Introduction to BC327


Introduction to BC327
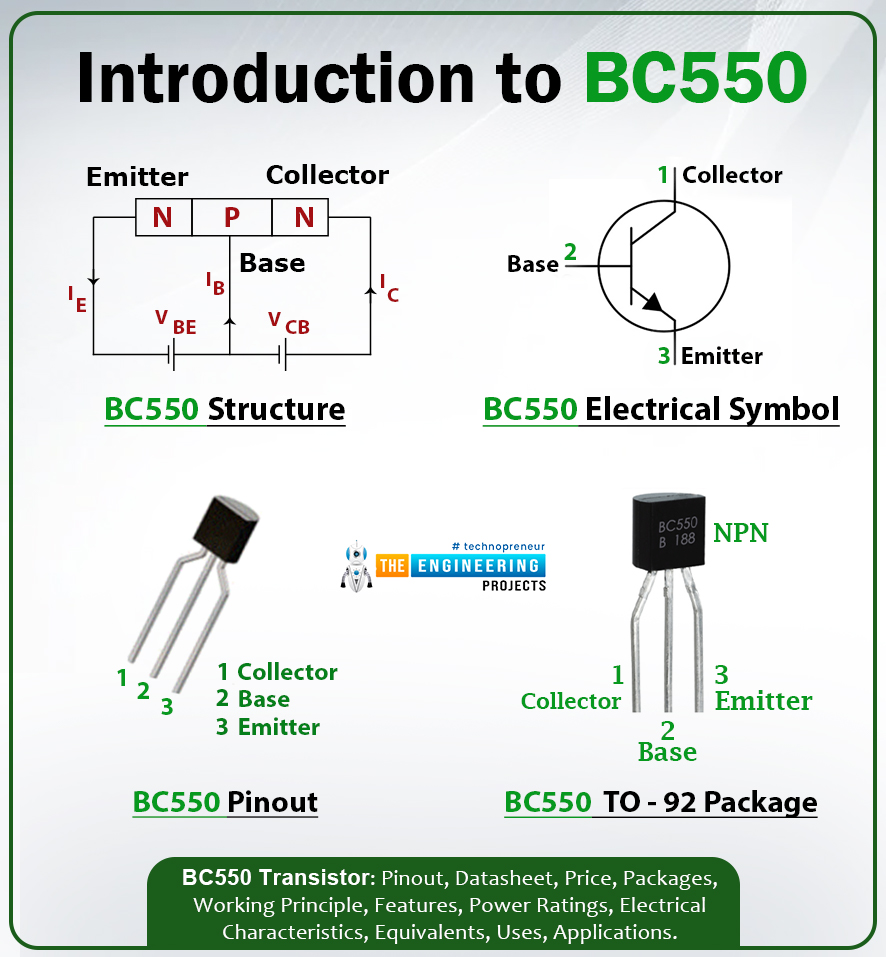
- BC327 is a PNP bipolar junction transistor that comes in the TO-92 package and is used for switching and amplification purpose.
- It comes with three pins named emitter, base, and collector that are mainly used for external connection with the electronic circuit.
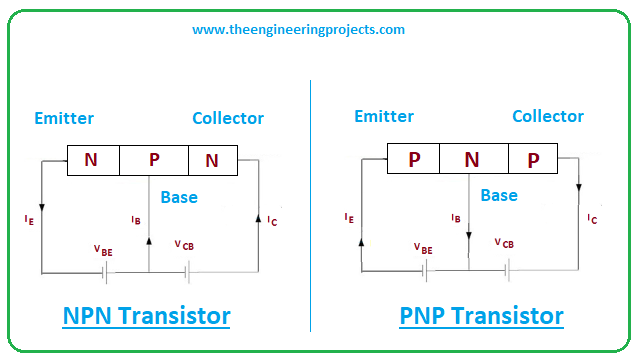
- BC327 is incorporated with three layers where one n-doped layer is sandwiched between two p-doped layers. The n-doped layer is negative while the p-doped layer is positively charged.
- This transistor incorporates 800mA collector current, hence it is easily employed to drive a variety of heavy loads.

