Hi Friends! Glad to have you on board. Thank you for clicking this read. In this post today, I’ll walk you through Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing.
Cloud computing has been around for many years while edge computing, on the other hand, has just become the prime topic of mainstream organizations. But what is the key difference between both edge computing and cloud computing, how do they work, can we implement both in the IT model of any business? These are the main questions that arise every time someone tries to get a hold of these terms. Don’t worry. We’ll discuss them in detail so you know when to pick a cloud model and when to choose edge computing.
Keep reading.
Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing
Before we go further to describe the comparison between edge and cloud, know that, both these infrastructures are independent of each other and companies separately employ these models based on their business needs and requirements. Edge computing favors the IT model of the company at times, while cloud computing is the answer to handle some issues.
What is Edge Computing?
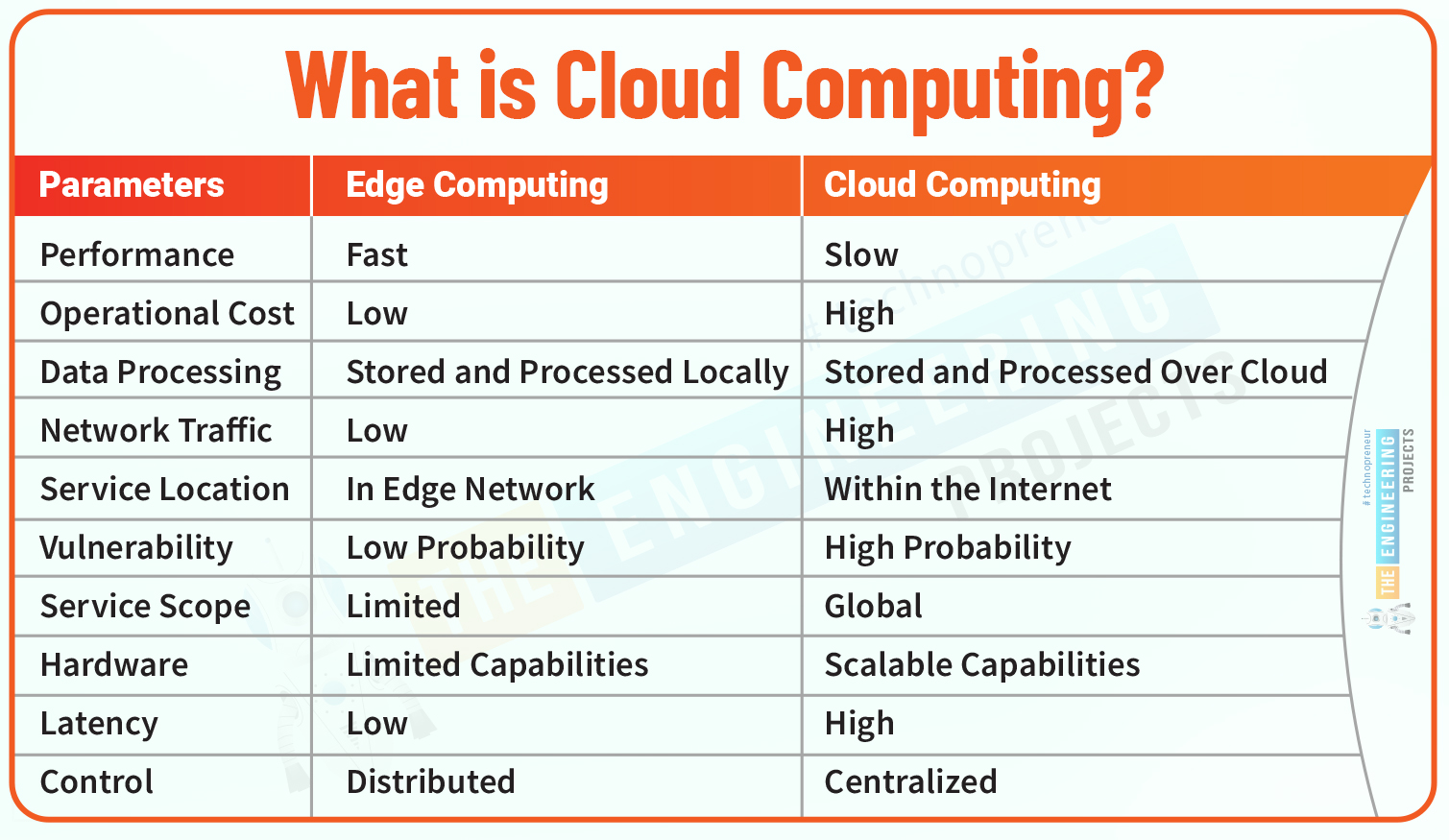
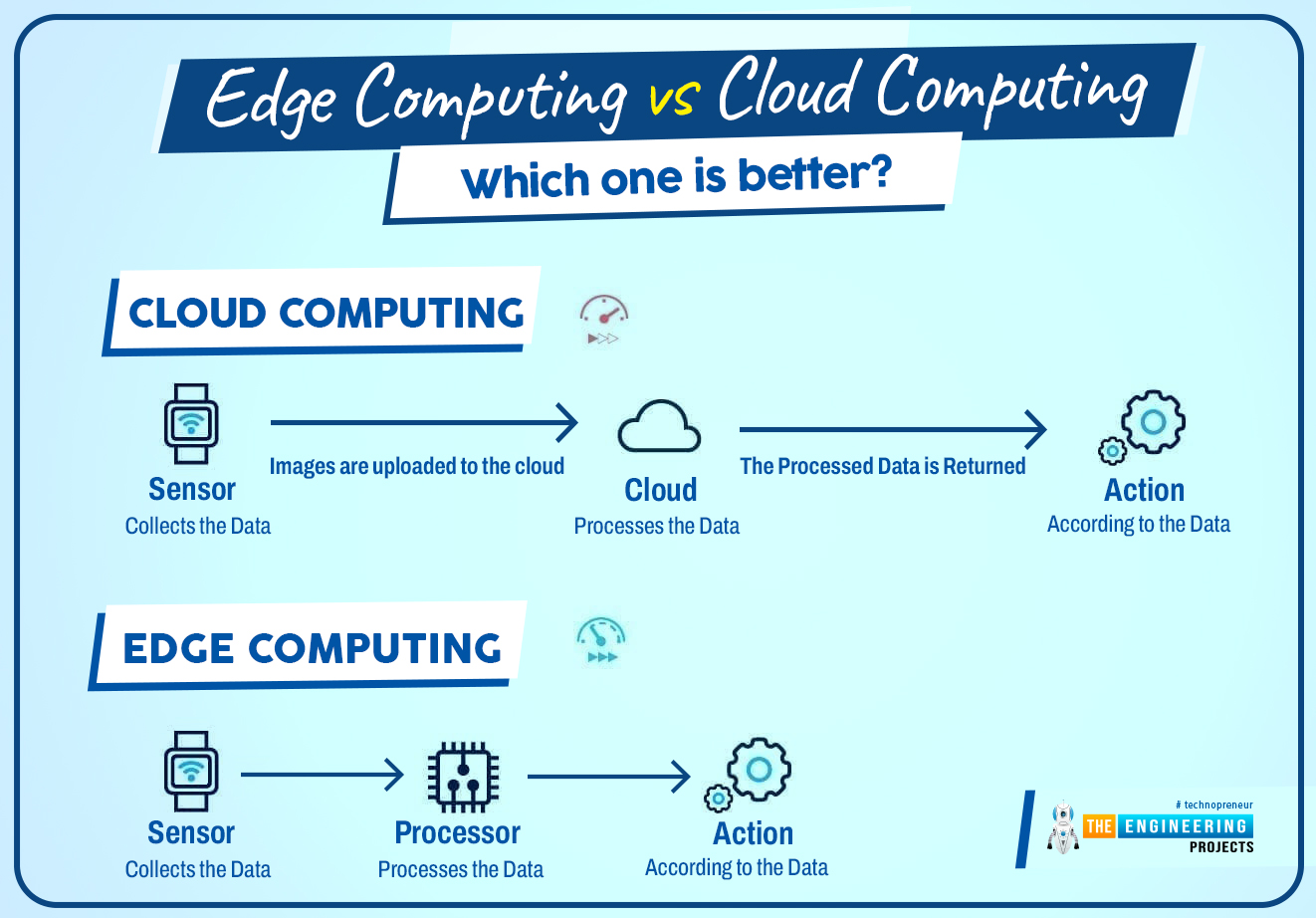
Edge computing is a distributed and decentralized computing infrastructure that brings computing power and storage near the edge of the network. Simply put, the data is handled or stored near the location where it’s produced. This reduces the bandwidth and removes the latency issues (latency is a time delay between actual action and processed action), requiring fewer data to be stored with improved quality. This phenomenon is ideally suited for applications that are time-sensitive and are dependent on the quick decisions to make. Know that the introduction of IoT devices for a variety of businesses is the main driving force of this edge computing development. Gartner predicts, “Around 10% of enterprise-generated data is created and processed outside a traditional centralized data center or cloud. By 2025, this figure will reach 75%.”
