Introduction to BC337


Introduction to BC337
- BC337 is an NPN transistor mainly used for lower power audio amplification and switching purposes.
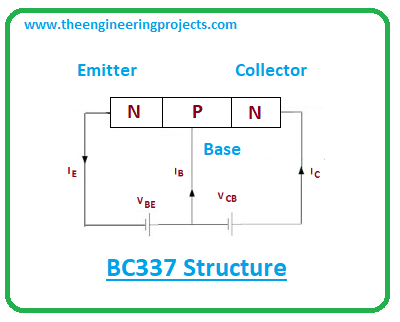
- It contains three terminals known as emitter, base, and collector. The small current chance at the base side is used to produce large current change at the remaining terminals. This phenomenon is used for amplification purposes.
- BC337 comes with three layers i.e. one p-doped layer and two n-doped layers. The p-doped layer is sandwiched between two n-doped layers. The base terminal is positive and the remaining two terminals are negative.

- As this is an NPN transistor the main charge carriers would be electrons. Although both electrons and holes take part in conductivity, electrons are major carries in this case as opposed to PNP transistors where holes are major carriers.
- It is important to note that NPN transistors are preferred over PNP transistors because the mobility of electrons is far better and quicker than the mobility of holes. In some cases, a combination of both NPN and PNP transistors is used in an electrical project.
- In this NPN transistor current flows from collector to emitter in contrast to PNP transistor where current flows from emitter to collector. In both cases, however, the base terminal is the main component responsible for the overall transistor action.
- When voltage is applied at the base terminal it gets biased and the emitter terminal starts emitting the electrons which are then controlled by the base terminals and thus collected by the collector terminal.
BC337 Datasheet
Before employing any component into your project, it’s always wise to scan the datasheet that helps you better understand the characteristics of the component. Click below to download the datasheet of BC337.BC337 Pinout
The following figure shows the BC337 pinout diagram.
- All these terminals are mainly used for external connection with the electronic circuit. All these terminals are different in terms of their functionality and doping concentration.
- The emitter terminal is highly doped as compared to the remaining two terminals. And the emitter terminal encompasses the entire current of the transistor. The emitter current is a sum of collector current and base current.
BC337 Pin Configuration
BC337 is mainly used in three configurations as follow: 1: Common emitter configuration 2: Common collector configuration 3: Common base configuration- Common emitter configuration carries the suitable voltage and current ratings needed for amplification purposes. This configuration is used for amplification purposes.
- The amplification factor demonstrates the nature of amplification. It is a ratio between collector current and base current and is denoted by ß.
- The current gain is another important factor that is a ratio between collector current and emitter current. It is denoted by a and is known as alpha. The alpha value lies from 0.95 to 0.99 but mostly its value is taken as unity.
BC337 Working Principle
- The base terminal plays a key role in starting the overall transistor action. When the voltage is applied at the base side, it gets biased and starts the electron action in the transistor. The base side actually acts like a control value that controls the electrons emitting from the emitter terminal which are then collected by the collector side.
- The small current at the base terminal is used to control large current at the remaining two terminals. This process is used in amplification purposes.
- BC337 also acts as a switch. When it acts as a switch, it converts the small current present at the one terminal side into a much larger current across the remaining transistor terminals.
- The base pin is positive with respect to both emitter and collector terminals. While the voltage at the collector side is always positive with respect to the emitter pin.
- The resistor is employed at the collector side to control the flow of current.
BC337 Power Ratings
The following table represents the absolute maximum ratings of the component BC337.| Absolute Maximum Ratings BC337 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Rating | Symbol | Value | Unit |
| 1 | Collector-Emitter Voltage | Vce | 45 | V |
| 2 | Collector-Base Voltage | Vcb | 50 | V |
| 3 | Emitter-Base Voltage | Veb | 5 | V |
| 4 | Collector Current | Ic | 800 | mA |
| 5 | Current Gain | hfe | 100 to 630 | |
| 6 | Transition Frequency | ft | 100 | MHz |
| 7 | Storage Temperature | Tstg | -55 to 150 | C |
- The collector-emitter voltage is 45V and the collector-base voltage is 50V. While the emitter-base voltage is 5V. The transition frequency is 100MHz.
- These are the stress ratings. Make sure these ratings don’t surpass the absolute maximum ratings, else they can damage the component and thus the entire project.
- Also, if these ratings are applied more than the required time, they can damage the device reliability.
BC337 Alternatives
The following transistors can be used as a replacement to BC337. The SMD alternatives of the BC337 are- 2SC3912 (SOT-23)
- 2SC3914 (SOT-23)
- BCX19 (SOT-23).
- 2SC3913 (SOT-23)
- BC817 (SOT-23)
- 2SC3915 (SOT-23)
- The PNP complementary to BC337 is BC327.
BC337 Applications
The following are some applications of the transistor BC337.- Used for switching and amplification purpose.
- Employed in electronic motors to control current.
- Used in the push button.
- Employed in robotics and instrumentation.
- Used in Darlington pair circuits.
- Employed in Astable and Bistable multivibrators.
BC337 Physical dimensions
The following figure shows the physical dimensions of the component BC337. It will help you audit the space required for the component before incorporating it into your project.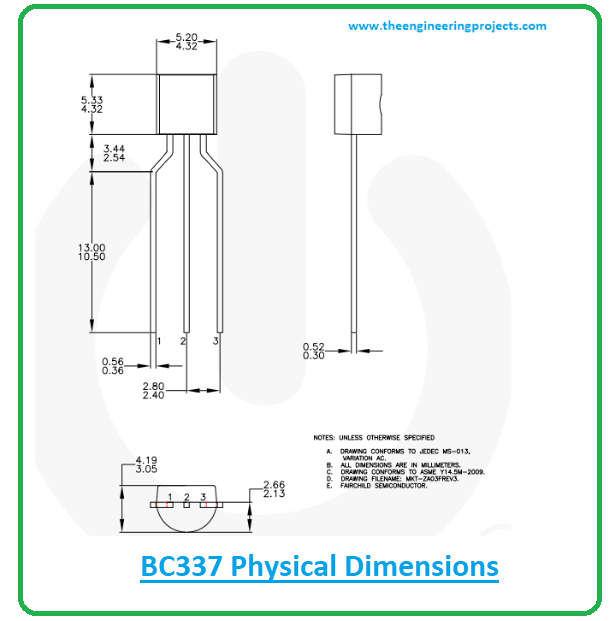
×
![]()








 1 user
1 user






 Continue Wishlist
Continue Wishlist





 Getting Started Guide
Getting Started Guide
 Help Center
Help Center
 Contact us
Contact us
 Doist Blog
Doist Blog
 Privacy
Privacy
 Security
Security
 Terms of Service
Terms of Service
 What's new: Channel Descriptions
What's new: Channel Descriptions





 Electronic Components
Electronic Components jameswilson
jameswilson 0 Comments
0 Comments








 2.3k
2.3k
 953
953
 921
921
 2.1K
2.1K
 Introduction to BC337
bc337 pinout
bc337 power ratings
bc337 applications
Introduction to BC337
bc337 pinout
bc337 power ratings
bc337 applications
 Saturday, August 15, 2020
Saturday, August 15, 2020