The rapid developments that have been achieved in the Light Emitting Diode industry more so in the area of high-power LEDs, have brought up a challenge on heat dissipation. The LEDs are always mounted on the printed circuit boards and they might end up bringing a lot of problems, especially on the heat generated from them. Without proper laid down structures to dissipate the excess heat will end up damaging the board. To solve this, designers have chosen to implement the use of metal core PCBs.

Definition of the Metal Core PCB.
- As the name indicates, the metal core printed circuit board (MCPCB) is made up of a metallic base as opposed to the traditional FR4 material.
- The metal core material is being used because it offers good heat conduction properties and hence the board will have an efficient heat dissipation mechanism.
- This heat is being dissipated as a result of heat buildup that originates from the electronics component during the operation.
- The purpose of the metal core is to ensure that it diverts the heat generated away from the crucial components of the circuit and moves it towards the less critical components such as the heat sink areas.
- This shows that this type of PCB board is significant for thermal management.
- When designing a multilayer MCPCB, the metal core layers should be spread on both sides of the board.
- Let us use an example of the 12-layer MCPCB board, the metal core will be at the bottom and the top layer and also at the center that is at the 6th layer.
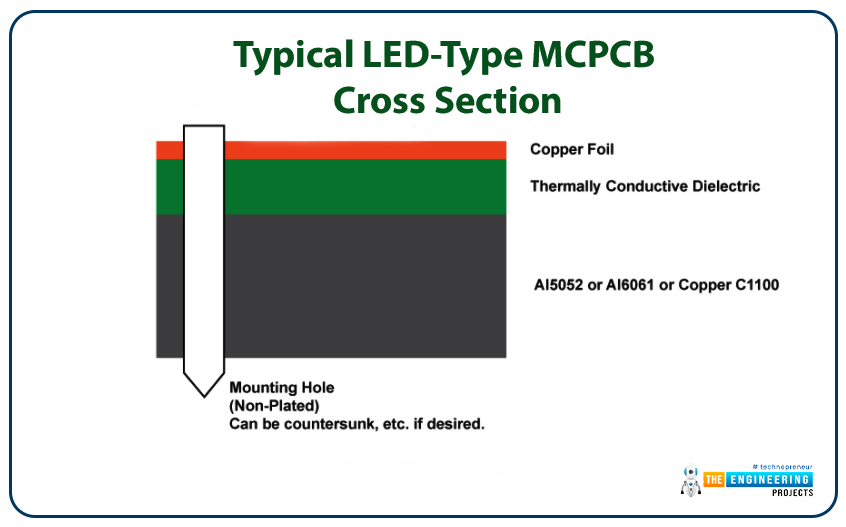
- They are made up of thermal insulating layers, metal copper foil and metal plates.
- For the purpose of our article, we shall have to use MCPCB as the abbreviation of this metal core printed circuit board.
Metal core PCB boards are special types of PCBs that have a metallic layer that is made up of copper or aluminum. This metallic layer is what gives it this name.
How to order Metal Core PCB?
There are many online PCB companies offering Metal Core PCB manufacturing. We are going to take the example of JLCPCB, a China-based online PCB Fabrication House. JLCPCB offers competitive rates and provides excellent results and is considered one of the best PCB manufacturers. You can place a PCB order on JLCPCB's official website.
- Open the JLCPCB official website and click on "Order Now" at the top.
