Hello friends, I hope you all are doing great. In our previous lectures, we have studied two types of diodes i.e. Basic PN diode and Schottky Diode. Today, we will discuss the third type of diode i.e. Zener Diode.
Zener Diode was invented by the American engineer Clarance Melvin Zener, so it's named after him. The specialty of the Zener diode is that it can operate in both forward-biased and reversed-biased directions. In today's post, we will have a look at its working, features, ratings, construction and applications. So let's get started with what is the Zener Diode.
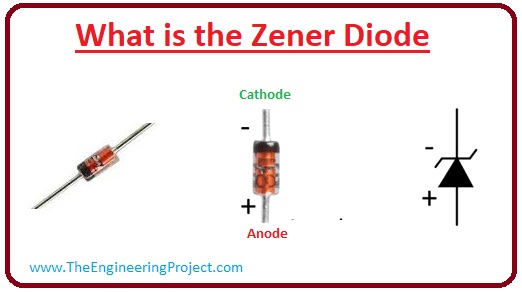
What is Zener Diode?
- The Zener diode is a special diode, that enables the current to flow not only from the positive terminal (anode) to the negative terminal (cathode) but also in the opposite direction.
- The doping of the Zener diode is more than the conventional diode, so its depletion part has less area.
- The general diode does not operate in the reverse biased condition but Zener diodes are specially manufactured for reverse-biased operation.
- Zener diode is mostly used in types of electronic devices like computers, laptops etc, it is the basic component of the electronic circuitries.
- It is used for power stabilizer circuitries to maintain the voltage level for a particular device.
- Zener diode also provides protection to any circuitry from over-voltage, particularly from ESD (electrostatic discharge). In ESD the current flows suddenly among two charged points by a short circuit or breakdown of insulation.
Breakdown in Zener diode
- There are 2 main breakdown areas in the Zener diode.
- Avalanche Breakdown
- Zener breakdown
- Let's discuss both of them one by one in detail.
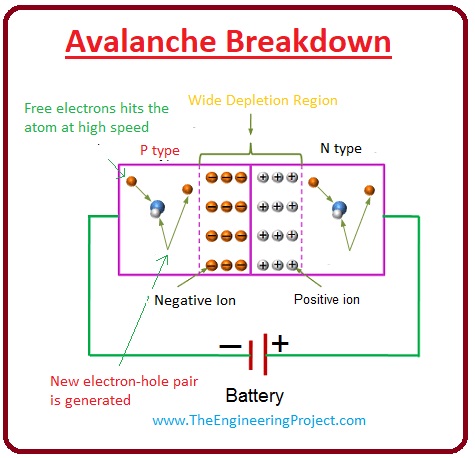
Avalanche breakdown
- This type of break-down not only exits in the Zener diode but also in the general diode due to higher voltage in reversed biased conditions.
- When the diode is in the reversed biased condition the minority charge carriers get larger energy from the source and move fastly.
- The high-speed charge carriers collide with the other particles and remove more electrons from the atom. These are traveling at a higher speed they also eliminate more electrons from other atoms.
- Due to the larger quantity of electrons, the backward current will flow from cathode to anode, in some conditions the general diode can be damaged.
- But the Zener diode may not burn because they are sketched to operate under those conditions.
- The avalanche breakdown voltage for the Zener is six volts.
- The given diagram explains the avalanche breakdown voltage.
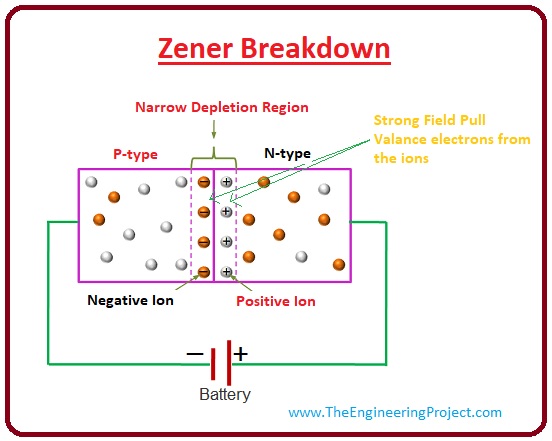
Zener Breakdown
- This type of break-down appears in the high doping diode like Zener, as this diode has less depletion area due to higher doping.
