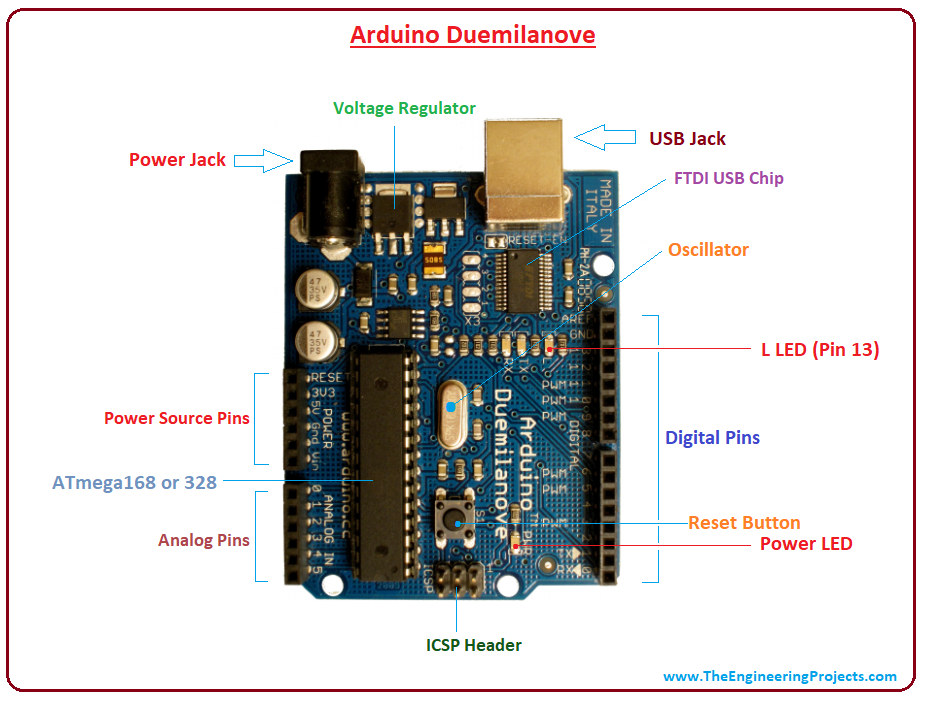
Introduction to Arduino Duemilanove
Arduino Duemilanove is a Microcontroller Board that is based on ATmega168 or ATmega328.- It comes with 14 I/O pins, out of which 6 are used as a PWM output Pins.
- The Flash Memory is different depending on the microcontroller incorporated into the board: 16 KB for ATmega168 and 32 KB for ATmega 328. Out of this total flash memory, 2 KB is reserved for a bootloader.
- This board can be powered up both ways: connecting with a computer using USB cable or using DC adopter.
- There is a built-in LED connected to digital pin 13, toggling between ON and OFF as you send HIGH and LOW respectively.
1. Arduino Duemilanove Features
Features of any device help you make a final decision before buying it for your project. Following table shows the main features of Arduino Duemilanove.| Microcontroller | ATmega168 or ATmega328 |
| CPU | 32-Bit ARM Chip |
| Digital I/O Pins | 14 |
| PWM Output | 6 (out of 14 I/O pins) |
| Analog Input | 6 |
| Flash Memory (Program Memory) | 16 KB for ATmega168 and 32 KB for ATmega 328 |
| SRAM | 1 KB for ATmega168 and 2 KB for ATmega328 |
| EEPROM | 512 bytes for ATmega168 and 1 KB for ATmega328 |
| Input Voltage | 7-12 V |
| Operating Voltage | 5 V |
| Oscillator | up to 16 MHz |
| Software Used | Arduino IDE |
| Reset Button | Yes |
| ICSP Header | Yes |
| USB Port | 1 |
| UART (Serial Communication) | Yes |
| SPI Protocol | Yes |
| I2C Protocol | Yes |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 40 mA |
| DC Current for 3.3V Pin | 50 mA |
- Three communication protocols available on the board will help in connecting the module with external devices.
- There is a slight difference in the memory used in the module based on the controller incorporated on the board. Before you intend to buy the module, make sure your technical requirements are quite in line with the memory space available on the board.
