Hi readers! I hope you are doing well and finding something new. Today the topic of discussion is “What is Metal 3D Printing? Its types, processes, and materials”. In today’s hi-tech world, one of the disruptive technologies that have gained attraction is metal 3D printing also known as metal additive manufacturing. Whereas most traditional manufacturing methods are mostly deductive, fabricating a product by first eliminating material to arrive at the desired shape and form, 3D printing systems deposit material and meticulously create the designed, high-performance parts that benefit the aerospace and healthcare industries as well as many others.
Take-up of metal 3D printing is already increasing – and rightly so – because it tackles targets such as material waste, production problems, and design constraints. Since organizations are searching for approaches that may help them retain competitiveness, it is an ideal enabling tool to transform manufacturing strategies and provide tailored solutions.

In this article, you will find information on metal 3D printing, the types of processes used in metal 3D printing, and the materials used. Let’s start.
JustWay offers Metal 3D Printing Services:
Precision and durability are key to manufacturing for all developers, groundbreakers, innovators, and companies. These qualities ensure high-quality results, reliability, and performance across various industries and applications. But where can you find expert Metal 3D Printing services?
JustWay offers Metal 3D Printing Services with high precision and efficiency at a low cost to bring your designs to life with great accuracy and strength. The advanced technology that we use can provide superior mechanical properties, and complex geometries, and ensure durability in your parts, making them functional. We specialize in aerospace, consumer electronics, robotics, automotive, and medical fields, offering fine surface finishes and rapid production time. Whether you need functional prototypes or end-use metal components, our Metal 3D Printing service offers the perfect balance of quality, speed, and affordability, enabling you to stay ahead in competitive markets.
Justway gives you 3D metal printing services with advanced technology. They use Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Digital Light Processing (DLP), Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), and Selective Laser Melting (SLM) to print and deliver the best services. They print products in all metals like aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and tool steel. They offer high quality and a variety of finishing options which include spray painting-high gloss paint, spray painting-matt paint, vacuum plating-high gloss paint, vacuum plating-matt paint, #1000 sanding, silkscreen, laser engraving, and dyeing.
Justway offers 3D Printing not only in metals but also gives service of plastic 3D Printing with high quality and finishing. They make products in all plastic types including ABS, Resin, POM, PEEK, Nylon, PETG, ASA, PC, and PALA. Moreover, Justway offers a wide range of services to its customers. They offer CNC Machining, 3D Printing, Sheet Metal Fabrication, Injection Modeling, and Utherane Casting. It offers seamless prototyping and production solutions.
Rapid Prototyping and Scalable Production
Versatile Materials and Advanced Processes
High-Precision, Cost-Effective Manufacturing
Fast Turnaround for Faster Market Entry
Whether you’re shaping the future of aerospace, robotics, automotive, medical, or consumer products, JustWay turns vision into reality. Innovate with JustWay—your trusted partner in manufacturing excellence! Contact us today!
Metal 3D Printing:
Metal 3D printing is additive manufacturing that makes parts from metal using digital designs as a guide. In this process layers of the part are added to create a part. The manufacturing technology provides for complex geometries, lightweight structures, and well-defined variations in geometrical features, depending on desire. It is applied in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries with zero material waste, thereby being very efficient in modern manufacturing.