- When the voltage provided to the diode increases, in a thin depletion area highly effective electrical field is established.
- When the reversed polarity voltage almost equals the Zener voltage, the electric field in the depletion portion is such strong that it pulls out the electrons from their valance shells.
- The outermost shell electron that gets enough power from the field will break out from the effect of the mother atom.
- The outermost shell electron that breakout from the effect of its mother atom will move freely.
- Due to the free drift of this election, the reverse current will flow in the diode.
- The less increment in the voltage will cause to move current very fastly at the Zener breakdown portion.
Difference between the Zener and Avalanche Breakdown
- Zener break-down occurs at less value of revered biased voltage while avalanche at the higher reversed biased voltage.
- Zener breakdown occurs only in the Zener diode as they have less area of depletion portion.
- The break-down area is such a region in which the Zener diode usually works.
Zener Effect
- Zener Effect is the category of the electric failure (breakdown) that exits in reverse biasing PN junction the strong statice field allows the electrons to move from the valance band to the conductive band of a semiconductor.
- Its name is due to the use of this factor in the operation of the Zener diode.
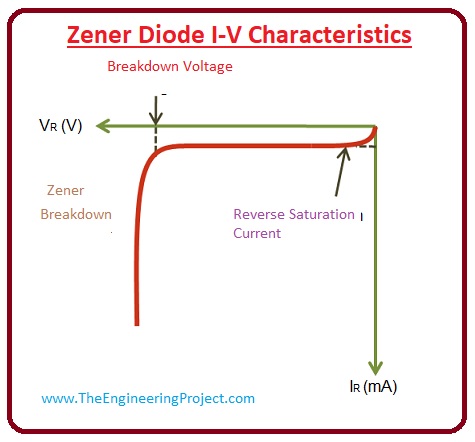
Zener Diode I-V Characteristics
- Zener diode works in the reversed biasing conditions is reversed biased mode its anode is connected with the negative terminal and cathode with the positive terminal of supply.
- In the given diagram, the reversing biasing effect of the Zener is shown in the curve between the current and the voltage.
- When we provide voltage to the Zener a small amount of the leakage current flows in the diode, till that point the applied voltage is less than the Zener voltage.
- When the value of applied voltage approaches the Zener voltage then a large amount of the reversed current flows in the diode and the curve suddenly changes its state from the flat to vertical.
- Due to the instant increase in the current value, the breakdown that happens in the diode is called the Zener breakdown.
- But, the Zener diode manifests a restrained breakdown that does harm the component.
- The quantity of the Zener breakdown voltage fluctuates according to the doping level of the diode.
- If the doping level of the diode is larger then breakdown occurs at a lesser voltage.
- If doping is less then breakdown happens at the higher value of the revered supplied voltage.
- Usually, the value of the Zener voltage for the diodes is (1.8) volts to (400) volts.