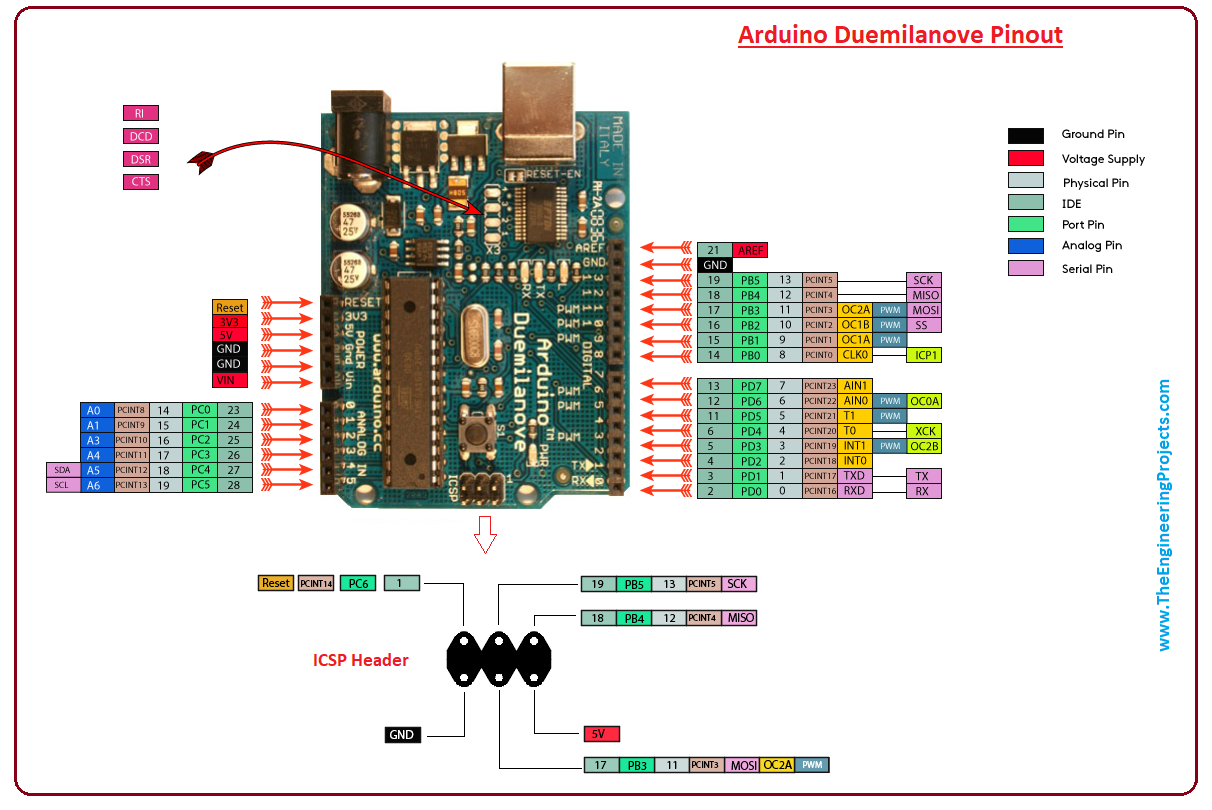
2. Arduino Duemilanove Pinout
Following figure shows the pinout of this Arduino Board.
- There are total 28 physical pins on the board and six pins are available on the ICSP header. Four female headers are available covering all physical pins for the connection with the external devices.
