
D13009K NPN Transistor Datasheet, Pinout, Power Ratings & Applications


Hello Folks! I welcome you on board. Happy to see you around. In this post today, I’ll walk you through the Introduction to D13009K. D13009K is a high voltage fast switching power transistor that falls under the category of NPN transistors. The collector current of this device is 12A which projects it can endure load under 12A. This chip is mainly used in amplification and switching applications. The small current change at one pair of terminals is used to produce a large current change across the remaining terminals. The power dissipation is 100W which features the amount of power this chip dissipates during the working of this integrated chip. I recommend you check out this post all the way through as I’ll demonstrate the complete Introduction to D13009K covering datasheet, pinout, power ratings, applications, and physical dimensions. Let’s get started.
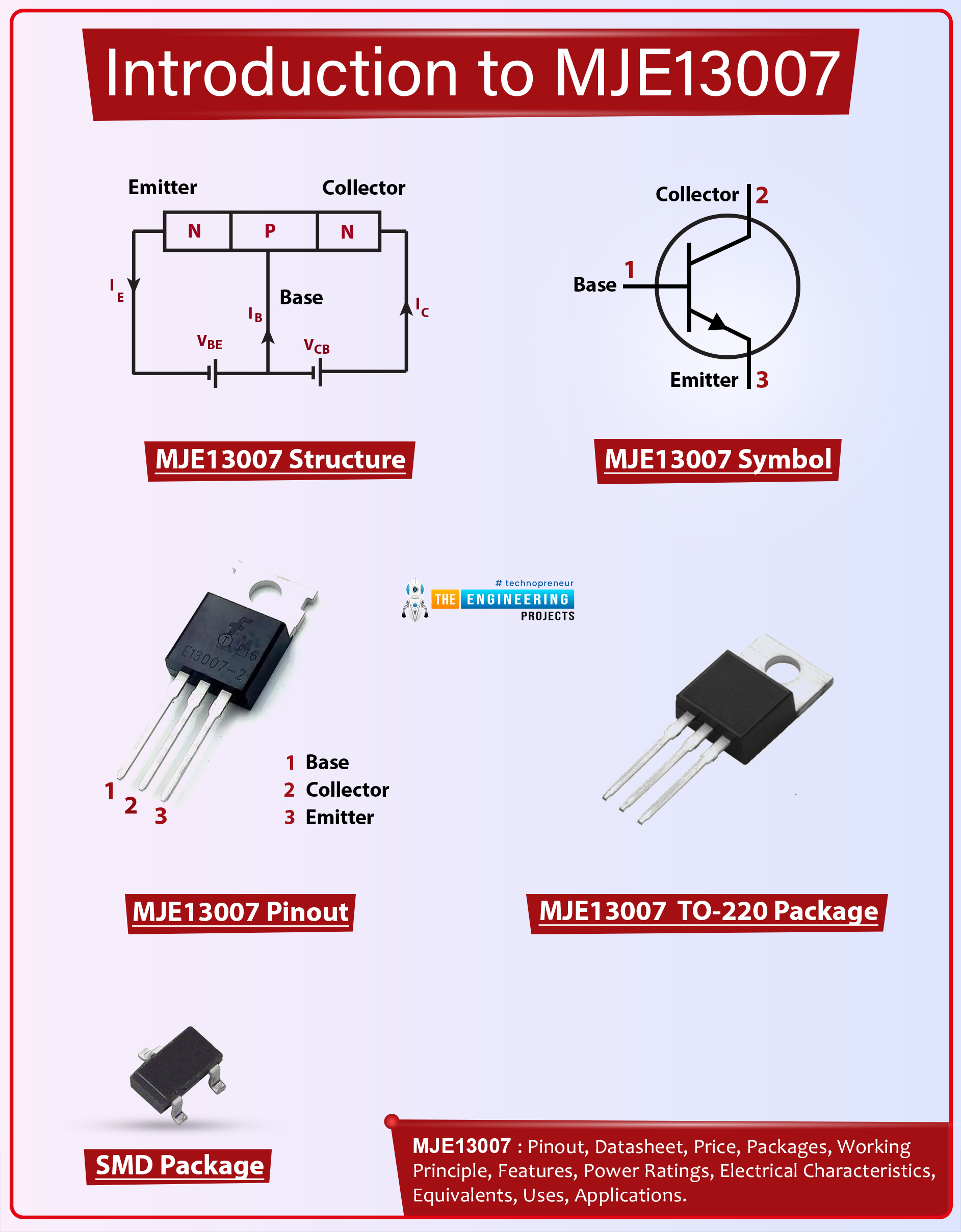
Introduction to D13009K
- D13009K is an NPN bipolar junction transistor that is a high voltage fast switching power device. It is widely employed for switching and amplification purposes.
- This component contains three terminals named base, collector, and emitter. It generates a large current across emitter and collector terminals by changing a small current at the base side. This phenomenon is used for amplification purposes.

