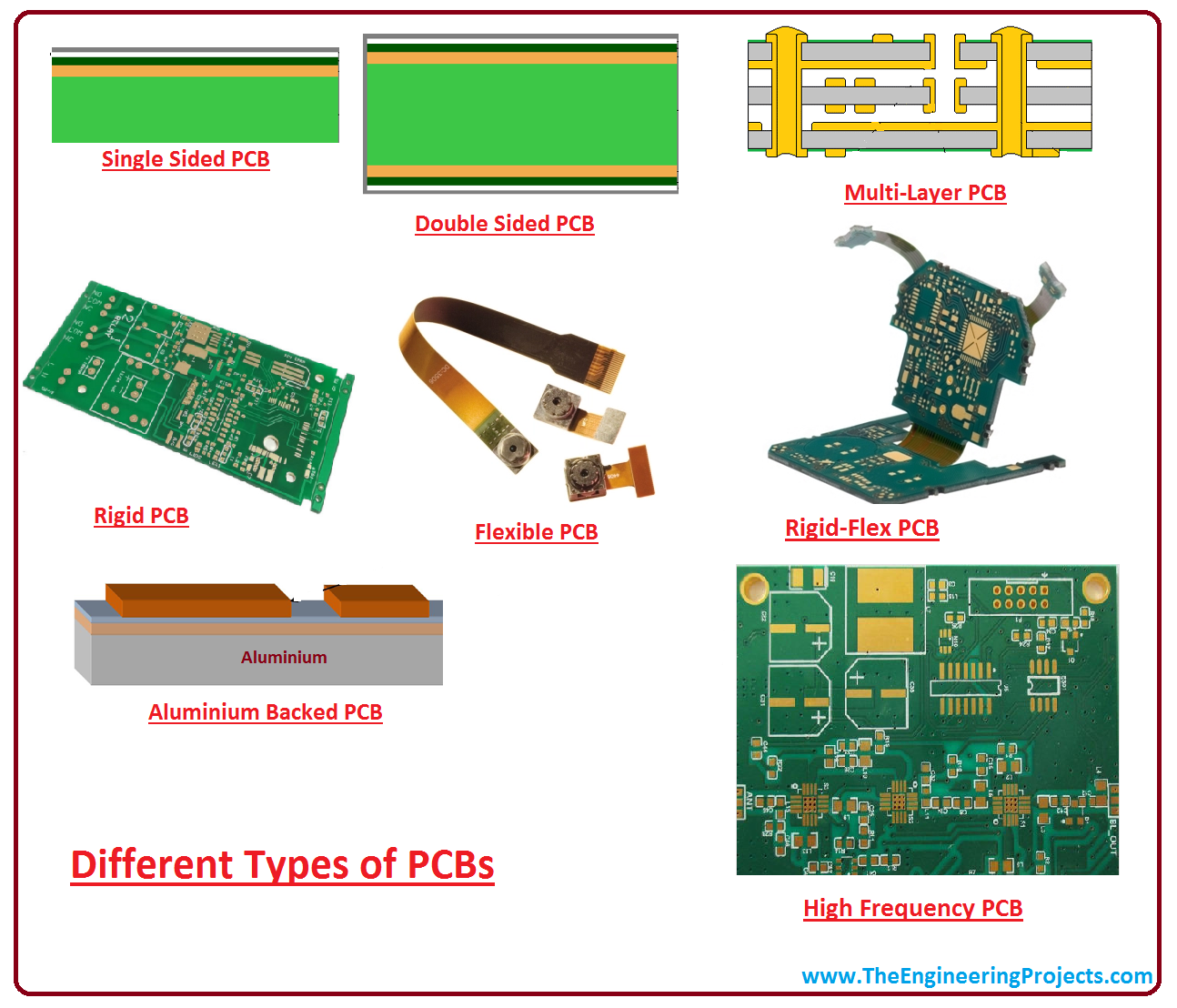
Different Types of PCB(Printed Circuit Board)
Hello Everyone! I hope you all are doing well. Today, I am going to share the 12th chapter in the PCB learning series. In today's lecture, we will have a look at the Different Types of PCB(Printed Circuit Board).