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing, on the other hand, is a centralized computing infrastructure where computing is carried out at the cloud with data centers that are located miles away from the data source. This process takes time because you cannot make quick and on-spot decisions since the produced data move to the cloud for processing before you make decisions based on the processed data. In cloud computing produced data moves to the cloud for processing while in edge computing the cloud comes near the produced data.
For instance, vibration sensors are installed in the industry to monitors the metrics of vibration caused by machines. If the sensors are connected with the cloud and vibration levels go above the required readings, it takes some time to shut down the machines since the first data produced by the sensors will go to the cloud for the processing which causes time delay and the machine will take some time to shut down. While if those sensors are connected with the edge device near the location where data is produced, and if readings go above the required level, the machines will get shut down immediately since the edge device is installed near the data source and it doesn’t require time to move that data to the cloud.
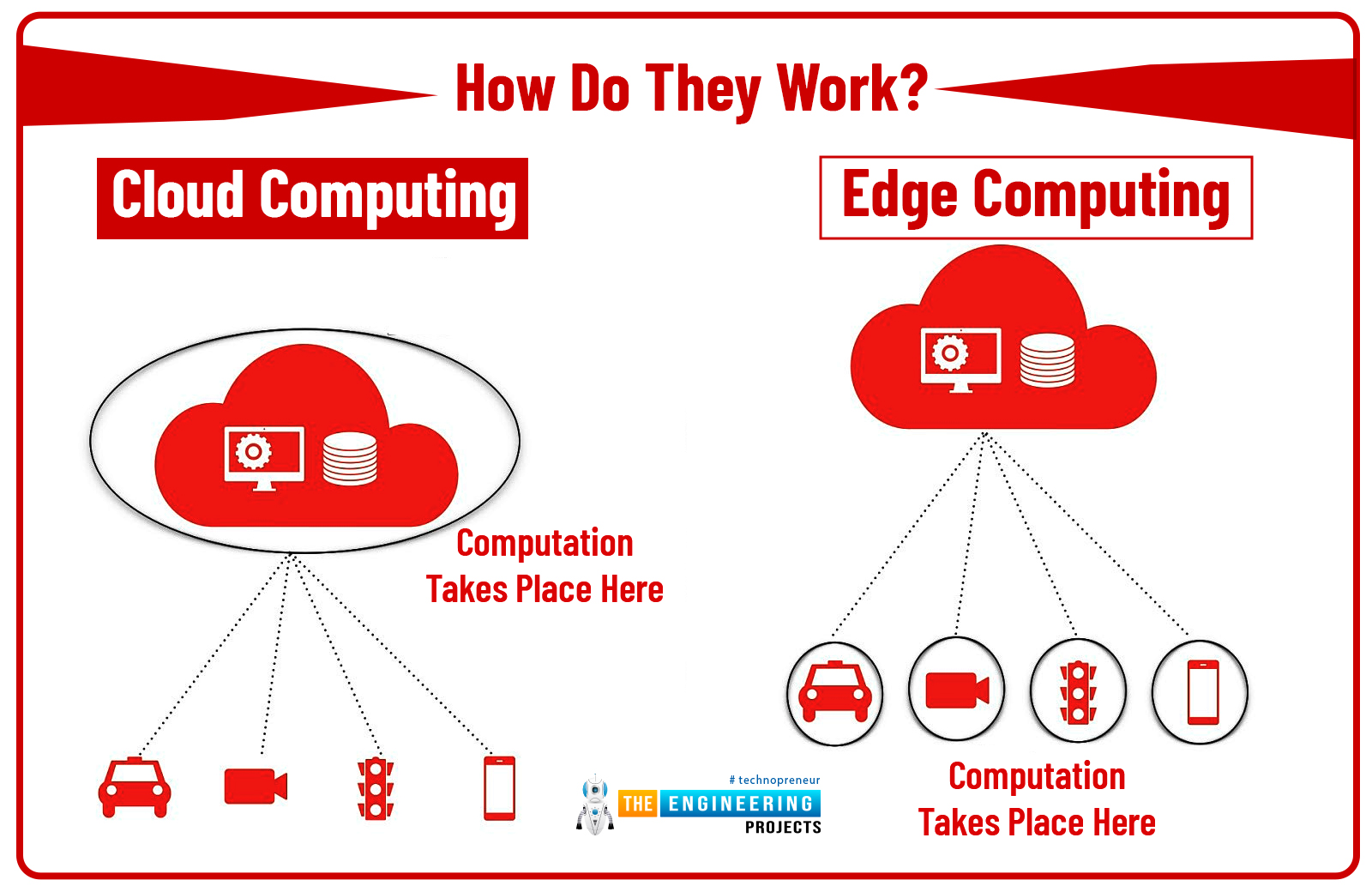
How Do They Work?