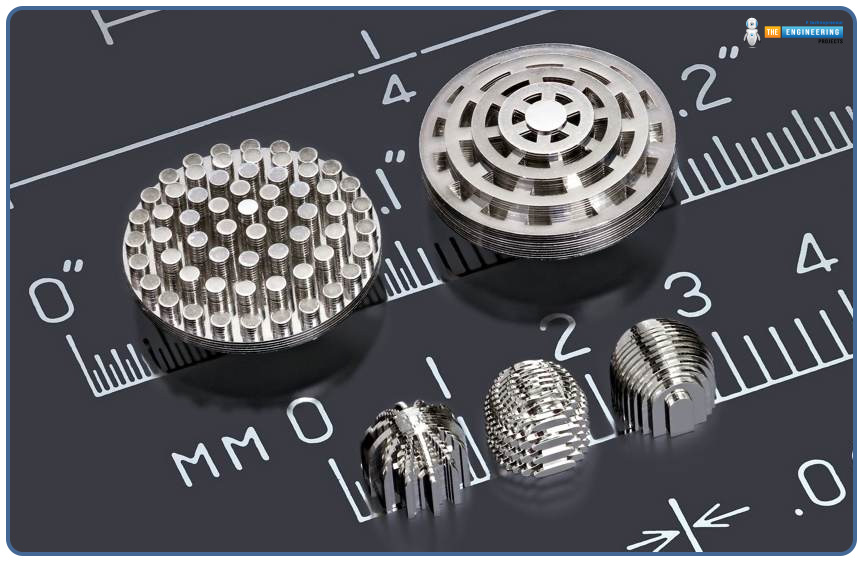

Origins and Development:
Metal-based 3D printing emerged from the earlier additive manufacturing technology that had emerged with plastics in the 1980s, including SLA and FDM. Material science and laser technologies improved steadily to enable adaptation of these principles to metals. By the early 2000s, technologies like Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM) started gaining commercial maturity, ushering in industrial metal 3D printing.
Contemporary Adoption:
The usage of metal 3D printing has been on the rise in the recent past, and the projected market growth rate is 28.1% while the market size is said to be $19.2 billion in 2030. Auto, aerospace, healthcare, and energy sectors have been stratum front runners in adopting this technology because of the excellent production of lightweight, strong, and complex parts.
Types of Metal 3D Printing:
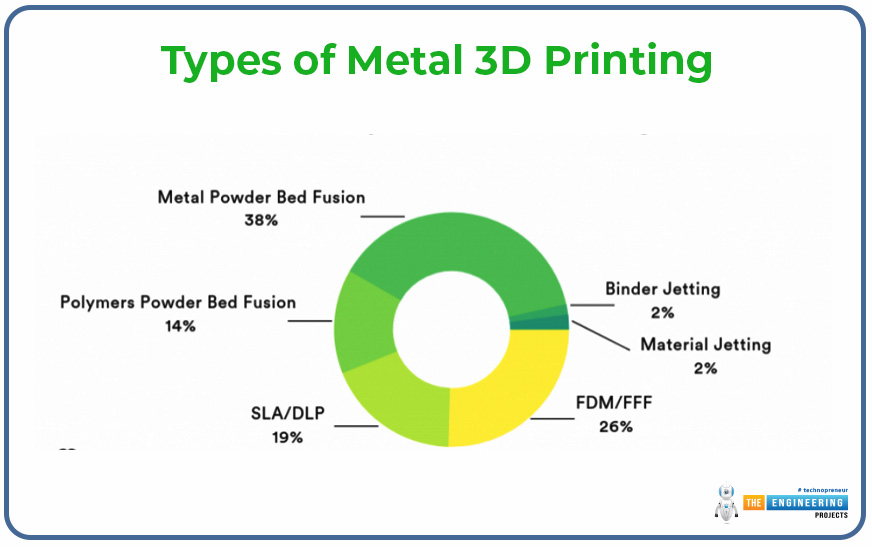
Powder Bed Fusion (PBF):
Metal-based 3D printing technology is the most widely practiced technique out of all which comes under the Powder Bed Fusion category. In an additive process, it works through a highly concentrated beam of light or electricity a laser or electron beam to fuse fine metal powder that is deposited in each layer of the build. Once a layer is melted, the pattern repeats, with one layer laid down at a time, adding up to the complete build. The core PBF technologies are:
SLM:
As a final step selective laser melting lets the metal powder melt and joining the layers deposit to create the parts solid. It has the capacity for high-strength materials namely titanium and stainless steel. The results are very strong, dense parts with great accuracy. Thus it is used suitably in aero and biomedical applications.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS):
DMLS is quite similar to SLM but the metals used and the parts built are less dense. DMLS is used for aerospace and medical applications and provides strong parts with good mechanical properties.
Binder Jetting:
Binder Jetting is where metal powder is spread layer by layer and the part’s powder is selectively bonded by a binding agent. Once the part is printed, it has to be exposed to a furnace used to sinter the part. This process strengthens and consolidates the metal further into a solid part. Binder Jetting produces parts much faster and is used extensively for prototypes and low- to medium-volume parts. It is also cheaper in certain applications but has slightly lower mechanical properties than PBF.