3. Arduino Duemilanove Pin Configuration
In the previous section, you have got a brief overview of the Arduino module pinout. Now, we will highlight the major functions associated with each pin, so you can anticipate what each pin is capable to perform, helping you use the relevant pin for your project.Digital I/O Pins
There are 14 digital I/O pins on the board that can be used as an input or output based on requirement. If you are working with sensors, these pins can be made as an input to accept the digital input from the sensor, similarly, if you are aiming to control the motor, these pins are used as an output for writing the required command to control the motors.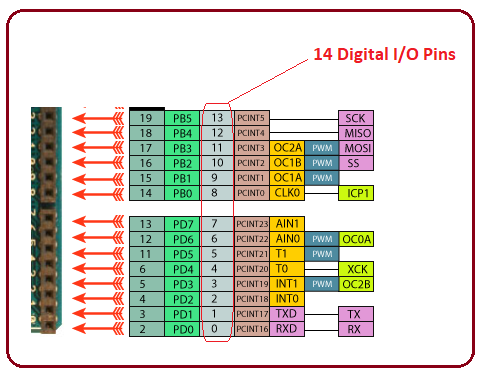
Analog Pins
There are 6 analog pins available on the board. These pins can accept any value, unlike digital signals that are designed to deal with only two values: HIGH and LOW. The following figure shows the location of analog pins on the board.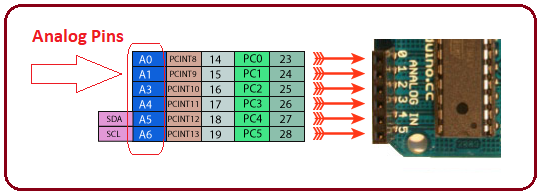
PWM Pins
There are six PWM pins (out of 14 digital I/O pins) incorporated on the board. PWM (pulse width modulation) is a process for getting analog results with digital means. These pins appear on the right side of the board as you place the board with power jack pointing upward. Following figure shows the placement of these pins on the board.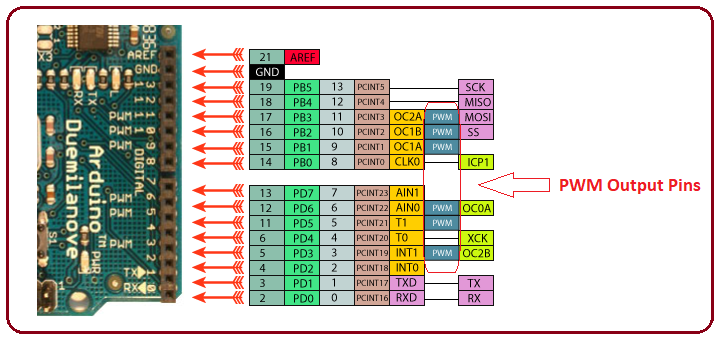
ICSP Header
ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) header is added that help to connect the board with computer and upload a sketch in case USB port is not available. This feature is mainly used to program Arduino with another Arduino.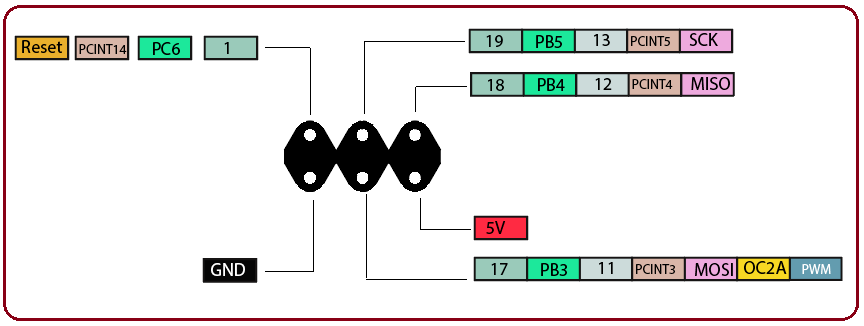
Power Source Pins
There are four main voltage sources i.e. Vin, 5V, 3.3V, AREF, available on the board. The Vin is the input voltage that ranges between +7 to +12 V and comes from the external power source. The board operates at 5V while 3.3V is the operating voltage of each pin. There are four ground pins on the board where one is reserved for AREF and another for ICSP header while remaining two are available for the board. The AREF is an Analogue reference voltage, used for analog pins. The following figure shows the power source pins.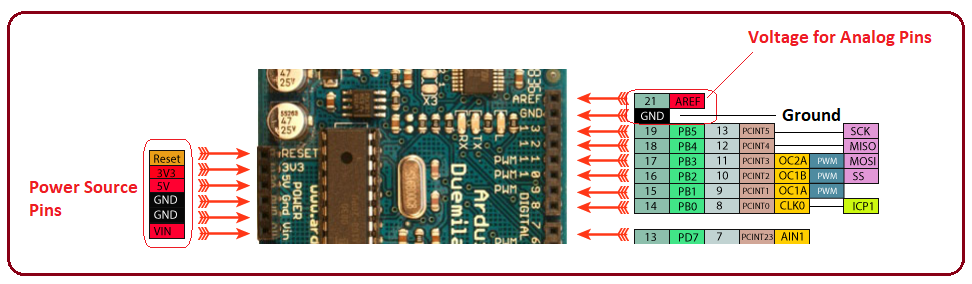
Communication Protocols
Common communication protocols like SPI, UART and I2C are available on the board. It is important to note that SPI communication is available on both: digital I/O pins and ICSP header pins.