Now we know what cloud and edge computing is, in this section, we’ll cover how these infrastructure work.
Three main components are used in edge computing:
- Cloud
- Edge device
- Device
In edge computing, an additional node is introduced between the device and cloud called edge device. This way no involvement of the cloud is required to manage, process, and store data. Instead edge device will serve this purpose.

It is important to note that, edge computing contributes to the cloud but it’s not a part of the cloud, and processing is done near the data source in the edge device. In cloud computing internet is necessary to maintain connectivity throughout the process to handle and store data in the data centers. While in edge computing, as the edge is not part of the cloud, you can still get results and process data without internet connectivity since the devices relying on edge infrastructure normally uses 5G or IoT (internet of things) technology to process data.
Two main components are involved in cloud computing:
- Cloud with data centers where is processed and stored
- Device (like a laptop, smartphone, tablet) where data is produced
Data is produced at the data source (device) and that data is then moved to the cloud with data centers where that data is being processed. Cloud computing takes more time to process data hence creating latency issues.
Advantages of Edge Computing
The following are the main advantage of edge computing.
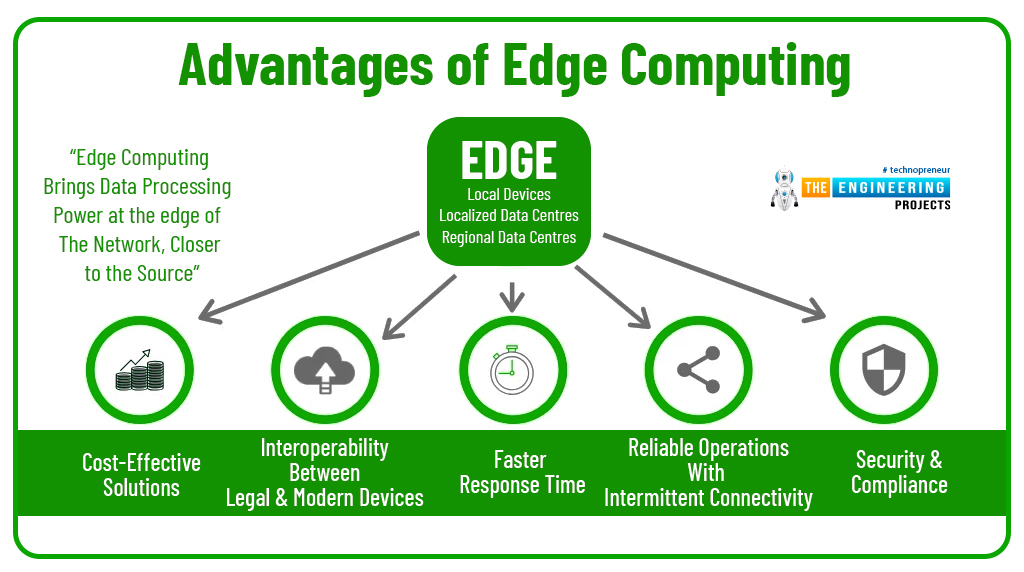
1: Improved Performance and low latency:
As touched earlier, the computing power and storage bring near the edge of the network in edge computing, removing the need for cloud resources to process data. This significantly improves the performance of the system, allowing the machines to make quick decisions based on the processed data. Using this infrastructure, you are adding the intelligent computing power near the source of the data which keeps the latency low which means you’ll get processed data quickly with improved quality. Experts say edge computing combined with 5G will reduce the latency, if not zero, to 1 millisecond.