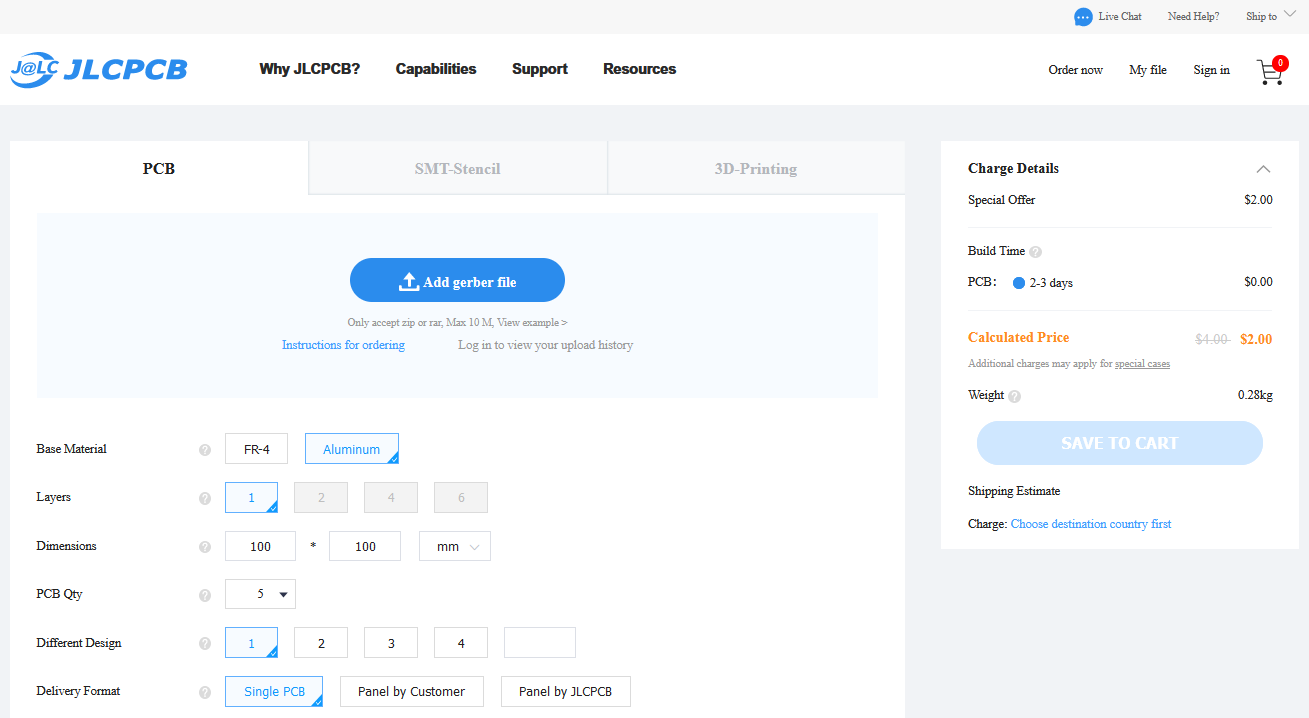
- As you can see in the above figure, I have placed an order of 5 PCBs of size 100x100mm.
- At the top, I have selected Aluminium, instead of FR-4.
- It has calculated the price to $2 for 5 Pcs and you will get the delivery in 2-3 days.
- They offer single-sided placement on the PCB board.
- JLCPCB has an extensive Library for SMT parts and you need to select the components from there.
- JLCPCB manufacture SMT Components in-house and thus gives the best results.
- JLCPCB places automated solder paste and then performs Solder Paste Inspection(SPI).
- I have attached the SMT Assembly screenshot in the below figure:
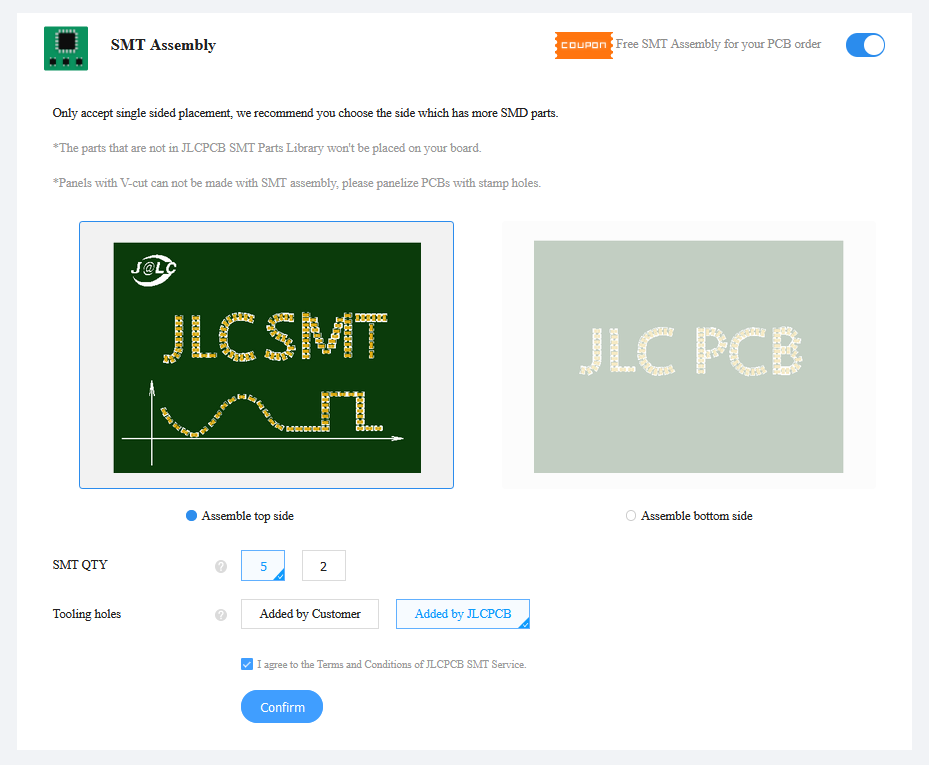
So, it's quite easy to order for manufacturing of Metal Core PCB on JLCPCB.
Layers of metal core PCBs