Directed Energy Deposition:
Directed energy deposition utilizes energy beams, including lasers to deposit energy that melts the metal powder or wire onto the substrate of the part. It particularly applies in the repair and generation of work material on existing part fabrication along with difficult contours. Most importantly, these processes can find excellent applications in the aerospace industry to repair turbines and other structures that have blade edges and components for which repair in the field is often desired. DED has the capability of making parts larger than most methods and has greater material deposition rates.

Metal Extrusion:
Another approach to 3D printing is metal extrusion, which consists of melted and pushed metal filaments through a nozzle and solidifies by forming layers due to cooling and sticking together. Generally, the printing of a part is usually sintered within a furnace so that the whole strength of the material can be attained. Metal extrusion is very useful for prototyping and also cheap when high accuracy or specific properties of materials do not come into play when it's just for some cheaper applications.
Electron Beam Melting (EBM):
Electron Beam Melting is closely comparable to Selective Laser Melting but the latter employs an electron beam for fusion of metal powder. The most widely used EBM technique has been practiced on titanium and cobalt-chrome alloys. It is common in aerospace and medical implants. It works under vacuum, so parts produced using EBM can have high density and strength.

Processes of Metal 3D Printing:
Design and Modeling:
It begins with making a 3D digital model of the part to be manufactured. In most cases, this is created using CAD, or Computer Aided Design, software. The model then gets translated into an STL file in fact or a similar file format readable by the 3D printer. A design for 3D printing should be optimized for printing with the geometry, support structures, and properties of the material to be taken into consideration.
Preparing the Printer:
After the 3D model is prepared, the metallic powder starts preparing the metal 3D printer. This involves:
Loading material:
Metallic powder 3D printers usually utilize metal powders, metal filaments, or wire as the material. These are loaded into the chamber of the printer based on the process that is being applied.
Configuring settings:
The printing parameters, such as layer thickness, print speed, and temperature, are set according to the material used and the desired final part properties.
Printing Process:
The actual printing process varies depending on the metal 3D printing technology, but generally follows these steps:
Layer-by-layer Deposition:
Here, the energy source in the case of a laser or electron beam print head for a printer selects the metal powder, wire, or filament and melt-fuses it onto the substrate by layer. Part-by-part builds are created starting from the bottom upward with each deposit accurately bonded upon the previous.
Fusing or sintering:
The metal is either melted (in processes such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM)) or sintered (in Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)), where metal powder particles are fused without fully melting them.
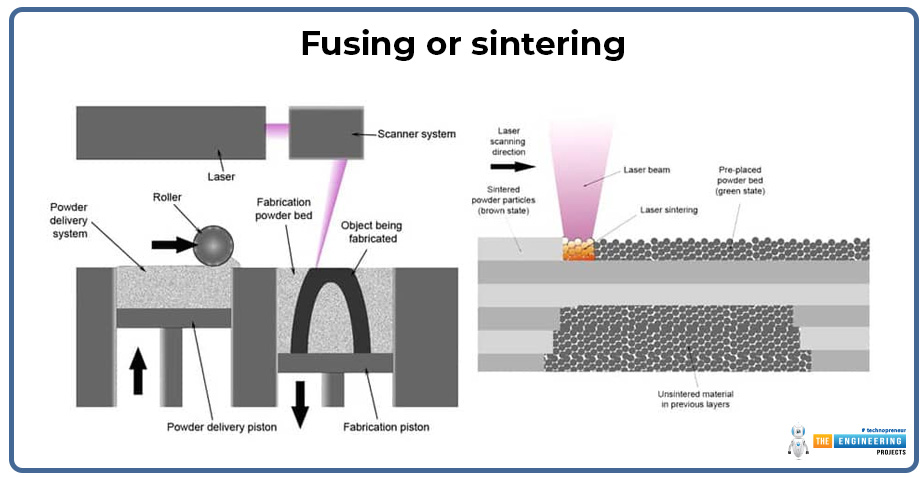
Cooling:
This section then cools after every layer is deposited and set. In some processes, cooling rates are controlled to reduce internal stresses that may cause the product to warp. For example, in EBM, or Electron Beam Melting, cooling is done in a vacuum to prevent oxidation and obtain optimal material properties.
