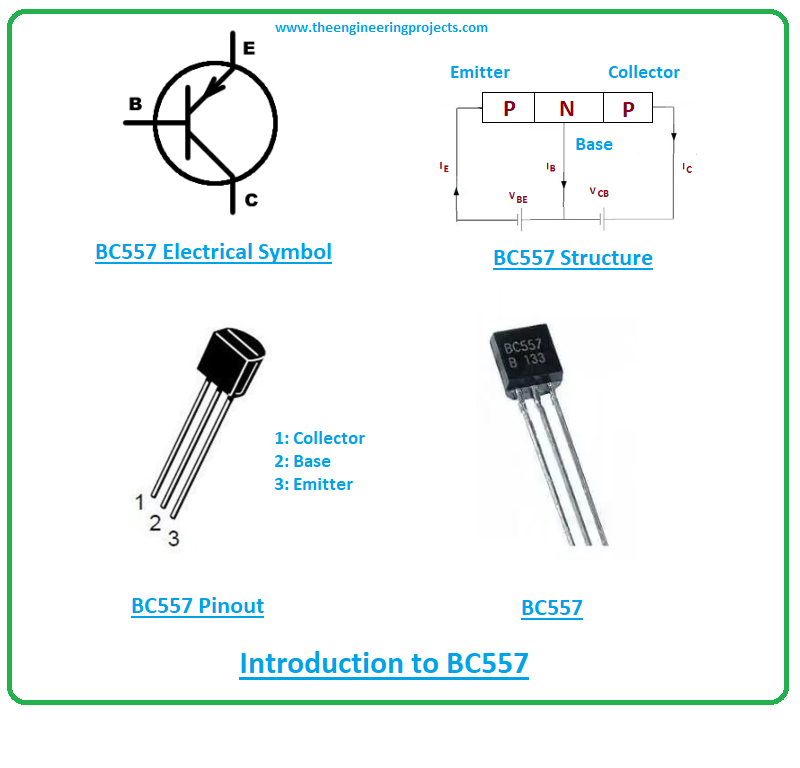
Introduction to BC557
- BC557 is a bipolar junction transistor that falls under the family of PNP transistors.
- As this is a PNP transistor, there will be no current at the base terminal when the transistor is turned ON and in that case, both emitter and collector will be forward biased.
- And when voltage is applied at the base terminal, the transistor is turned OFF and both emitter and collector will be reverse biased.
- It carries three terminals called collector, base, and emitter that are commonly used for external connection with the electronic circuit.
- All these terminals are different in terms of their size and doping concentration. The emitter is highly doped against both collector and emitter terminals.

- BC557 contains there layers i.e. two p-doped layers and one n-doped layer. The n-doped layer lies between the two p-doped layers. Here the base terminal is negative while emitter and collector will be positive.
- The maximum collector current is 100mA indicating we cannot drive loads through the transistor that utilizes more than 100mA current.
- It is mainly used for amplification purposes. Amplification is the process by which transistor boosts the small input voltage into a large output voltage i.e. small audio signal will be amplified into a large audio signal.
BC557 Datasheet
If you want to download the BC557 datasheet, click the link given below. This will help you understand the main characteristics of the BC557 transistor.BC557 Pinout
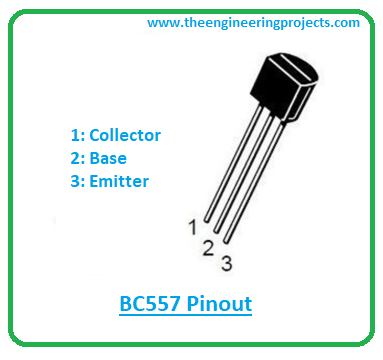
BC557 contains three terminals that are known as:- 1: Collector
- 2: Base
- 3: Emitter
BC557 Working Principle
- In PNP transistor holes are majority carriers as opposed to NPN transistors where electrons are majority carriers. Although holes are majority carriers, the base terminal still plays a key role in the overall action of the transistor.
- Now holes are emitted from the emitter instead of electrons in the NPN case, and they are collectors by collector terminal.
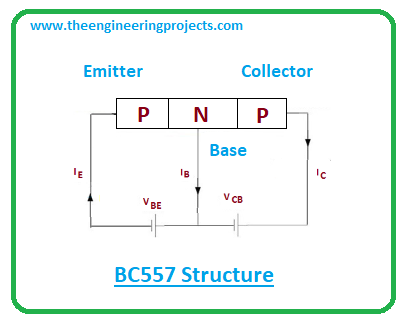
- BC557 is called the current controlled device where small current present at the base side is used to control the large current at the remaining terminals.