2: Better Control Over Data:
As you know, cloud infrastructure is completely owned and managed by the cloud service provided, giving you less control over the data to be managed and stored. While edge computing gives you better control over data since the data is managed and stored locally without the involvement of the cloud.
3: Reduced Cost:
Edge computing is less expensive compared to cloud computing since less bandwidth is required and no large amount of data needs to be stored. You only need the required data to make real-time decisions. Moreover, connectivity, data migration latency issues are pretty much expensive in cloud computing. Edge computing removes the requirement of enormous bandwidth since no large amount of data is stored in data centers. Nowadays companies prefer edge computing over cloud computing because of its low operational cost and improved and optimal system performance.
4: Data sovereignty:
Since data is stored and processed near the data source, it allows companies to keep their sensitive data within the local area network. It provides added advantage to companies obsessed with the security of their data.
5: Scalability:
The company’s requirement of IT models varies as the business grows over time. Purchasing dedicated cloud resources is not a wise move since you’re not sure what business requires as the customers' needs and requirements change. The main advantage of edge computing is its ability to scale it as per the activities of the business. Edge computing gathers and processes data locally with dedicated hardware called edge device, setting you free from depending on the software environment of data centers in cloud computing.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
The following are the main advantages of Cloud Computing:
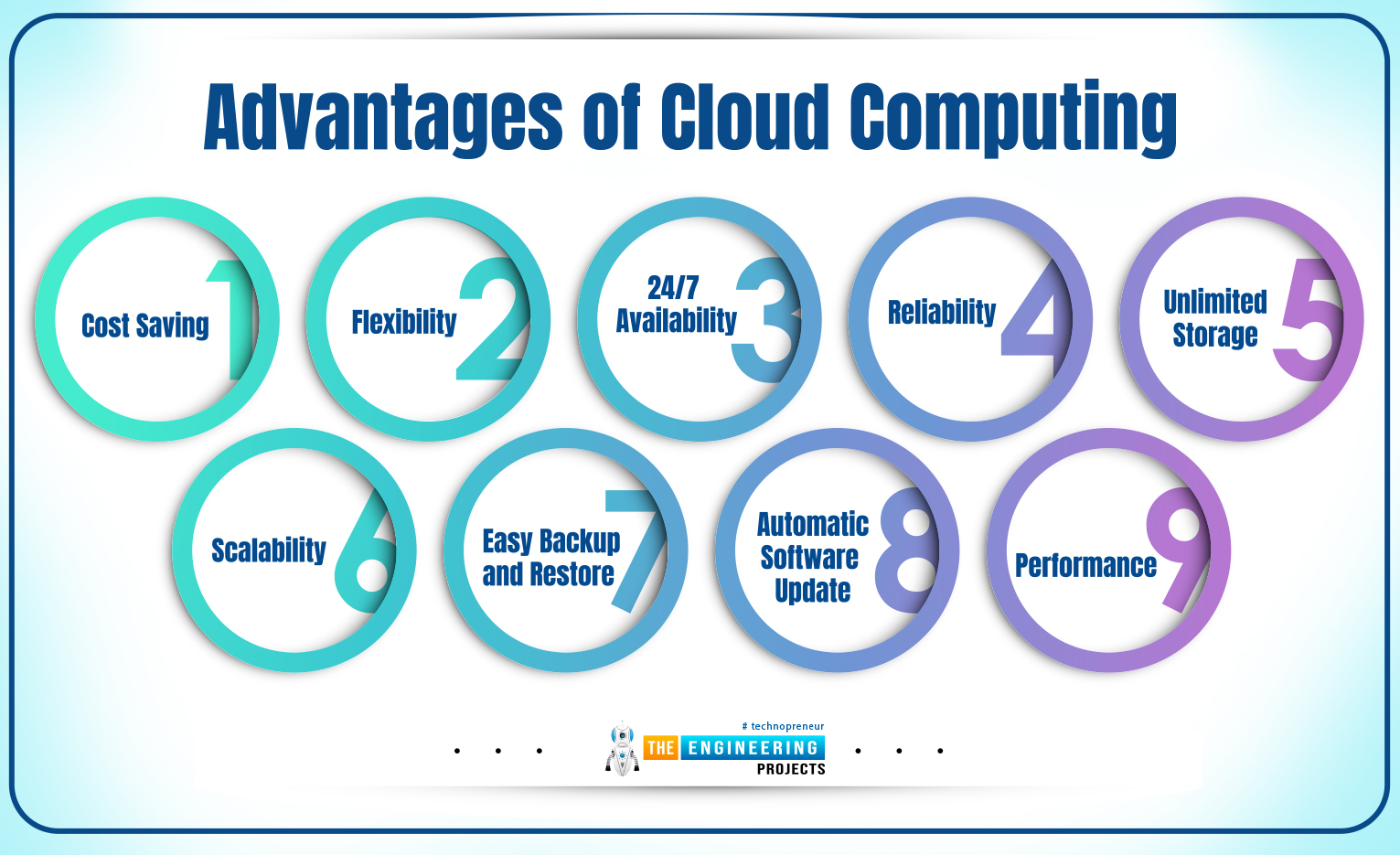
1: Backup and Disaster Recovery
In cloud computing data is stored and processed in the cloud which means it creates the backup of your data. In case of emergency, if your data is deleted or compromised, you can collect a copy of the electronic file stored in data centers of the cloud. Organizations of every size use cloud computing to create a backup of their important data. As the company grows, the requirements of the data to process and store also grow which makes cloud computing an important part of the company’s IT infrastructure.