- The emitter-base voltage is 9V which details that it requires 9V to start the transistor action and bias this device.
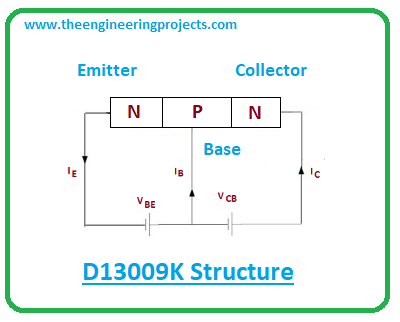
- D13009K contains three layers. Two are n-doped layers and one is a p-doped layer. The p-doped layer sits between the two n-doped layers.
- Bipolar junction transistors are divided into two main types i.e. PNP transistors and NPN transistors.
- The D13009K is an NPN transistor where electrons are the major charge carriers. It is important to note that these devices are called bipolar devices because both holes and electrons are responsible for the conductivity inside the transistor.
- In NPN devices, electrons are the major charge carriers and in PNP devices, holes are the major carriers. Moreover, NPN transistors are preferred over PNP transistors since the mobility of electrons is faster and efficient than the mobility of holes.
- This bipolar junction transistor is a current-controlled device as opposed to MOSFETs that are voltage-controlled devices and carry pins like a drain, source, and gate. The drain side replaces the emitter, the source replaces the collector and the gate replaces the base pin in bipolar junction transistors.
D13009K Datasheet
Before you embed this chip into your electrical project, it’s wise to check out the datasheet of the device that features the main characteristics of the device. Download the datasheet of D13009K by clicking the link below.D13009K Pinout
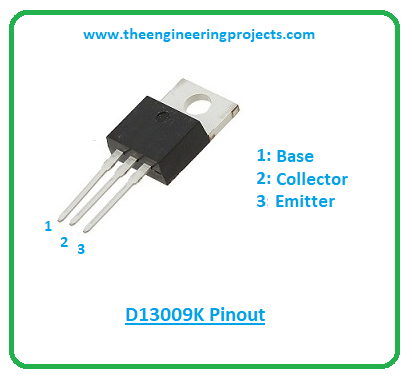
This power transistor contains three terminals named:- Base
- Collector
- Emitter
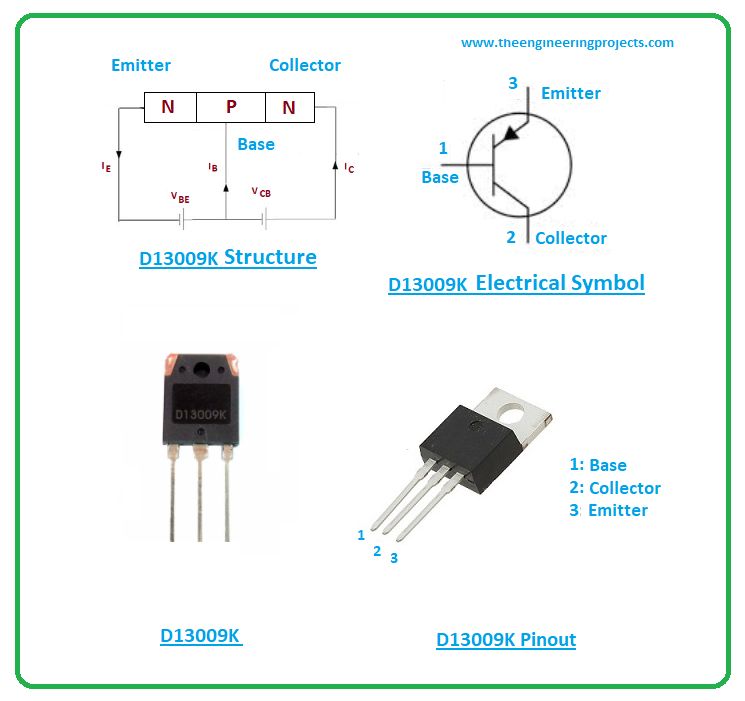
D13009K Working Principle
- This device comes with high breakdown voltage and carries high current capability. It is a highly reliable product and features a high switching speed.
- The working of this device starts from the base pin. When you apply voltage at the base terminals, it will bias the device and start the transistor action. And current starts flowing from collector to emitter terminal.
- In NPN transistors current flows from collector to emitter terminal and in PNP transistors current flows from emitter to collector terminal.
- These bipolar devices are not symmetrical. This means if you try to exchange the collector and emitter side, it will prevent the terminals to work in forward active mode and force the terminals to work in reverse active mode.