When you compare the metal core PCB with other traditional standard PCBs you will realize that it has special layers. The total number of these layers on the PCB will be determined by the total number of conductive layers that you really need. They can be of single or multiple conducting layers. The layers can be categorized into three types
- Base layer
- Copper layer
- Dielectric layer.

Base Layer
- The layer is made up of metal and this is the reason the PCB has the name.
- Since it is made up of metal, the board can withstand a lot of temperature and pressure compared to the traditional FR-4 PCBs.
- The board is also very strong, lasting and durable.
- The metal core base plays the role of the heat sink where it spreads the heat away from the components a role that cannot be achieved by the use of the fans.
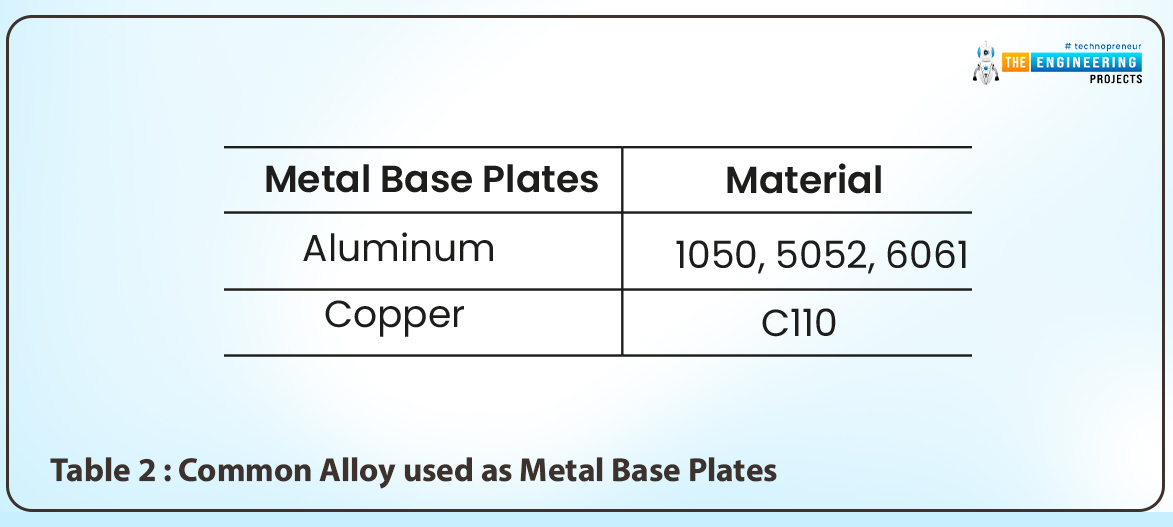
- This base layer can be made up of different metals although the most used types of metals are Aluminum and copper.