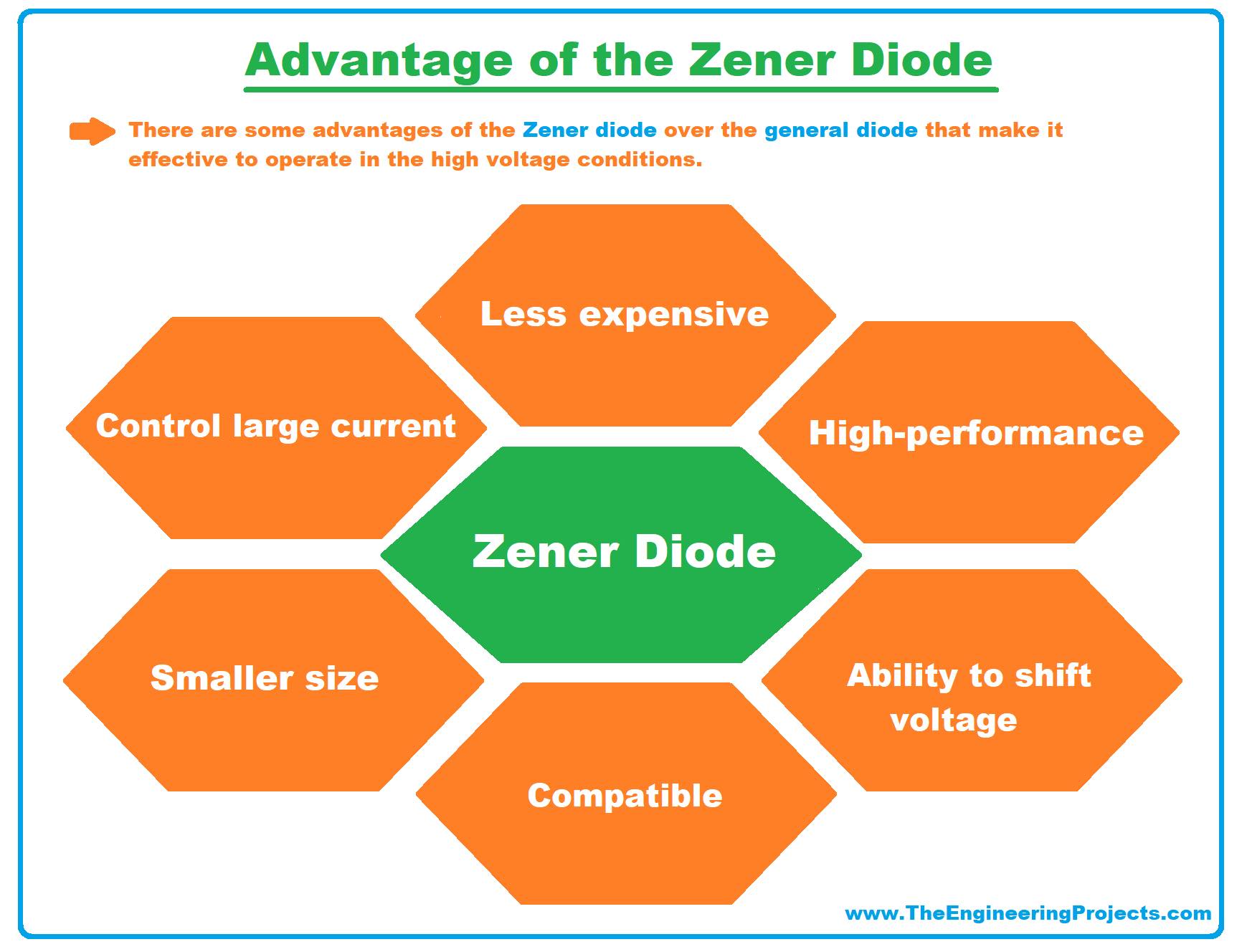
Advantages of Zener Diode
- There are some advantages of the Zener diode over the general diode that make it effective to operate in high voltage conditions.
- Its power consumption capability is higher than the normal diode.
- Its efficiency is very high.
- It is available in a smaller size.
- It is a less expensive diode.