2: Low maintenance cost
If you store data in local data centers, you require capital expense to install, handle, maintain and scale those data centers. With cloud computing, you no longer need to handle and manage the separate data centers since your data is stored in the cloud globally managed and supported by data centers.
3: Pay-as-you-go service
The cloud service providers often offer pay-as-you-go packages which means you can customize the computing resources as per your requirement. As the business grows, the activities of the business also go complex, getting a customized package from the cloud service providers helps you vary the plan as per your exact needs and requirements.
4: Flexibility
Cloud computing offers more flexibility to businesses compared to organizations using traditional local data centers. You need to upgrade your IT infrastructure if you want more bandwidth to handle the onslaught of data, while with cloud computing you can request more bandwidth instantly. Still, it depends on the service provider you pick for cloud computing, not all providers are equal, some are better than others. So make sure you put the dedicated effort into figuring out which service provider will more efficiently complement your business.
5: Mobility
Cloud data is easily accessible to anyone around the world. Considering the growing usage of mobile devices like smartphones and tablets is a great advancement to make the data accessible for anyone anywhere in the world. This works for businesses working with freelancers and remote employees who are not part of on-site staff. It provides better work-life balance to employees and adds flexibility to the working environment of the company.
6: Automatic Software Update
Think about on-site IT infrastructure and drills it needs to routinely update and maintain local data centers. This is not the case with cloud computing since the software involved in this model updates themselves automatically, setting you free from the hassle of manual updating.
Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing – Which one is better?
If you’re still reading this post, it means you got to know what both edge and cloud models hold and their advantages. It’s too early to say which one is better since both models are different and are employed based on the business needs and requirements.
If you want the backup of your data and are not concerned about the time it takes to store and process that data, cloud computing is the solution. For the large volume of data to store and process, cloud computing is used. And if you’re concerned about the time it takes to process data, then edge computing is the solution. Using this infrastructure, you can make quick and better decisions for the activities that are time-sensitive. For example in the case of automatic cars you need to make an instant decision about the car’s fuel consumption and the route it takes to reach the destination. Similarly, to successfully use the facial recognition feature to unlock the mobile, you need instant data to be processed to unlock the screen. Here edge computing works far better than the cloud model since cloud computing takes a lot of time to process facial features to unlock the screen.
Latency is another issue that edge computing handles better. For instance, the live feed you record with surveillance cameras. If these cameras are connected with the cloud, it will increase the latency and you’ll get the processed video after some time. This is not the case in edge computing. If motion sensors are installed near the surveillance cameras, in this case, the monition sensor itself will work as an edge device, and it providers immediate feed of the live recording without time delay.
What the Future Holds?
More companies, no doubt, are adopting edge computing at an accelerated pace, still, it’s too early to say if this is the end of cloud computing. The Cloud model holds its values when it comes to storing a large amount of data. However, with the inception of AI and IoT devices, processing capabilities become the major concern instead of storing a large amount of data. This projects that cloud computing will remain relevant for the development of the company’s IT models, and it will work with edge computing to provide better and instant processing capabilities.
That’s all for today. Hope you’ve enjoyed reading this article. If you’re unsure or have any questions, you can reach out in the section below. I’d love to help you the best way I can. Thank you for reading this article.