We are familiar with the PCB, it is a printed circuit board that contains traces, lines and paths to electrically connect electronic components. It consists of a substrate on which copper conducting material is laminated for creating an electrical connection between components.
Let's dive in and explore these types of PCB boards:
Types of PCB(Printed Circuit Boards)
Following is the list of available types of PCB types. You can choose any PCB based on your requirements:- Single-Layer PCB
- Double Layer PCB
- Multilayer PCB
- Rigid PCB
- Flex PCB
- Rigid-Flex PCB
- High-Frequency PCB
- Aluminium Backed PCB
1. Single Layer PCB
- A single Layer PCB contains only one layer of conductive copper foil.
- One side of the base material(substrate) is laminated with metal(normally copper) that is used to build an electrical connection between the components soldered on the board.
- Copper is mostly used for creating a conducting path because it acts as a good conductor and comes with low resistance.
- A solder mask is used on top of the copper layer which provides solid protection.
- On the top of the solder mask, there exists a silkscreen coating that is used for marking the elements on the board.
- Single-layer PCB is an ideal choice for beginners, as mostly used in simple electronics which don't involve complex circuitry.
- They are easy to manufacture and less time-consuming.
- Cheap cost and easy availability make these PCBs an ideal choice for hobbyists.
- These low-cost boards are widely used in many applications including stereo components, calculators, cameras, power supplies and printers.
2. Double-Layer PCB
- Double-Layer PCB contains two layers of copper material and substrate material is present in between these copper layers.
- Both layers are connected to each other using holes(called vias) drilled into the boards.
- Components on these PCB boards are connected using two technologies i.e. Through Hole Technology and Surface Mount Technology.
- Double-sided PCB features a moderate level of complexity and is mostly used in applications including automotive dashboards, LED lighting, vending machines, amplifiers, HVAC system, instrumentation etc.
3. Multilayer PCB
- Multilayer PCB contains multiple layers of copper and is designed with a combination of single-sided and double-sided PCB boards.
- A layer of insulation(substrate material) is placed between each board in order to provide protection that prevents the components from burning in case of excessive heat.
- Multiple layers allow the professionals to design complex designs which help in accomplishing complex electrical tasks.
- The extra layers incorporated in the multilayer design are very helpful and often used for preventing electromagnetic interference emitted by the design itself.
- Multilayer PCBs are widely used in a number of applications including Satellite systems, GPS technology, Data storage, File servers and Weather analysis systems.
4. Rigid PCB
- Rigid PCB has a hard base material(substrate), normally of fiberglass/epoxy resin and provides strength to the circuits by making them rigid.
- A computer motherboard is an ideal example of a rigid PCB that is composed of rigid substrate material.
- The motherboard is a multilayer PCB that is designed to distribute electricity from the power supply and helps in creating a conducting path between different parts of the computer including CPU, RAM and GPU.
5. Flexible PCB
- Flexible PCB can flex or transform into any shape based on needs/requirements.
- Flexible PCBs are also referred to as Flex Circuit and use plastic material in contrast to rigid PCBs, which use fiberglass that provides rigidity and strength to the PCB.
- The conducting material used in these PCBs is mostly composed of polyester, polyamide or PEEK (Polyether ether ketone).
- These PCBs pertain to a high level of complexity and come with different layers ranging from single-sided, double-sided or multi-layer flex circuits.
- The flexible nature sets these PCBs apart from others as they can be folded and wrapped around the corner.
- In order to avoid environmental hazards, flexible PCBs are composed of materials that are resistant to high-temperature oils, corrosion-resistant, waterproof and shockproof.
- These flex circuits are used in a wide range of applications including Flex solar cells, LCD fabrication, Cellular telephones, automotive industries, Laptops, cameras, LEDs and many more.
6. Rigid-Flex PCB
- Rigid-Flex PCB is manufactured when a flexible PCB is combined with a rigid PCB.
- This gives both flexibility and strength to the electronic product.
- Rigid-Flex PCB is more expensive and difficult to design as compared to Rigid or Flexible PCB.
- Less space required to construct a whole circuit and minimum weight makes these PCBs an ideal choice for handheld electronic devices including pacemakers, automobiles, cell phones and digital cameras.