Post-processing:
The printed metal part undergoes post-processing to fine-tune its mechanical properties and finish:
Support removal:
Most metal 3D printing processes require support to be printed during the process itself. These are usually made of the same material but should be removed from the part when printed.
Sintering or heat treatment:
In some processes like Binder Jetting, parts are sintered in a furnace to remove binders and fuse the metal powder into a dense, solid part. Heat treatment can also be used to alter material properties like hardness or strength.
Surface finishing:
Depending on the application, some metal parts would require additional surface finishing operations, such as polishing, sanding, or coating, to improve the texture and appearance of the part.
Inspection and Testing:
The post-processing part then undergoes tight quality control and testing to satisfy the standards and specifications required. This may include the following:
Dimensional inspection:
A measurement of the part to get its dimensions and tolerances.
Mechanical test:
Test whether it is stiff, flexible, or of whatever kind the part is.
Non-destructive testing:
Methods in this category include techniques like X-ray inspection or ultrasonic testing to discover inner flaws or holes that can impair performance.
Metals for 3D Printing:
Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel is also expected to be one of the most widely used materials for 3D Printing because of its versatility, strength, and corrosion resistance. Good for uses where it will be applied in the aerospace business, automobile, and in the health sector.
Common Grades: 316L, 17-4 PH
Properties: These characteristics include high strength, high corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and good formability.
Applications: For medical implants tooling aerospace and automotive combined and many other parts.
Titanium:
Titanium is famous for its high strength-to-weight ratio and has excellent corrosion resistance in oysters, high-performance surroundings, and conditions. It is very light but very highly tensile and compatible with living tissues.
Common Grades: Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-4V ELI (extra low interstitials).
Properties: High mechanical strength, low weight, better corrosion resistance, and suitability for biomedical applications.
Applications: Engine Aerostructures, Medical Prosthetics, and Orthopedic implants like total hip replacements, various high-performance Engineering application Parts, and OEM auto components.
Aluminum:
Aluminum is light and has relatively strong strength though it is highly resistant to corrosive materials. It is applied in sectors where the product’s weight is most important.

Common Grades: AlSi10Mg, Al-6061
Properties: Non-ferrous material: It is light in weight, has a good strength-to-weight ratio, does not get corroded easily, have good machinability.
Applications: Airplane manufacturers, automobile manufacturers, and power, and other mechanical parts (composites) industries.
Cobalt Chrome:
Cobalt chrome demonstrates high strength, excellent wear, and extreme temperature resistance. Its alloy is found in medical implants and aerospace applications.
Properties: It has strong strength, wearing resistance, anticorrosive properties, and good high-temperature stability.
Application: It contains applications such as medical implants and aerospace components together with industrial ones where wearing is needed.
Nickel Alloys:
Nickel-based alloys are mainly for high-temperature applications and are generally for those application conditions that reach extremes. In principle, the material is used within the gas turbine, jet engines, and chemical processing areas.
Common Alloys: Inconel 625, Inconel 718
Properties: Excellent strength against a high-temperature environment, resistance to corrosive action, and excellent mechanical characteristics.
Applications: Aerospace (blade in turbine); gas turbines of the high-end performance engineering field.
Copper:
Copper possesses excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, which is one of the prime reasons why copper is very useful for 3D printing. In those applications, where dissipation of heat is critical, it is very specifically useful.
Properties: Good electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion-resistant.
Applications: Heat exchangers, electrical parts, and components demanding efficient heat transfer.
Bronze:
Bronze Alloy contains copper with tin or other metals. It shows mechanical strength, resistance to corrosion, and aesthetic appearance. They are widely used for decorative or artistic objects.
Properties: Corrosion resistance, strength, aesthetic look
Applications: Decorative items, jewelry, and industrial components.
Steel Alloys:
In metal 3D printing, high-utilization steel alloys, especially tool steels and other strong alloys are used to make strong, high-performance parts.
Common Grades: Maraging steel, H13 steel
Properties: High strength, durability, resistant to wear
Application: Tooling, car parts, molds, or any industrial use where high strength is required
Gold and Silver:
Other precious metals like gold and silver are printable especially used in jewelry and high-end, custom production.