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is commonly used to send data between microcontrollers and small peripherals such as sensors, shift registers, and SD cards. It comes with separate clock and data lines, layered with a select line to choose the device for communication.
Similarly, I2C is a two-wire interface that contains two main lines known as SDA and SCL where former is s serial data line that carries the data and later is serial clock line that is used to synchronize all data transfers over the I2C bus.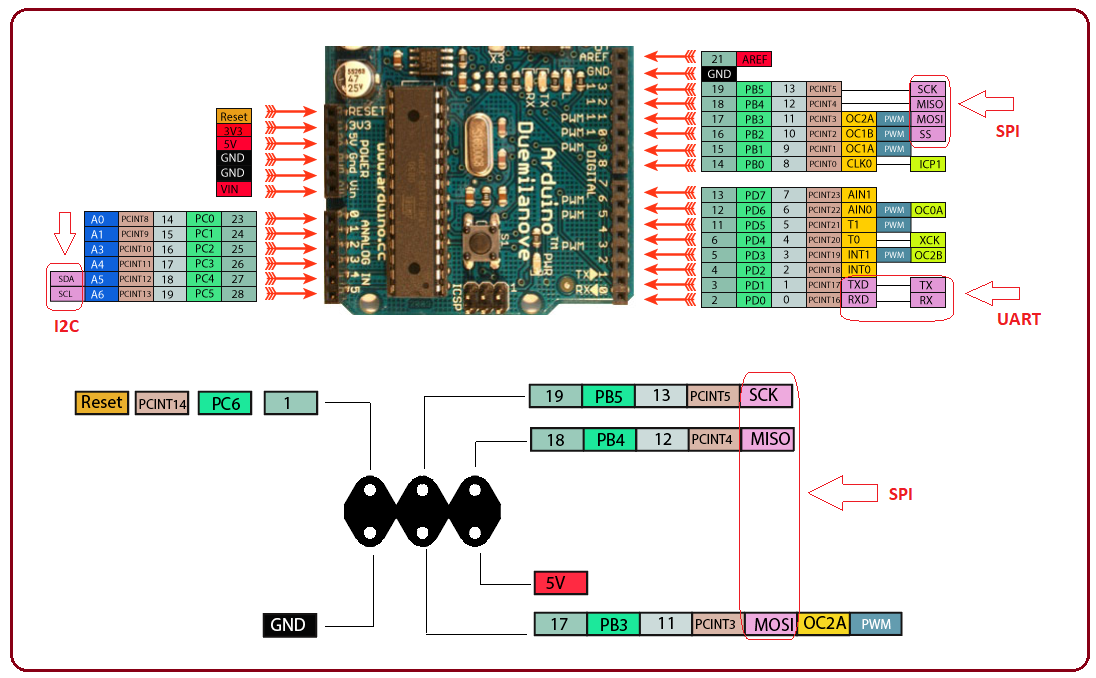
4. Programming and Communication
Almost all modules falling under the Arduino family are programmed using Arduino IDE - Official software introduced by Arduino.cc for programming Arduino Modules. This software is compatible with common operating systems like Windows, Linux or MAC.- You need to take care before installing the software version for your system i.e. if you want to download Arduino IDE App version, you must have Windows 10 installed in your system as app version is not compatible with Windows 7 or 8.1.
- Arduino never fails to keep your budget at the bare minimum as no external burner is required to burn the code inside the module due to Module's built-in bootloader, however, if you aim to insert a new controller on the module, you have to install the bootloader again using IDE software.
- Software comes with a compilation option that allows you to see the code compilation on the bottom of the screen as you upload the code, generating a code hex file which then is transferred to the board.
5. Arduino Duemilanove Projects and Applications
Arduino Duemilanove comes with a wide range of applications and features a number of peripheral features. Following are some major applications it can be used for:- Student Projects
- Industrial Automation
- Health and Security Systems
- Embedded Systems
- Motor and Sensor Control