7. High-Frequency PCB
- High-Frequency PCB is slightly different in terms of construction and material used for traditional PCB and is capable of transmitting signals over 1GHz.
- These PCBs are often composed of materials like polyphenylene oxide, Teflon, and glass-reinforced epoxy laminate.
- Small dielectric constant makes Teflon, an expensive choice for high-frequency PCB and it also provides low water absorption and small dielectric loss.
- You must take some things into consideration before choosing high-frequency PCB for your projects like dielectric thickness, dielectric constant and power dissipation.
- The dielectric constant is the most important feature when it comes to choosing high-frequency PCBs because if the dielectric constant changes too quickly and is unable to maintain a constant state, it leads to corrupting the digital signal which affects the overall performance of the signal.
- Similarly, dielectric loss is directly proportional to the signal loss and it also affects the signal transmission quality. Smaller dielectric loss leads to smaller signal loss.
- High-Frequency PCBs, if used in a wet environment can affect the dielectric constant.
- The material selection for making these PCBs is very important, the material you pick must be resistant to heat and hazardous chemicals and provides strength and durability to the PCB surface.
8. Aluminum-Backed PCBs
- Aluminum Backed PCBs are similar to copper PCBs with some exceptions i.e. Substrate in aluminum-backed PCBs is made up of aluminum.
- These PCBs are coupled with insulating material that provides less thermal resistance, avoiding the heat from transferring to its backing.
- Aluminum is inexpensive, making almost 8.23% of the planet's weight, and leads to the most economical manufacturing process.
- PCBs made up of aluminum are easily recyclable and non-toxic in nature.
- Aluminum is very durable than its counterparts like fiberglass or ceramic and pertains to less damage during the installation and manufacturing process.
- And aluminum is an ideal choice for dissipating heat from the circuit components, allowing the heat to transfer into the atmosphere rather than transferring it to the rest of the board.
- Aluminum Backed PCBs are widely used in high-output power applications including power supplies, automotive lights, traffic lights, motor controllers etc.
- Aluminum-baked PCBs also pertain to high mechanical stability and have the capability of bearing high mechanical stress.
- In contrast to fiberglass boards, aluminum-backed PCBs provide less thermal expansion, allowing the copper foil and insulation to stay placed on the board, hence helping in increasing the overall lifespan of the board.
That's all for today. In the next tutorial, we will have a look at the Single Layer PCB in detail. I hope you have enjoyed these different types of PCB. However, if still you feel any doubt or have any questions, you can ask me in the comment section below, I'd love to help you according to the best of my expertise. Stay tuned!
How to make PCB using CNC Milling Machine
How to make PCB using CNC Milling Machine
- Technology has been evolved in an amazing way and make our lives easy and practical.
- Now you don't have to depend on the manual methods of making PCB that also involves some risk and doesn't give high precision.
- Creating a PCB with using milling machine gives you a flexibility to modify your PCB board into any shape based on your needs and requirements.
- Before you get a hold of making PCB, you must create a schematic diagram and PCB prototype in order to give a clear idea what components you will be using and how they are connected using different paths and traces.
- If you are electronics hobbyists or some professional, first knowledge you must get is making a PCB on your own. It will make you independent from other manufacturer who can cost heavily and ask for two or three days to deliver the PCB into your address.
- If you get familiar with making your PCB using milling machine, you can make your PCB right away with little knowledge.
- Before you starting making PCB using milling machine, you must learn how to use milling machine in proper way in order to create quality end product.
- First thing you must consider for making PCB using milling machine is that it can be costly than creating PCB using etching method.
- But it is not as risky as etching method because it involves no chemical reaction what so ever.
PCB Designing
- Designing your own PCB is very easy and any one can do it. It involves two steps.
1: Schematic Diagram
- You must start with creating a schematic diagram using Eagle software.
- Schematic diagram gives clear overview what kind of components you would be using in your design and how they are connected with different paths and traces.
- This diagram won't indicate the actual path that you would be transferring on the actual copper board, because lines and paths you use creating a schematic diagram can be differently aligned on the PCB board.
- Schematic is only for giving knowledge that even common man can anticipate how different components are connected on the boards.
2: PCB Layout Designing
- Next step is making a PCB layout design. This design will define the actual circuit design that will be incorporated on the copper board.