- Aluminum is the most preferred metal because of its cheaper prices but copper is the best when it comes to performance but is more costly.
- The thickness of this base is determined by the customer requirement or the designer specification although it is in the range of between 1 and 4 mm.
Copper layer
- It is the first layer that is present in all types of PCBs.
- It is the conduction layer that helps in the transiting of the electric signals.
- In other places, they refer to it as the circuit layer since this is where all the conductive circuits and even paths are made.
- The thickness of this layer is determined by the requirements and according to the project layers.
Dielectric layer
- This is the most important layer in the MCPCB which you will not find in the FR-4 PCB.
- We have noted that the top layer is the copper layer and the bottom layer is the metal core layer. We know that these layers are conductive and in between than they are separated by the dielectric layer which acts as the insulator for separating the two conductive layers.
- By separating the copper and the metal layer, the dielectric protects them from electric shorts.
- The main purpose of this layer is to aid in heat dissipation. It picks heat from the top copper layer, passes it through it into the metal core where it is dissipated completely.
- The size of the dielectric layer should be kept as thin as possible so that it does not have any effect on the overall thickness of the final board.
Types of metal core PCBs.
There are three major categories of the MCPCB as discussed below;
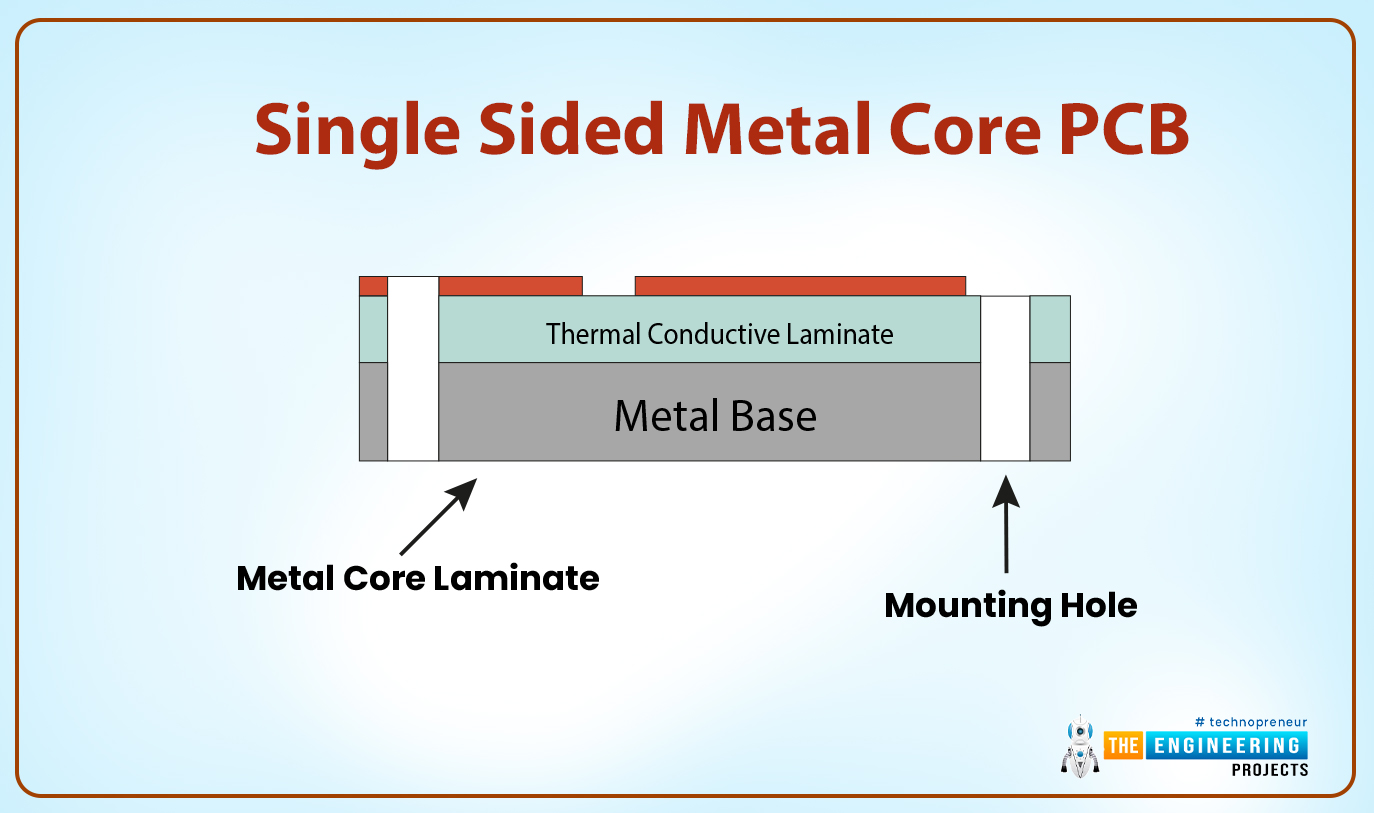
Single-sided metal core PCB
This type of metal-core PCB has the copper traces printed on one side of the board and the board comprises of the following;
- The solder mask.