- The different doping concentration of these devices is responsible for the lack of symmetry in these transistors.
D13009K Power Ratings
The following table features the absolute maximum ratings of D13009K.| Absolute Maximum Ratings of D13009K | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin No. | Pin Description | Pin Name | ||
| 1 | Collector-emitter voltage | 400V | ||
| 2 | Collector-base voltage | 700V | ||
| 3 | Base-emitter voltage | 9V | ||
| 4 | Collector current | 12A | ||
| 5 | Power dissipation | 100W | ||
| 6 | Base current | 6A | ||
| 7 | Operating and storage junction temperature range | -55 to 150C | ||
- When you’re working with the component, make sure the ratings don’t exceed the absolute maximum ratings. Otherwise, it can affect the entire project.
- The collector-emitter and collector-base voltages are 400V and 700 respectively. And total power dissipation is 100W which shows the amount of power released during the working of this chip. The junction temperature and storage temperature ranges from -55 to 150C.
- Plus, don’t apply these ratings more than the required time, else they can affect device reliability.
D13009K Applications
D13009K is used in the following applications.- Used in energy-saving lights.
- Used in Bistable and Astable multivibrators circuit.
- Used in high-frequency power transform.
- Employed to support loads under 12A.
- Used in voltage regulator circuits.
- Used in a common power amplifier.
- Incorporated in modern electronic circuits.
- Used in electronic Ballasts.
- Used in the high switching power supply.
D13009K Physical Dimensions
The image below shows the physical dimensions of D13009K.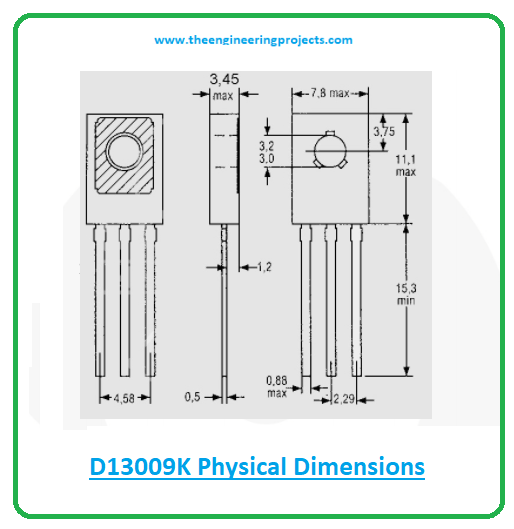








 1 user
1 user






 Continue Wishlist
Continue Wishlist





 Getting Started Guide
Getting Started Guide
 Help Center
Help Center
 Contact us
Contact us
 Doist Blog
Doist Blog
 Privacy
Privacy
 Security
Security
 Terms of Service
Terms of Service
 What's new: Channel Descriptions
What's new: Channel Descriptions





 Electronic Components
Electronic Components jameswilson
jameswilson 0 Comments
0 Comments








 2.3k
2.3k
 953
953
 921
921
 2.1K
2.1K
 Introduction to d13009k
d13009k pinout
d13009k features
d13009k applications
Introduction to d13009k
d13009k pinout
d13009k features
d13009k applications
 Thursday, February 18, 2021
Thursday, February 18, 2021