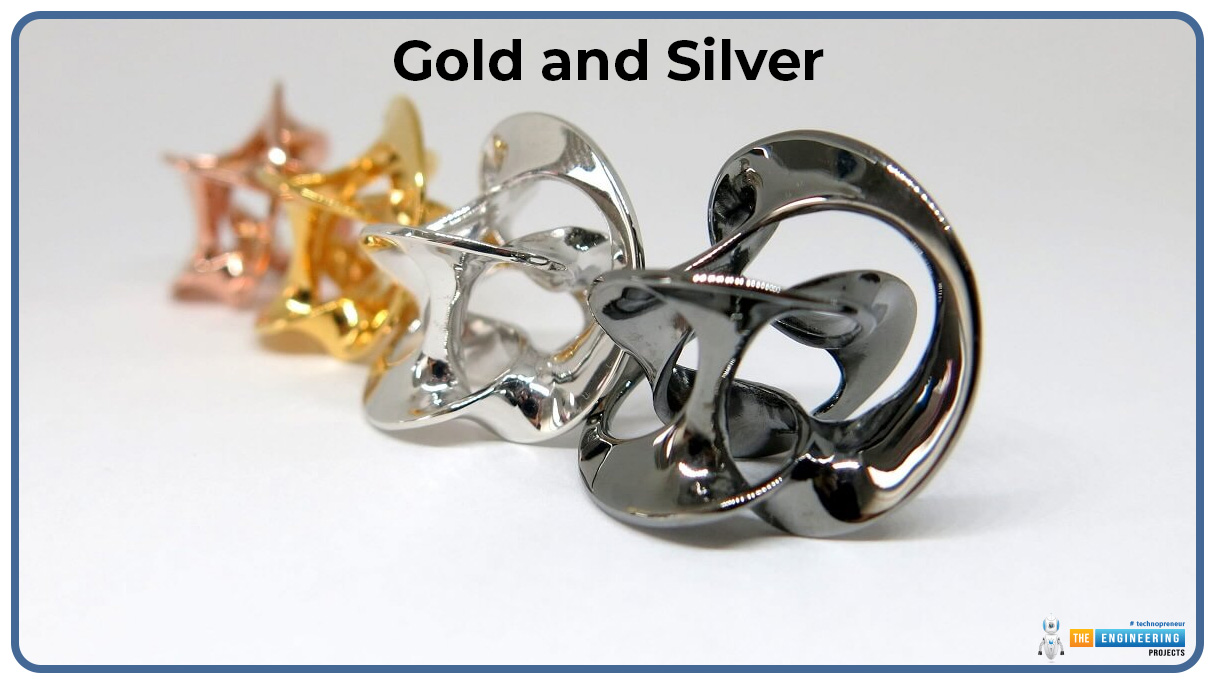

Properties: Aesthetics, corrosion resistance, excellent formability.
Applications: Jewelry, luxury goods, and ornaments.
Maraging Steel:
Maraging steel is an ultra-high-strength steel alloy, used for printing metal in 3D for pieces that need extreme tensile strength, not easily deformed when stressed.
Properties: Ultrahigh tensile strength and toughness with little tendency to crack.
Applications: Aerospace, tooling, and very high performance in mechanical parts
Invar Steel:
This is a Ni-Fe alloy that is held to be the best alloy material for extremely low expansions with heat.
Properties: Small thermal expansion but high tensile strength and modulus.
Applications: Aerospace, metrology, and precision instrumentation.
Conclusion:
Metal 3D printing changed the game in manufacturing. That meant complex, high-performance parts for aerospace, automotive, medical industries and more could be produced. Stainless steel and titanium, nickel alloys, and precious metals like gold are the metals that can be chosen to meet the designer's specific needs.
Because of each metal's unique properties, metal 3D printing offers solutions ranging from lightweight aerospace components to more durable tooling and biocompatible medical implants. Its ability to minimize waste and optimize designs makes it an important part of modern manufacturing today. The coming years will see the inclusion of new materials and better process development that expands its possibilities toward more innovative, effective, and sustainable modes of production.