- The copper circuit.
- The metal layer performs as the conductive link.
- The integrated circuit components
- The dielectric layer
The single-sided board also has a dielectric layer that is sandwiched between the copper and the metal core layer.
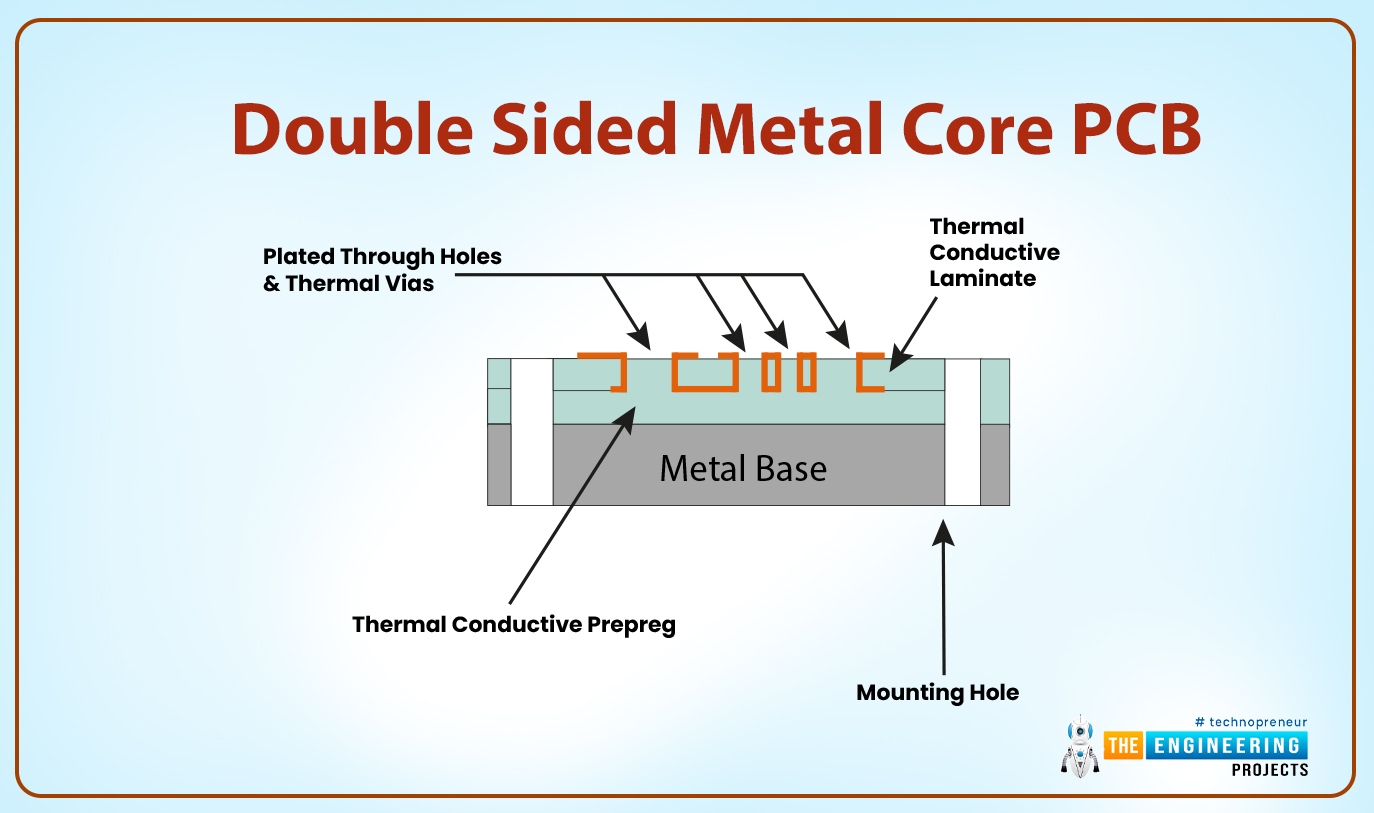
Double-sided metal core PCB
- This type of MCPCBs comes with a metal layer that lies between two conductive layers of the board. It also has a dielectric that is sandwiched between the copper core and the metal core.
