These circuits are created by the combination of linear components such as resistance and non-linear components like transistors and diodes. These clipping circuits are also known as the slicers. In today's post, we will also have a look at such circuits that are consists of diodes, their uses and their working. So let's get started with What is Diode Clipper.
What is Diode Clipper?
- The diode limiter is the other name for diode clipper circuits, these circuits reshape the input waveform by removing some part from positive half or negative half according to requirements.
- Diodes clipper circuits can be used for the modification of the input signal according to the load requirements, the most used diodes in these circuits are Schottky and Zener diode with the general diode.
- Such clipper circuits that comprise of the diodes are used as the voltage limiter in different engineering projects and instruments.
- As we are familiar with the working of the diode as rectifier it operates when its positive end is linked with the positive terminal of the battery and negative terminal with negative of battery but in case of opposite polarity it does not operates.
- The working of the diode clipper circuits is also similar to the rectification by the diode.
- Now we discuss the different circuits for the practical observation of the diode clipper circuits.

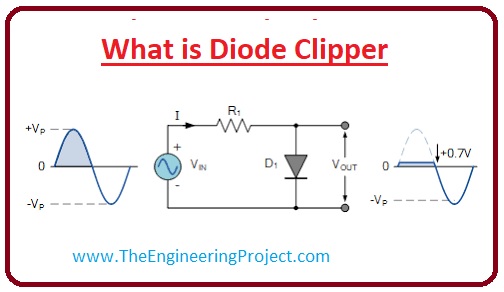
Positive Diode Clipping Circuit
- In the given below diagram, you can see that circuit one diode is connected to resistance and input supply in forwarding biasing conditions.
- The positive in the name of circuit suggest that this circuit will eliminate the positive cycle of the input signal.
- Due to forward biasing the diode will operate only in the positive half as the operating voltage for the diode is 0.7 volts so there will be only 0.7 voltage loss across resistance and other will convert into the dc.
- When the negative half comes on the diode it does not work and provides higher resistance like open switch resistance.
- In the given diagram you can observe this phenomenon.
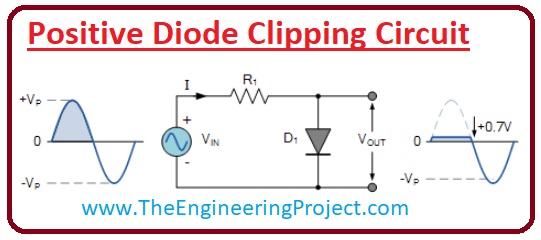
Negative Clipping Circuit
- From the name of the circuit, we can conclude that it will eliminate the negative half of the input signal. It is shown in the given below circuit.
- When the positive half of the input signal comes on the terminals due to reverse biasing there is no change in the signal due to higher value resistance.
- When the negative half of the wave comes, in this case, the diode is forward biased, so the current will pass through it and the voltage drop across this diode will be 0.7 volts this is the voltage for the starting operation of the diode.
- In the given figure, you can see this process with the detailed.
Biased Diode Clipper
- This clipper circuit consists of an external voltage source with the diode in series for the cutting of the input supply.
- There are 2 main types of biased diode clipper circuits.
- Positive Biased Diode Clipper
- Negative Biased Diode Clipper
- Let's discuss these two in detail.
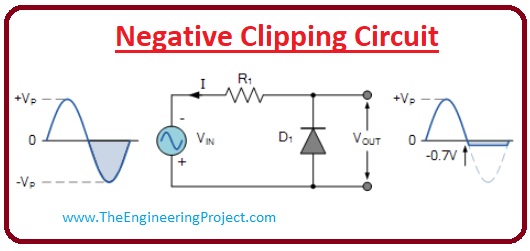
Positive Biased Diode Clipper
- In this kind of clipper circuit, some part of the positive half of the input signal is eliminated and there is no variation in the negative half of the signal.
- When the input voltage at positive is larger than the voltage source connected with the diode then the diode will cut the larger voltage and the output voltage will be equal to the biased voltage.
- During the negative cycle, there is no variation in the voltage and this cycle will be shown completely at the output.
- For example, if the voltage at the input is five volts and biasing voltage is two volts than the output voltage will be 2 volts other three voltage will be cut by this circuitry.
- It is because if the input voltage value is lesser than the voltage source (biased voltage) connected with the diode then behaves in reverse biased conditions and it will stop the biasing voltage flowing through the diode.
- If the value of the voltage is higher than the bias voltage diode is working in forwarding biased mode and the current start to pass through the load resistance.
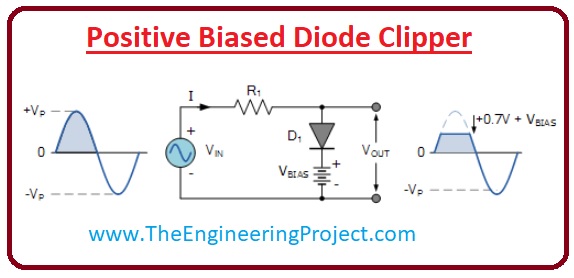
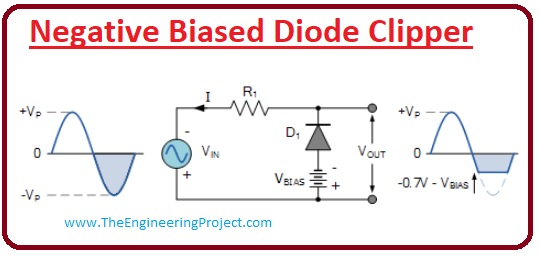
Negative Biased Diode Clipper
- In this type of clipping circuit, some portion of the negative half of the input signal will be eliminated. And there will be no effect on the positive half of the wave.
- If the voltage at input has a positive value than the diode will be in the reverse-biased mode.
- So it will behave like an open circuit and all the voltage will be appearing across the output resistance.
- In the case of the negative half if the voltage is higher than the biased voltage the diode is now working in the forward biasing condition. And the exceded value will be removed from the waveform, the resultant waveform is drawn in the given figure.
Applications of the Diode Clippers
- These are some important applications of the diode clippers that are described here.
Reshape the Waveform:
- These circuits are used to vary the physical structure of the input wave according to our project requirements.
- By using these circuits the sine waveform can be changed into a square, rectangle or any other shape according to the circuit.
Circuit Transient Protection:
- Transient currents are very dangerous for any circuits that can damage our complete circuit, to stop all these transients current clipper diodes are also effective and can remove these transients.