- Recall, when the transistor is turned OFF there is a current at the base side and when the transistor is turned ON there is no current present at the base terminal.
BC557 Power Ratings
The following table represents the absolute maximum ratings of BC557.| Absolute Maximum Ratings BC557 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Rating | Symbol | Value | Unit |
| 1 | Collector-Emitter Voltage | Vce | 45 | V |
| 2 | Collector-Base Voltage | Vcb | 50 | V |
| 3 | Emitter-Base Voltage | Veb | 5 | V |
| 4 | Collector Current | Ic | 100 | mA |
| 5 | Power Dissipation | Ptot | 500 | mW |
| 6 | Peak Collector Current | Icm | 200 | mA |
| 7 | Junction Temperature | Tstg | 150 | C |
- The transistor’s amplification capacity is determined by the amplification factor that is a ratio between collector current and emitter current. It exhibits the actual value of the current or input audio signal that the transistor can amplify.
- Make sure, these ratings remain under control and don’t exceed the recommended values.
- If values surpass the standard values, they can affect the overall performance of the component, and thus damage the project you’re working on.
- Also, if these ratings are applied with maximum time, they can ultimately affect device reliability.
Difference between PNP and NPN Transistors
- Though both transistors are used for amplification and switching purposes, there are few exceptions.
- In PNP transistor, the current flows from the emitter side to the collector side and in case of NPN transistor current flows from collector to emitter, however, in both cases, the base is the main terminal that controls the amount of current.
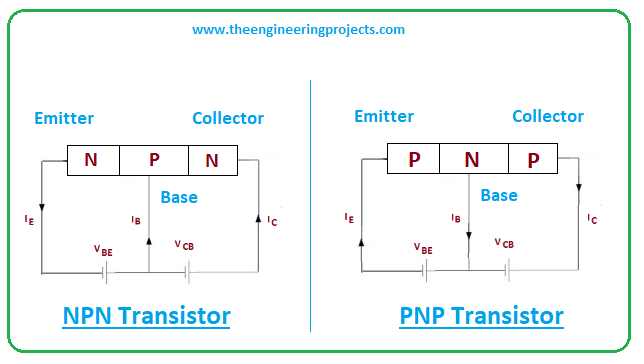
- In PNP transistors, base controls the number of holes and in NPN it controls the number of electrons. As conductivity is carried out by electrons in NPN transistors, they prove handier for amplification purposes compared to PNP transistors because the mobility of electrons is far better and quicker than the movement of holes in PNP transistors.
- In PNP transistor the base side is negative compared to both emitter and collector while in case of NPN transistor base side is positive compared to remaining terminals.
- The emitter terminal is both cases is highly doped and carries the 100% current of the transistor.
- Both NPN and PNP transistors are different in terms of the applied source voltage.
BC557 Alternatives
BC557 equivalent alternatives are:- BC558
- BD140
- TIP42
- BC157
- S8550
- 2N3906
- 2SA1943
- TIP127
BC557 Applications
BC557 is used in the following application:- Used for switching and amplification purpose
- Used to drive load under 100mA
- Employed in robotics and instrumentation projects
- Used in motors for controlling current
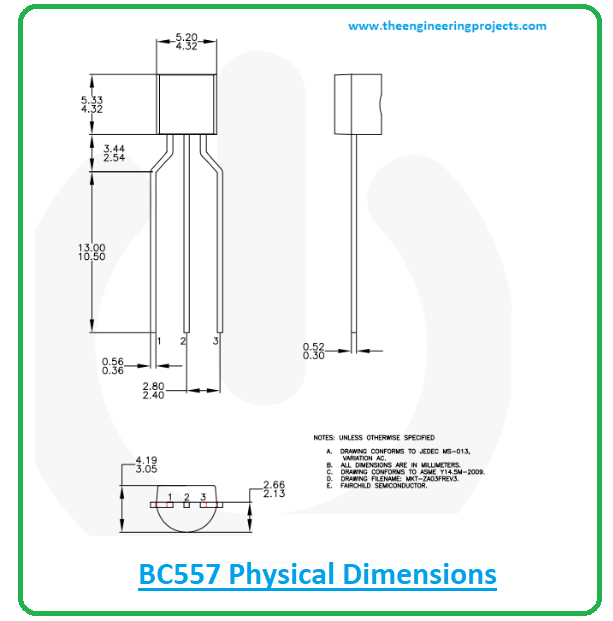
BC557 Physical dimensions
The following figure shows the physical dimensions of BC557 to help you evaluate the desired space of your electronic project.