- The metal core is usually the conductor.
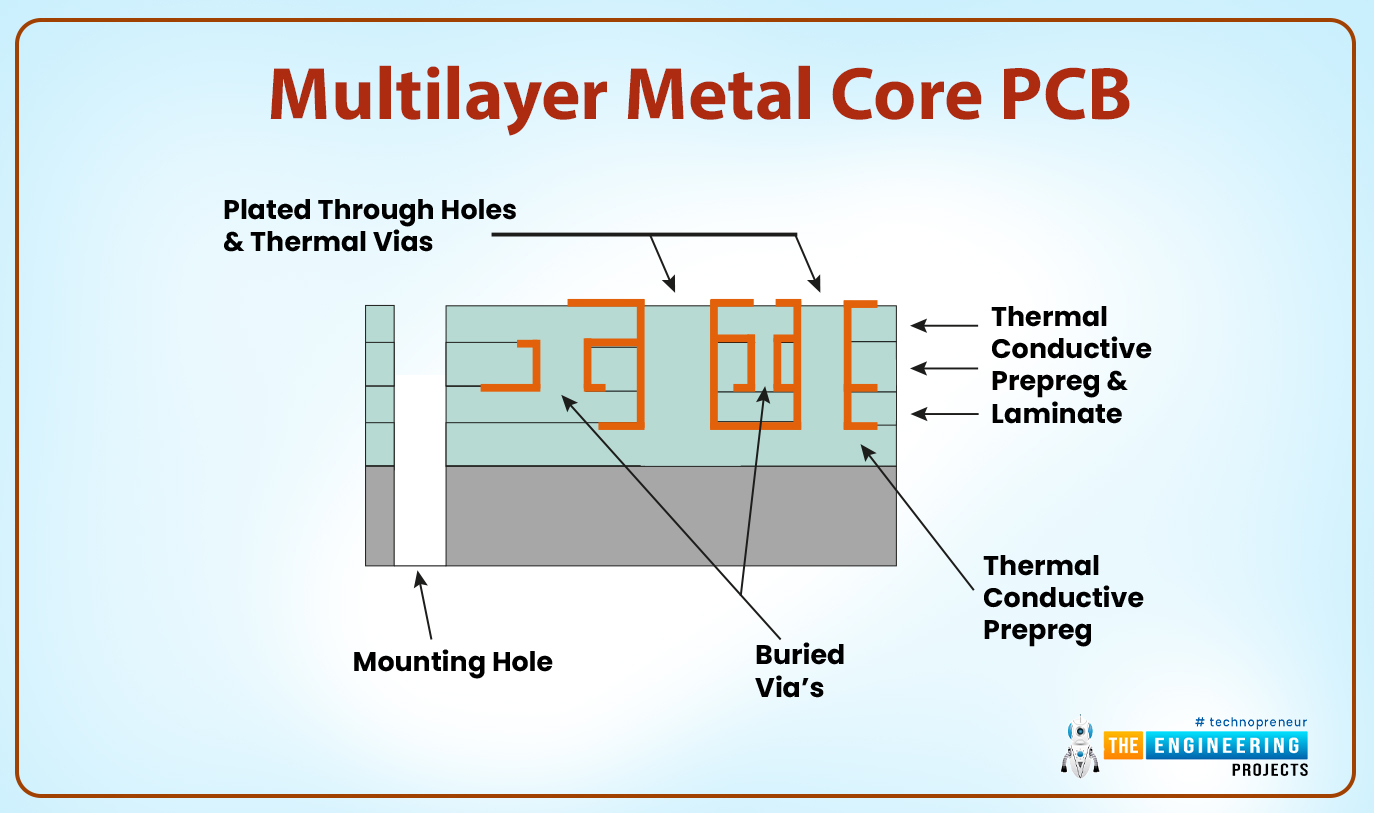
Multilayer metal core PCB
It comes with over two layers hence having a structure that looks like the FR-4 type of PCB materials.