- There are many software you can use to create PCB layout design including PCBWizard, Cadsoft Eagle, Proteus and many more.
- PCB layout design covers less space than schematic diagram and it can be easily placed in a tight space based on your requirements.
- Be careful when you create PCB layout design and avoid the short circuit for the sake of covering the as less space as possible.
Making PCB using Milling Machine
- Now you are all done with your schematic diagram and PCB layout design.
- There are two ways to create PCB i.e additive method and subtractive method. In additive method we add copper on the predefined trances on the board and in substractive method we remove unwanted copper from the copper clad, leaving behind the copper traces that electrically connect different components.
- In milling machine we will use substractive method where we use copper placed on the predefined lines and will remove unwanted copper.
Milling Process
- Milling process will take no more than 30 minutes however it depends on the thickness of the bit and the size of the PCB and the number components and their alignment it would carry.
- PCB milling is the method which involves removing the unwanted copper from the board to create paths, and signal traces according to the layout design.
- It is totally non chemical process which can be achieved in lab environment and involves no hazardous chemical and gives a quick turnaround if you intend to make number of PCBs.
- The quality of PCB depends on the milling accuracy and sharpness of the milling bits you use for milling.
- The rotational speeds of milling bits have little or no effect in the quality and precision of PCB.
- You need to practice this process of making PCB using milling machine if you are using milling machine for the first time.
- You will be able to make high quality product with greater precision if you take few precautions prior to making PCB.
- Software used for PCB milling is provided by milling machine manufacturer.
- Software can be divided into two categories i.e. Raster and Vector.
- Software that utilizes raster calculations comes with lower processing resolution than vector based category because it is dependent on the raster information.
Mechanism
- PCB milling machine makes use of advanced CNC milling technology.
- The milling machine controller is controlled by software that receives commands and machine control information through serial and parallel port.
- The controller is able to monitor the positioning features that are capable of moving the milling head and control spindle speed.
- Spindle speed depends on the type of system you use and it ranges from 30,000 rpm to 100,000 rpm.
- Higher spindle speed comes with higher accuracy and better precision.
- The whole positioning system consists of stepper motor for x and y axis and pneumatic piston for z axis and simple DC motor is used to control the spindle speed.
- In order to control higher speed, RF spindle motor control is used.
- More advanced drive systems come with monitored stepper motor that provides greater control during milling and drilling process.
Other Processes
- After completing the milling process, you can solder required components into the board based on your needs and requirements.
- There are two ways to place and solder the components on the board. One is through hole process and other is surface mount process.
- Through hole process involves inserting the leads into the PCB hole and then connect to the pins of right components.
- This process becomes obsolete as it is an older process and occupies more space.
- Surface mount technology is an advanced method in which components are mount on the board surface and then soldered to the right components.
- This process occupies lesser space than through hole process and is an ideal choice for most of the professionals.
- Be sure to take appropriate measure before soldering the components. The solder you use for soldering the components mostly consists of lead that is considered as a toxic material.
- And the fumes created by the the soldering can be hazardous to health.
- It is better to clean and extract the fumes before you discharge them into the environment.
- You must take safety measures before you start milling the board. You should wear safety goggles, use the drill bit carefully and put your hand away from the board when spindle is active.
Advantages
- PCB milling process comes with a lot of benefits because it involves no hazardous chemical and is an ideal choice for mass production.
- Best part is that CNC milling can be used for multiple purpose i.e milling, drilling and cutting.
- You can change the bits based on your needs and requirements.
- Some PCB boards that are easy to create using PCB milling process are very difficult to create using wet etching process that also involves manual drilling afterwards which costs lot more than regular milling process.
Alternative Methods
- Laser etching is a great alternative to both chemical etching and milling process.
- This process is an ideal choice for most of the applications because it involves no direct contact with the board and it removes the material without physically touching it.
- When it comes to high precision and greater accuracy, laser etching process is preferable and is mostly used for advanced microwave and RF designs.
- This process involves low power consumption, delivers high accuracy, doesn't make use of lubricants and abrasive material and pertains to low wear and tear and needs less maintenance.
- However, this process also comes with some limitations and is expensive as compared to other processes.