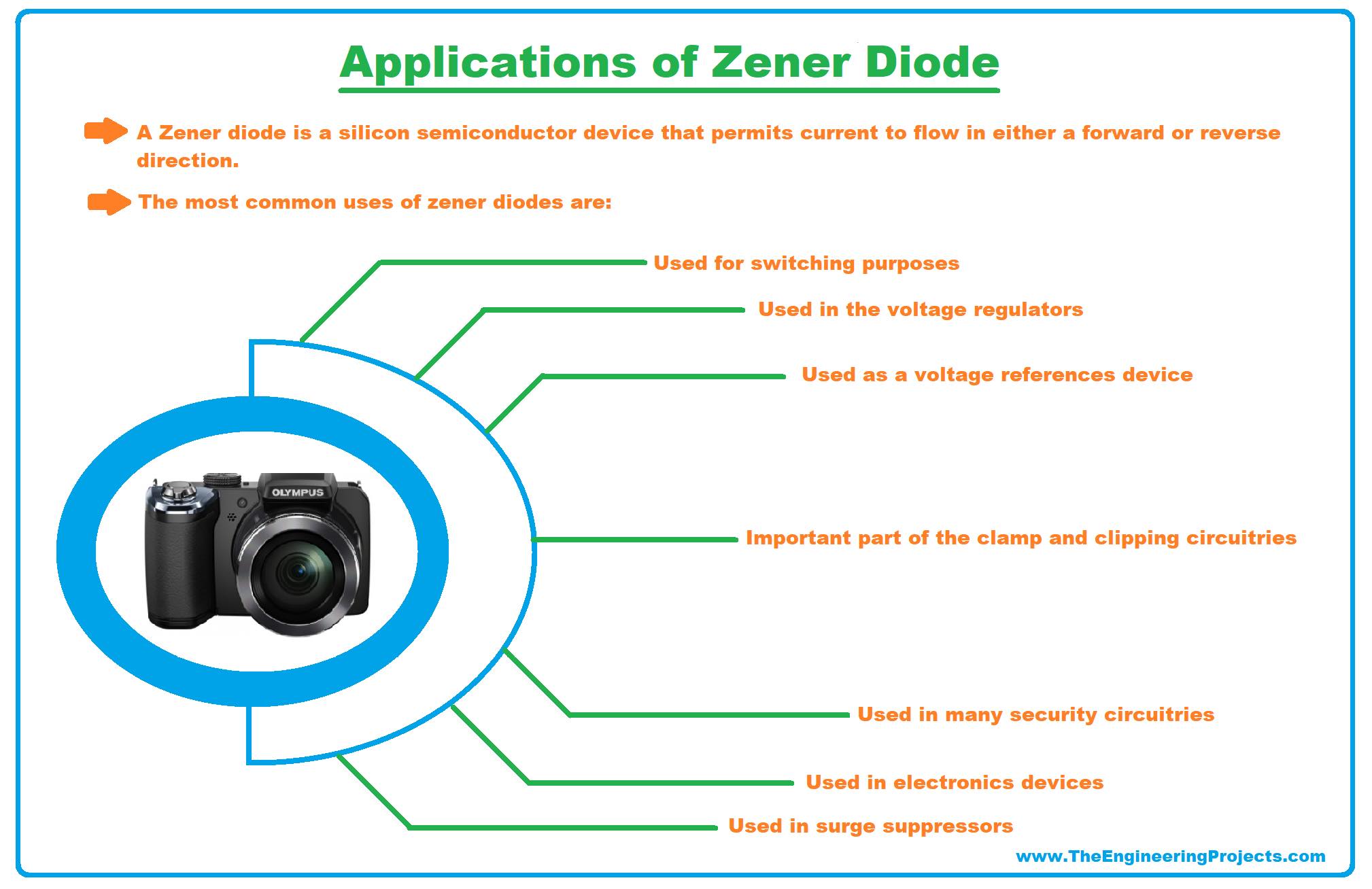
Applications of Zener Diode
- These are some applications of the Zener diode.
- It is commonly used as a voltage reference device.
- It is used in voltage regulators.
- It is used for switching purposes.
- Zener diode is an important part of the clamp and clipping circuitries.
- It is used in many security circuitries.
- It is also used in electronic devices like mobile laptops, computers, etc.
So, it is a detailed article on the Zener diode, I have each and everything related to the Zener diodes. If you have any questions about it ask in the comments. Thanks for reading take care until the next tutorial.





































 Tutorials
Tutorials zahidali
zahidali 1 Comments
1 Comments



