- Collector dissipation is 625mW while the maximum current gain is 630 which makes it a suitable pick for audio amplification purposes.
- Transistors are mainly divided into two types named NPN and PNP transistors this BC327 transistor belongs to the PNP transistor family.
- Both transistors are different in terms of their charge carriers used for conductivity.
- Electrons are major carriers in NPN transistors while holes are major carriers in PNP transistors.
- When two diodes are combined from the cathode side, they constitute a PNP transistor where the N-doped layer represents the base side while the other two p-doped layers represent the emitter and collector respectively.
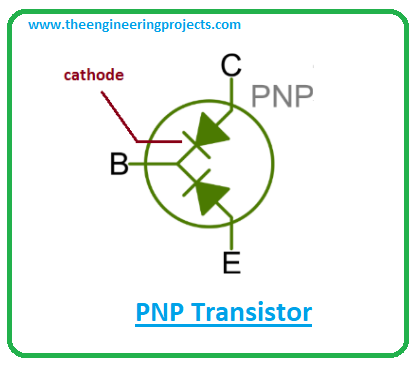
- You know it already, the movement of electrons is far better and faster than the movement of holes. The reason NPN transistors have a leg over PNP transistors for their quick response in conductivity.
BC327 Datasheet
- To understand the component thoroughly, it’s always wise to sift through the datasheet.
- Download BC327 Datasheet by clicking the button below:
BC327 Pinout
BC327 comes with three pins named 1: Emitter 2: Base 3: Collector The following figure shows the pinout of BC327.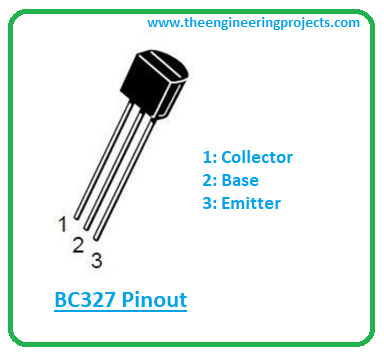
- These pins are used for external connection with the electronic circuit. The small current change at the base terminal produces a large current change across other terminals.
- The base terminal plays a key role in differentiating both NPN and PNP transistors.
- In NPN transistor current flows through the base side when voltage is applied while in PNP transistor no current flows through the base terminal when the transistor is turned ON.
BC327 Working Principle
- When current flows through the base terminal in this PNP transistor, the transistor is turned OFF, and on the other hand, when there is no current at the base side, the transistor is turned ON.
- PNP works the same as NPN transistor but in the opposite fashion. The base still controls the large current across other terminal but here current flows in the opposite direction i.e. from emitter to collector.
- And instead of electrons emitted in the case of NPN transistor, holes are emitted by the emitter in PNP transistor that are then collected by the collector.
BC327 Power Ratings
The following table shows the absolute maximum ratings of BC327.| Absolute Maximum Ratings BC639 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Rating | Symbol | Value | Unit |
| 1 | Collector-Emitter Voltage | Vce | 45 | V |
| 2 | Collector-Base Voltage | Vcb | 50 | V |
| 3 | Emitter-Base Voltage | Veb | 5 | V |
| 4 | Collector Current | Ic | 800 | mA |
| 5 | Collector Power Dissipation | Pc | 625 | mW |
| 6 | Junction Temperature | Tj | 150 | ºC |
| 7 | Storage Temperature | Tstg | -55 to 150 | ºC |
- These are stress ratings that can make or break your entire project. Make sure ratings don’t exceed these absolute maximum ratings else you may compromise your component.
- Similarly, if these ratings are applied for more than the required time, they can affect the reliability of the device.
