What is Thermistor
- A thermistor is a resistor whose value of the resistance alters with the change of the temperature.
- The word thermistor is a combination of the two words first is thermal that means heat and second is resistance.
- In electrical circuits, the thermistors are used to stop the inrush current from the circuitries, as they are also sensors with the variation of the resistance they indicate about current.
- There are the 2 main categories of the thermistors first one is the NTC (negative temperature coefficient) and second is PTC (positive temperature coefficient).
- Negative temperature coefficient thermistor is such resistor whose resistance value falls with the increment of the temperature.
- NTC (Negative temperature coefficient) thermistors are mostly used for the resistance computations and to limit the value of the current in different circuitries.
- The positive temperature coefficients are such thermistors whose resistance value increases with the increment in the temperature.
- The PTC used in circuitries to provide protection against the overcurrent in the circuitries.
- These resistors are formed by crushing the oxides of the different metals using different methods for their creation.
- The main difference among the RTD (resistance temperature detector) and the thermistor is that RTD is manufactured by different metals while thermistors are formed by ceramic substances.

Working of Thermistor
- The resistance of the thermistor varies with the variation in the temperature. For calculation of the thermistor's resistance ohm-meter can be used.
- If we can find the accurate variation in the resistance of the thermistor with the variation in the temperature than we can easily find the value temperature by the resistance value.
- The material used for the creation of the thermistor defines how much variation will occur in the resistance.
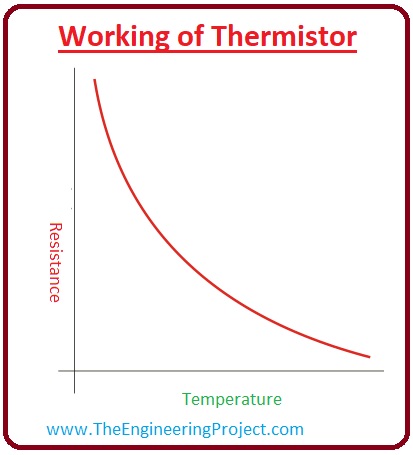
- If we draw graphical representation among the resistance and the temperature than we will get the non-linear curve. It is shown in the given figure.
Construction of Thermistor
- For the production of the thermistor powder form of the 2 or more than the two oxides of metals blend to form paste-like arrangments.
- Then the different wires are inserted into this paste of metallic-oxides for the circuit connection, after that this composition is put into the oven for the removal of the water and to make it solid.
- After drying the paste solid obtained from the oven will be covered with the glass coating to provide protection from the moistures.
- In market numerous types, configurations and size of the thermistors are available.
- The smaller size thermistors have dia of 0.15 to 1.5 mm and their shape is similar to grains.
- These resistors are also available in the ring-like arrangements that formed during moulding of the thermistor that has dia of three mm to twenty-five mm.
- The resistance values that are used in a thermistor is one kilo-ohm, two kilo-ohms, ten kilo-ohms, etc.

Types of Thermistors
- There are two main types of the thermistors first one is the NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient ) and the second one is PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient).
- Let's discuss them with the detailed.
- This kind of thermistors is constructed by pressing the disc made by different semiconductors.
- When the temperature of these thermistors increases, the energy of the electrons of the material also increases, then they start to flow in the structure of the thermistor.
- The current due to movements of these electrons can be described in a given formula.
I = (n.A.v.e)
- In the above-given equation the 'I' is the current.
- 'n' is the no of the electrons.
- A is the area of the thermistor.
- 'v' is the speed of the electrons.
- 'e' is a charge of the electrons, its value is 1.602 10^-19.
- The current produced by the movement of the electrons can be found by the ammeter.

PTC Thermistor
- In this thermistors, the increment in the value temperature also increases the resistance and decrement in temperature will decrease the resistance.
- As NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistors are commonly used but PTC is used for special circuitry like to provide protection. It also works as the replacement of the fuses.
- The operating temperature range for this thermistor is among the sixty Celcius and one twenty-degree Celcius.
- In special-cases its operating temperature can be zero to two hundred Celcius.

Comparison between Thermistor and Thermocouple
- Now we describe the differences between the thermistor and thermocouple with detailed.
- The temperature measurement range for the thermistor is fifty-five celsius to plus one fifty-five celsius.
- It used for the measurement of the temperature.
- The thermistor shows the non- linear behaviour for the resistance and the temperature.
- In the case of the NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) the increment of the temperature will decrease the resistance.
- It can very easily assemble in the circuitries there is no need of special modification for the thermistor.
- The operating range for the thermocouple is from minus two hundred to minus three-fifty for 'T' category, 'J' category temperature is ninety-five to seven sixty celsius, category 'k' has a temperature range from ninety-five to twelve sixty celsius.
- Its accuracy is higher.
- Its working principle is that it finds the value of the different at its terminals then find temperature using these voltages.
Applications of Thermistor
- These are some applications of the thermistors.
- The thermistor used for the calculations of the higher frequency energy signals.
- The thermal conductivity of the different substance can be found by the thermistor.
- It also used to calculate the composition of different gases.
- The pressure of the liquids can be calculated by the thermistors.