- However, this type of board is much complicated in its design.
- For this type of board to achieve maximum performance, it utilizes too many components, grounds and the signal nature.
Process for the production of the metal core PCBs.
Let us have a look at the steps that can be followed in the design of the metal core printed circuit boards as listed below;
- The first step is the creation of the design and the output. This can be done by the use of electronic design automation software such as KiCAD, Proteus, Altium, OrCAD, etc.
- Check the DFM and after checking, by using a film print the copy of the designer.
- Use the printed film to print the MCPCB and while undergoing this process, it is advised that you do it in a very clean environment to ensure that your outcome will have no errors.
- During this process, you might end up with excess copper and therefore you have to use a chemical to etch the excess copper and remove it.
- Ensure that you have punched all the alignment in a well-organized line.
After this step, you now need to confirm the digital image that you have with the original Gerber files from the designer using an inspection laser to confirm if you have done the right thing.
After the confirmation that you have done the right thing, now the design can be moved to the final process of the design. This final step involves the unpacking of the PCB layers accordingly. We are supposed to locate the drill points and this can be done by the use of the x-ray locator.
Now the board is supposed to undergo the process of plating and deposition of copper where the whole PCB is electroplated with the copper layer before the board is taken through the final process of v-scoring and profiling.
MCPCBs metal bases
The aluminum substrate
The PCBs that are made out of aluminum offer very smart heat dissipation and a good heat transfer mechanism. Aluminum PCBs are very light in weight and are used in LED lighting applications, electronic communication and audio frequency equipment. Listed below in the characteristics of the aluminum substrate;
- The thickness should be between 2 to 8 mm.
- Has a thermal conductivity that ranges between 5 to 2 watts per meter kelvin.
- The peeling strength of not less than 9lb/in