Difference between PNP and NPN Transistors
- The BC327 transistor carriers the same characteristics as NPN transistors with a few exceptions.
- In the case of PNP transistors, all current directions and voltage polarities will be reversed compared to NPN transistors.
- The NPN transistor sources current through the base terminal while PNP sinks current into the base terminal, the reason it’s also called a sinking device.
- In PNP transistor the base terminal is more negative than the emitter terminal. And all these terminals are different in terms of their doping concentration.
- The emitter terminal is highly doped and comes with 100% current of the transistor while the base terminal is lightly doped and is responsible for the transistor action and controls the number of holes emitter from the emitter which are then collected by the collector.
- The collector terminal is bigger compared to other terminal and is lightly doped.
- Both NPN and PNP also differ with respect to the applied source voltage i.e. in case of NPN transistor source voltage is applied at the collector side while in case of PNP transistor source voltage is applied at the emitter side.
- A load resistor is also used while working with this BC327 PNP transistor that controls the current in the collector terminal.
- Plus, biased voltage is applied at the base terminal that initiates the transistor action and it is coupled with the base resistor to resist and limit the current flowing through this terminal.
BC327 Alternatives
The following are alternatives to BC327. The pinout settings of the alternative may differ from the actual BC327. It’s wise to check the pinout of the transistor before employing it in your electronic circuit. NPN Complementary of BC327 is BC337. Since they both form a complementary pair, they can be employed together in many electronic projects.BC327 Applications
BC327 comes with the following applications:- Used for signal amplification and switching purposes.
- Finds application microcontrollers to drive heavy loads.
- Used in audio amplifiers and multiple preamplification stages.
- Employed to drive loads under 800mA.
- Used in push-pull configuration circuits.
- Used in medium-speed switching and high-frequency amplifiers.
BC327 Physical dimensions
The following figure shows the physical dimensions of the BC327.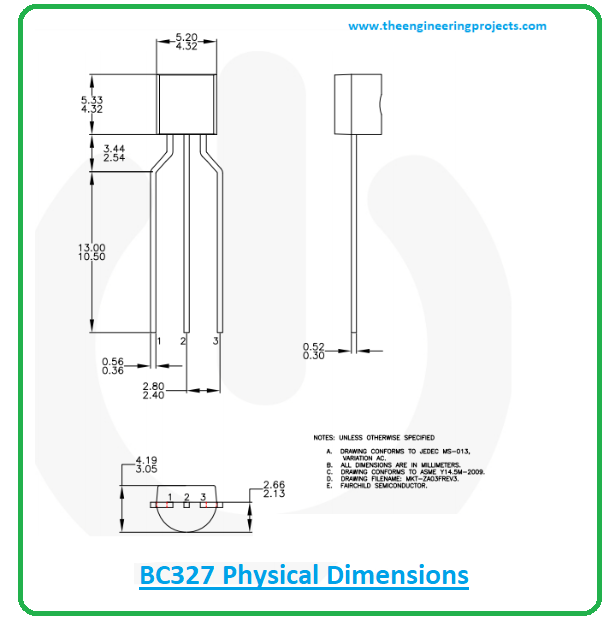
×
![]()








 1 user
1 user






 Continue Wishlist
Continue Wishlist





 Getting Started Guide
Getting Started Guide
 Help Center
Help Center
 Contact us
Contact us
 Doist Blog
Doist Blog
 Privacy
Privacy
 Security
Security
 Terms of Service
Terms of Service
 What's new: Channel Descriptions
What's new: Channel Descriptions





 Electronic Components
Electronic Components jameswilson
jameswilson 0 Comments
0 Comments








 2.3k
2.3k
 953
953
 921
921
 2.1K
2.1K
 Introduction to BC327
bc327 pinout
bc327 power ratings
bc327 applications
Introduction to BC327
bc327 pinout
bc327 power ratings
bc327 applications
 Saturday, July 11, 2020
Saturday, July 11, 2020