- The soldering strength; safety factor of 288 degrees centigrade for more than 180 seconds.
- Has Greater than 3000V of breakdown voltage
- 0.03 dielectric loss angle.
- Flammability of UL 94V-0.
- The size of the panel is 18” x 24”.
Copper base
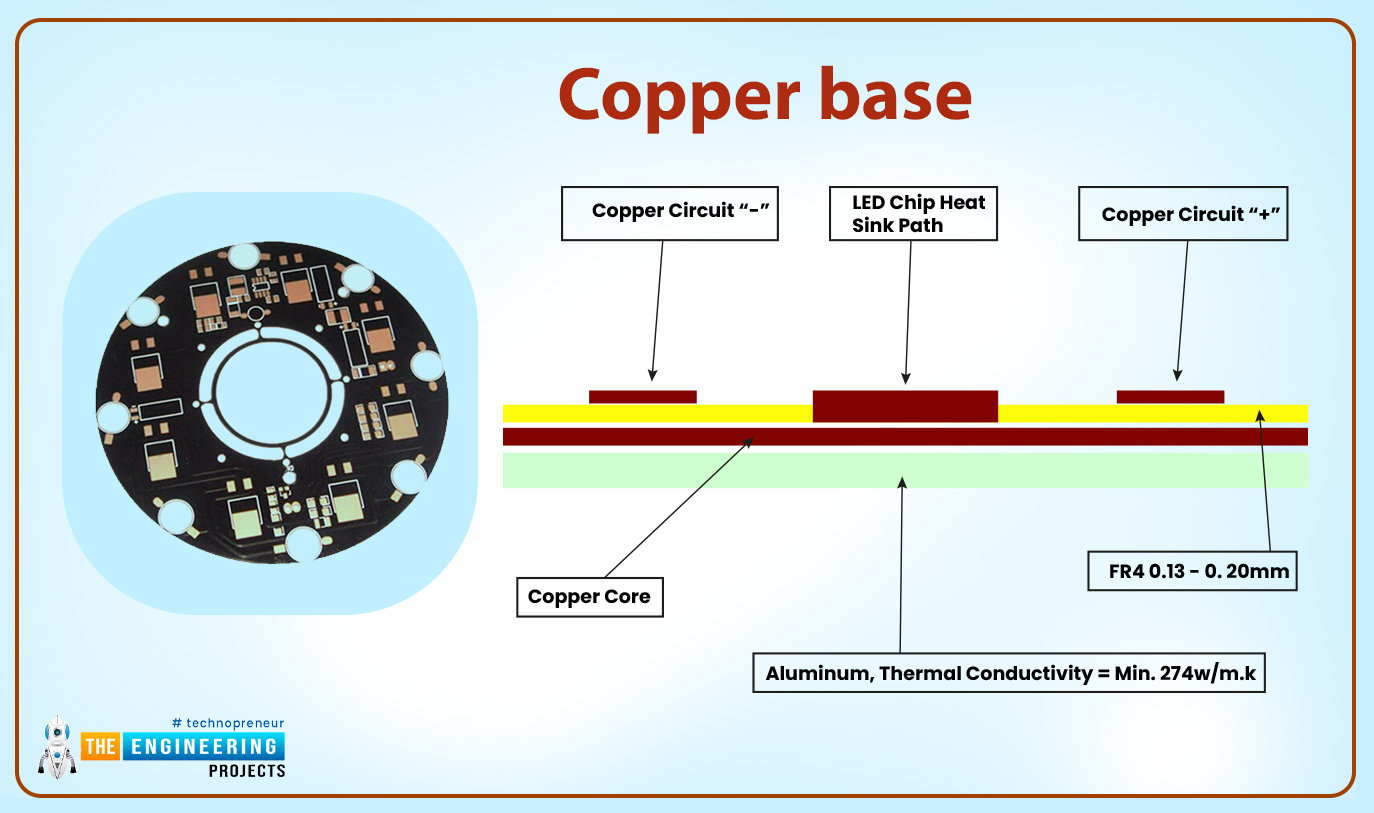
PCBs made out of the copper core have better performance than those made out of aluminum. But aluminum is preferred to copper by most clients because copper is more expensive. Another disadvantage of copper core over aluminum is that copper boards are heavier and involve a tough process of machining. Copper has a higher rate of corrosion as compared to the aluminum core.
The benefits of the MCPCBs
- The metal boards can undergo etching to control the way heat that is generated by the components flows.
- These boards are very important in high vibrations systems since the components cannot fall off due to strong mounting on the metal core.
- Metals are harmless and can be recycled.
- With metal, you expect a more durable product as compared to the normal epoxy boards.
- Metals have high thermal conductivity characteristic and this means that it provides a faster means of heat transfer.
Applications of the MCPCBs
This type of board finds great use in the field of LED technology. Some of the applications are listed below;
- Light-emitting diodes both in the backlight unit and the general lighting.
- Heat sinks and heat spreaders for cooling systems.
- Power regulations and automobiles are more so in hybrid car systems.
- Used in the semiconductor thermal insulation boards. semiconductors are the top heat emitters in the PCBs and this heat requires a better method to manage it which can be offered by the MCPCBs.
- Amplifies for audio. Amplifiers can be made from the FR-4 material, but if you need quality, best performance and reliability, I would advise the use of the metal core PCBs.
- Used in the hybrid and the electric motor control system and motor drivers. These are applications that generate a lot of heat that a normal PCB cannot withstand. For this reason, MCPCBs are best suited for such applications.
- Used in the modern solar panels
- Used in the control of motion.
- Finds application in the solid-state relays.



